We walk around, people say something negative, in scrutiny, as criticism - and we believe it, we take it to the heart, and it looks as if we are taking it very personally.
We are not sensitive - there is issue with high suggestibility. Mesmerism. We are easily hypnotized by other people - due to self hatred. This leads to RSD issues, too.
We start to think ahead of abusers and we try to protect ourselves from their potential aggression and punishment - and this keeps is in the state of high suggestibility. This is not self esteem issue as CBT tries to make us believe. CBT itself is narcissistic abusive bias tool - and we believe in that crap too.
Learning more about Rejection Sensitivity - I noticed something that previously I ignored, something that was on auto pilot:
- that when I am talking to someone new, someone I do not know closely how they think - I would feel social in the first 5 minutes but then I would feel as if I am boring to them and I need to leave them alone
- this happens when I am totally alone and I go to some place - after a while I feel as if I am not wanted
- closely related is when I know someone well - I do not feel close enough to invite to organize a meeting with them assuming they would say yes out of pity or if we meet - that the next time I am suppose to meet or visit - I would feel like I am in the way.
Toxic shame takes over my beliefs and convictions - and I am convinced that I bother other people. And I do not want to waste their time, to worry about me, to take up their time. And I am not aware of it, this is going on as auto-pilot.
This toxic shame is also present when I need something, when I need to ask someone for help or assistance - even when this is their job.
-
(20-6-2025)
How would I react in the same triggering socially anxious situations - if I were not panicking and fawning?
What would I say and what my behaviour would look like if I did not use my usual responses, reactions and mode of thinking?
If I remove my copy paste mechanisms how to cope with stress - then trauma responses would kick in.
In social anxiety - that is Fawning and Freezing.
Then we have the question of how to handle trauma responses - how to heal the trauma. The CBT solution is to attack the symptoms. So if I remove fawning- I will become borderline because I will be angry and attack others when they trigger me. Therefore removing symptoms create new symptoms. Instead of self help industry superficial advice that does not help but makes new problems - we need healing.
Healing Freeze response - is what I wrote about Ventral Vagal - creating safe place and self compassion. When we feel social anxiety - it is due to abuse. We are in the presence of npd bpd predatory abuse - which means psychopaths and sociopaths are in some kind of power, some kind of authority and they freely abuse us - and this is why we feel social anxiety.
Power position might be a thief, bully, mobbing at work, system abuse - something that is outside of our control to fight back and to assert ourselves. The idea of detachment here cannot be applied - since the abuse is coming from the external source - mad man having agenda to harm and cause pain to the target. No matter how much we detach - the pain will come from the external source. It is like a wild fire and us being in the nature around it - we cannot detach if the fire is coming - it will burn us alive. We cannot pretend that there is no fire - it will burn us. Or a wave coming - we cannot detach from reality and pretend that danger is not coming.
If we are able to run - or if we are able to face it - no matter what we do, there will be anxiety. Since the cause of anxiety is abuse. The trauma.
So we are only left with healing the trauma. Be kind to yourself, forgive yourself, not being hard on oneself for being abused. There will be a lot of shame and guilt for being abused, thinking we could do more or that we should show who is the boss and end up in endless drama and arguments with someone in power position.
The better solution is collecting data - and then if possible - move away from the abusers.
Example of how CBT is misleading us - is CBT is telling to the socially anxious to expose. But if we read resources about how to handle Freeze trauma response, there is advice:
"Avoid triggers: Be mindful of situations, people, or places that might trigger your freeze response, and try to minimize exposure. "
Exposure to abusers, evil people, psychopaths and sociopaths in power - someone who is not listening to us, someone who is not caring about the harm and pain they cause to the target of abuse - exposure will not help us to remove anxiety. Exposure to psychopaths and sociopaths will traumatize us.
Healing long term means knowing where I feel safe, where there is no abuse.
The advice to get outside of comfort zone is ignoring the abuse and psychopaths in power positions.
Due to previous abuse - we did end up feeling like bad object whenever there is stress and when psychopaths invent some problems and manipulation and control. Exposure to abusers will not make us stronger - it will make us use trauma responses and self blame, feeling like bad object as reaction to someone's abuse and manipulation and coercive control and exploitation and oppression.
IFS Model makes sense regarding the panic and worry and rumination. With social anxiety - our logic will be trained to calm down and to be rational and to realize that there is no real danger like tiger out there. But the panic that we still feel - even though we logically know that the stress is not that much dangerous as we feel it - comes from the trauma stuck inside our body - and that is IFS Model. Parts of ourselves that are baby inside us, that need bringing up the baby so that it feels safe in adult world. What happens with CBT is that we add wrong explanations - that anxiety is dangerous, that it is something to remove, that anxiety blocks us from living. CBT instructions will mix up the trauma and our logic. Now we will get panic about our logic, our cortex brain - which is normal and it does not need any intervention. CBT will now make us feel like we cannot trust our logic neither - nor our brain nor our body. And that CBT explanation will cause us to Fawn, we will resort to trauma responses such as Freeze - being unable to talk and move - since we distrust ourselves.
The triggers that we feel as panic and anxiety - are related to trauma. Being falsely accused, being attacked, being around anti-social behavior, around someone who cannot communicate and does not want to listen, someone who is difficult, someone who is pathological liar, creates conflicts and has agenda to exploit the target and to manipulate and to control.
These triggers will activate the inner parts that are holding on to trauma - and we will feel panic and worry and rumination and shame and blame.
With CBT explanations - we won't do anything to help ourselves. Through Prussian education system - CBT is forcing us to abuse ourselves, to numb ourselves, to deny reality, to ignore reality, to fawn, to people please, to be a doormat for abusers. This way we will have learned helplessness and we will misinterpret empathy with codependency. We will believe that not speaking the truth means we are being kind and nice because we do not trigger abuser and their temper tantrums. We believe that by being friends and speaking to abusers we have empathy and we do not want them to feel the pain so we are good person when we stay trauma bonded with people whom we should cut contact or gray rock them if we are unable to cut contact with them.
For example - bullies operate like Trump forcing Canada to join his union. With CBT we would go along with whatever abusers demand from us, no matter how much unreasonable and dangerous and disgusting their requests are. Yet we have seen that few months later - after Canada did not do anything about his lunacy requests - when he met with Canadian PM, he made statement that they have different opinions. So - he did nothing about it. His bullying was an empty threat. That is what abusers do - they scare the victim for the hope that victim will automatically fawn - without any actual punishment or assault. Simply through words that the target of abuse will shut up and obey. With CBT - we will end up like that, we will fawn. Because CBT is misdirecting and provides wrong explanations what is social anxiety. CBT is telling us to distrust our brain - since it appears as if social anxiety comes from the brain. It doesn't. Our brain is working fine - anxiety that we feel, rumination, flashbacks, worry - this is coming from the body and trauma stuck in the nervous system, it is body trauma. Our logic is working fine. If our brain had an aberration - we would not have triggers. We would experience panic all the time - without any pattern. When we isolate and avoid - when we cut off from the source of pain and abuse - our panic and social anxiety vanishes. If our brain was diseased and in disorder - then no matter where we go, and no matter if we are on a vacation or in a safe place - we would still feel panic all the time. With social anxiety we will feel anxiety only around abusers. And it is called social + anxiety. It is not called self anxiety. We get anxiety due to toxic people around us who are hostile and manipulative and controlling.
-
(31.8.2025)
Social anxiety is described as neurotic state - being in worry, being depressed - but CBT does not explain what happens when other people around us are neurotic and they influence our own mood. Because angry, hostile person appears as deity. It is necessary to break the spell, being mesmerized by someone who is triggering - by seeing such people as neurotic - weak, mentally ill, abnormal, dysregulated, someone who cannot be trusted or cannot be lean onto for advice or support or truth or facts. Believing that rude, loud, obnoxious, aggressive person is correct - leads to taking responsibility for their own emotional dysregulation. Taking responsibility for someone being a jerk - as if it is my own personal fault and responsibility for their anger. To break this spell - emotionally immature personalities must be seen as neurotic - all the labels which CBT and NT society is placing on the socially anxious: cowards, weak, lack in social skills, abnormal, psychotic. Socially anxious end up with those labels that toxic people projected onto them.
Not applying the knowledge.
As autistic trait. The reason why I do not apply knowledge:
- fear of punishment, that someone will attack me when I do something better and new and unsuspected out of the box
- not being secure in my capabilities and values and worth and identity
- empathy as in the meaning that I do not want someone to suffer while I progress, I want to be in trenches with those who do not know better
- drawing attention of onlookers
- do not want to brag
- do not want others to envy me
People pleasing and Fawning.
We might think that the cure for being a doormat is to become rude and jerk - as it is often said in self help industry. I believe that when we fawn - this is also connected to our Super Ego and our values. We value socialization and friendship and fair play - hence we will tend to fawn. We will basically listen and watch for input from other people and then change our behavior accordingly. But the problem starts when the other person is abusive and predatory and demands too much. That is where fawning becomes dysfunctional since it does not serve a purpose of socialization and being friendly.
It also depends on situation where we are -
are we hosting someone and they exploit us?
Are we guest at someone and we need to obey their culture rules.
Or is it neutral situation like colleagues at work where we share the space and tasks.
Moving on.
I noticed that once I make some kind of action - that I feel sorrow to toxic people and to the toxic place. I seem to forget that I am leaving the abuse and the desert where nothing can grow. There are no opportunities here for me. Only exploitation and pain and suffering and depression.
By going away and finding the new world I will fill in the gaps and holes that I could not fulfill in the desert.
Social anxiety is a reaction to the desert. To a place and to people where there are no opportunities only draining and complaining.
Without support. Without help. And this has nothing to do with character flaw - as social anxiety appears as issue with will power due to fears and anxious feelings.
New helpful analogy.
It would be the liver - once we know the unknown symptoms are due to junk food and drinks - we can make ourselves healthy by changing the diet.
In the same manner - social anxiety is the symptoms of unhealthy place and unhealthy energy - from the external which we soak in and then we end up being focused on fixing unsolvable problems and being stuck in depression.
-
(3.9.2025)
Chamber of security.
I noticed that with social anxiety we will tend to modify and construct our life around the imposed safety. It is like our private world where we feel safe. There is nothing wrong with that - except when it starts to interrupt with the real life.
In such safe zone we will start to have unrealistic expectations of life.
This is what happens with narcissistic personalities too - it is hall of mirror. The only difference is that with narcissists - when reality clashes with this fantasy world, they get angry and become hostile and exhibit rage - which often times is directed at people who are nice and kind - socially anxious.
On the other hand - when reality clashes with our expectations - unlike narcissists who are directed outwardly to hate and attack - we immediately feel depression coupled with bad object towards ourselves. We believe that nothing will ever be safe and happy again, it takes a lot of time to rebuild the security in the world and we feel burden of shame and guilt - which we usually carry but this time it is exposed and we feel this burden of sin and blame and disgust towards ourselves - which is very dangerous. Internalized toxic shame, depending on the external stress can end up with serious self injury.
In this chamber of safety, it is like Ventral Vagal, what Ventral Vagal should be and feel like - but we do it in our minds. We fuse our interests and try to merge with reality. Usually this is done through isolation and avoidance when for example we cannot participate in external activities.
We need to be aligned with reality.
Our goals, expectations need to be realistic.
In order to work with reality - when sudden problems and issues pop up randomly in life - it is important that we are flexible and that we are willing to learn and to improve, to educate ourselves. With narcissism - the person refuses to accept reality and they will most commonly attack and explode and be anti-social. If we live in a shame-based culture ambient - we will tend to interpret angry rude people as deities, as someone who is strong and stoic, we will tend to believe that such person is competent since they have the bold attitude to be rude. This way when we are in contact with such people, whenever there is stress and problem - we will be on the receiving end, we will be scapegoated as the problem and over and over again toxic people will abuse us. We will see their accusations as true, we won't question their authority and agenda - and we will agree to whatever coercion they are forcing us to be controlled and manipulated.
And because we are also trapped in a chamber hall of mirrors, where no new information can penetrate - we do not have crucial information such as recognizing the coercive control, narcissistic abuse, we have no education how to handle abuse and bullying - except our own previous coping mechanisms which we will copy paste - usually being silent, not being allowed to disagree, not be able to say no. We will also experience panic when we try to voice out our side of the story. Then we will interpret this panic as us being wrong, defected, abnormal, not competent and not allowed to stand up for ourselves nor to advocate for ourselves.
We need to start to know this chamber. This self inflicted prison. Usually - we will feel panic and fear outside of comfort zone - so we will not tend to think about our own prison - since it is painful and negative.
Our task should be that we let the sunshine in. That we see where we are. The next time we are in panic stress situation - that our chamber is now well lit - so that we see what is happening inside us when social anxiety strikes.
This way - we can introduce new ideas which previously were not available - such as imperative of placing our own needs into focus, focusing on our well being. This way - our brain will have new instructions to look after, brain will be compelled to look around for our health and our interest - something that previously was not programmed into our thinking and problem solving.
CBT tells us that we hate our brain and our so called cognitive distortions. This way we keep the darkness in our chamber, in our prison. So the next time we are abused, the next time we need to solve a problem which is important for our safety, our finances - without knowing our own chamber we will tend to think and process problems from our childhood learned copy paste instructions - usually that will be to please the abuser and to fix anger of the abusers, someone who disrespects us. We will place their anger as our shame and blame and guilt - and then we will worry about that a lot - and we will be stuck in this loop of worry without knowing how to stop it, we won't even know we are stuck inside it. All we will know is that we feel bad, we don't know where to go and we feel urge to please angry person as the only goal in life.
Inside the chamber of our comfort zone - anything that happened in the past will be mirrored - and it will appear to us as intrusive memories. Since we do not have new experiences to be in our primary focus - we are left with incidents where we were disrespected, we will now experience The Zeigarnik effect - since our brain will try to resolve whatever was appearing as incomplete in the past. We will think about solutions and actions and words and explanations we could come up with at that time in the past - but since it is done and we cannot time travel back to the past - we can never complete those tasks, so we get stuck in a loop.
Usually we will think how we are weak and how we should be strong and confident. So this way we will also experience toxic shame and guild and embarrassement - about something that is locked in the past. We will forget all other things that happened - and we will focus on our guilt, on us being bad and incompetent - since this is the message we got in abuse.
It is important that we do not blame ourselves for our comfort zone.
Coaching and various people with whatever self help agenda - may turn socia anxiety into fear issue - and tell us to leave our comfort zone in order to become stronger and that we remove social anxiety. It does not work like that. Because when we expose ourselves to more issues and problems - we will tend to copy paste our tools which are self defeating. We won't think up better tools - since our primary focus will be to please the abusers at our own expense.
When we experience abuse - we will tend to protect ourselves with wishful thinking (believing what you want to be true) - however this must be seen in social anxiety as coping tool. It is not us being lazy as coaching and CBT will suggest. This is not problem with will power. If we remove our beliefs which are part of echo chamber - we will feel depressed. It can backfire. We can harm ourselves - since we won't have tools to build and construct life based on reality.
Instead of self pathologizing ourselves for protecting ourselves from the pain - we need to introduce new tools without destroying our base.
This inner comfort zone - is also the place of our Ventral Vagal identity.
What we like and what we prefer is stored in this place, too. So if we remove our inner comfort zone place, we will also remove our happiness and our identity and what we like. This is why CBT is dangerous and harmful therapy. With removing social anxiety - it is also removing this inner comfort zone ambient.
In real life - CBT idea of destroying social anxiety will end up - as we won't know what to speak about after we say Hello. We won't know what to do when there is no structure - like social settings. We won't know what to wear, what to talk about, what we like and what we dislike. And then - we will copy paste neurotypical methods - we will observe what other people speak and do - and then we will go along with the others. And this won't end up well. Other people do not like to be stalked and observed and mimicked. Others won't feel comfortable with someone following them and doing and asking for the same things. Also - we will attract toxic people who seek someone as supply - someone to abuse and discard, someone who has no identity so the target that is easy to manipulate and order command around as pleased.
When we realize we can add to our comfort zone new ideas - and that we have natural ability to come up with being creative and form new ideas - based on the reality - we can then construct our future in better ways than we are doing it right now.
With trauma and abuse - we do not know our identity.
We do not know what we like and dislike. When we are faced with stress and disrespect - all our previous comfort zone chambers will be crumbling down, and it will take time to rebuild inner safety, what we like. Instead we will be in defense mode, we will attend to our immediate needs. And this will make us stuck in surviving and addictions and being stuck.
CBT and coaching tell us that we should expose to our fears.
That we should find some job like in retail where we will be forced to talk to people.
From my own experience - social anxiety will not go away. We will fawn, we will copy paste our previous tools how we handle the abuse. We won't start talking - we will put on a mask, fake social mask and that will be highly stressful.
Instead of hating our social anxiety, instead of hating our comfort zone - we simply need to add more to it. More awareness, more reality. Knowing what we like. And knowing how to handle abuse and how to remove ourselves from toxic people.
With CBT - we won't be able to handle abuse when it happens - in any other way than through hating ourselves and through being a slave to the abuser.
We got to know who we are. What is our personality. Who is the person inside us - so that we do not have to invent it along the way.
With exposure - we will be open to abusers and manipulators and angry people who are unable to control their own emotions.
Due to exposure to previous abuse we will tend to see angry people who disrespect us as correct parole officers whom we must silently obey. We won't see angry people who cannot control their emotions as emotionally immature.
Also we will have operant conditioning where we are afraid of their punishment.
That will be the driving force to isolate, to dissociate, to serve angry people. Fear of some kind of punishment.
But this fear of punishment - when around abusers will not be imaginary fear. Abusers really use punishments - they use threats and control and manipulation to force us to walk on eggshells around them,
and this way we live in fear.
When we live in fear - we do not have Ventral Vagal ambient in external reality.
The only way we can be secure - is to build our isolation, avoidance to feel safe.
The correct way would be that we pull out this safe zone chamber into our external reality.
What makes us happy that we enjoy in the external world and that we express ourselves and create what we are able to create - what makes us happy and secure inside - that we do it externally.
Clothes we wear. Music we listen. Talking. Creating.
When we live in fear - in social anxiety we do not do that outside. We withdraw to our world, we do things alone and think a lot and worry and have intrusive thoughts since nothing else happens around us - so we have a lot of free space for intrusive worry fueled with shame and guilt and external abuse.
Social situations should be easy - we should know social norms and when we express ourselves that we align our expressions with social rules. What makes us happy that we do not cause distress in other people.
And here is the root problem - toxic people will hate it.
They make us shut up, they make us isolated and withdrawn - since they dislike anything positive and nice. They nitpick and criticize and mock and yell scream when we do not walk on eggshells around them.
The critical ingredient in building our identity and our future - needs to take into account toxic people and knowledge and education how much their unfair destructive criticism is to us.
As such - when we build our life - we need to be honest and authentic to ourselves so that our jobs, hobbies, likes, dislike are aligned with what we truly want and believe. When we are fake - we will attract fake people - who will criticize and attack what we like and be in constant drama and conflict about what we want.
We need to be realistic about our expectations and our identity and what are social rules. We got to know what is reasonable.
In our developmental years - we never learned that. Instead - we have learned that we must be quiet, that we must be fake, that we must not want things, that our opinions do not matter and that we must align our life towards toxic people and their needs.
The fear and social anxiety and perfectionism and pain and shame - comes from toxic introject inside us and from external element - toxic people being abusive. We have installed their toxic unrealistic expectations about how our life should be fine and okay and approved - so we will feel when we do not achieve those imposed standards.
When we are having social anxiety - we need to be aware of our comfort zone - and to realize - that social anxiety is based on reaction to abuse. When we remove our comfort zone - we will make social anxiety worse. CBT tell us to develop fake social mask and to remove our caprices - which CBT labels as cognitive distortions.
We need our comfort zone to handle the abuse and to give us directions where we belong. Without it, we won't know how to handle abuse, stress, shock - and then we will be stuck in survival mode, defense mode and in fawning, following and being dependent on toxic people who exploit us.
It is crucial to know that showing what we like - will attract toxic people judgement, mocking, bullying. We need to be aware that toxic people will try to make us feel ashamed for doing what we like.
The point is - to know social situations should be fun and interesting. When we feel threatened, when we feel socia anxiety - then it means that something is wrong - that someone is triggering our fears and coping mechanisms and survival mode.
When we know borderline abuse as the cause of social anxiety - then it is easy to look for people who suddenly change their mood, who are unable to control their reactions, who are easy to explode and who have some kind of punishment - judgmental manners how they interact with people, being both emotionally immature and them lacking social skills.
So we need to know what it means when someone lacks social skills:
1) Personal finances
2) Highly controversial topics
3) Personal health issues
4) Gossip
5)Criticizing others
6) Excessive self-focus
7) Intrusive personal questions
8) Unsolicited advice
We need to know in advance - that meeting or witnessing or hearing about some person who looses their temper - will trigger our social anxiety trauma.
In the same way - anyone exhibiting low social skills like being intrusive - will trigger our social anxiety.
And that our coping survival mechanisms will be triggered to - to serve them, to become their slave and to remove our needs and our well being from the equation. That we will blame ourselves for feeling social anxiety. And we we are not aware why - we will follow CBT explanations and then we will believe that we are wrong, and as such - we must follow toxic people. We will disregard our own opinions and our needs and we will become preoccupied in pleasing the angry person, calming them down and trying hard to make them understand and accept us and to stop hating us and that they do not think badly about us.
When we are aware of our identity - we know our reputation follows us. So if someone is choosing to be angry at us - then we will know that decision of angry person to hate - this is not measuring tape of our worth and value.
I noticed that when someone is angry, when I am under stress, when I will expose and when there is potential that I will meet angry people - that I tend to forget my regular daily tasks, something that people with ADHD report a lot to have problems.
So to help myself - I written down my daily tasks - even though I know majority of them - it does help when I step outside of comfort zone and when my mind is now spinning scenarios about what might go wrong and how to find better solutions to problems and issues.
The point of well being and own needs - is to place awareness into construction of future which otherwise would not be considered due to being stuck in alarm survival mode. When we are under stress or in comfort zone - we won't allow our values and purpose in oure awareness. We will simply exist doing what we can within the prison capabilities, like being stuck in toxic job.
It is like not being aware that allowing our needs and well being to define our future will prevent us from toxic stress - this won't be in our awareness. We will place someone's expectations and approval and judgment as our guiding light.
your_recovery_matters
@recovery_your
Jun 2
How come No one notices how hurt and drained you are, but everyone notices the anger and frustration..
The idea that there
are two worlds, experienced in different ways, was also central to René
Descartes’s rationalist philosophy. Unlike Plato, however, he did not think of the
material world as a “shadow” of an ideal reality. It is not the world that is
imperfect, but our senses, which can be deceived and cannot be trusted to give us
a true idea of the world around us. More reliable is our ability to reason, with
which we can experience the ideal world and get a better understanding of things
as they actually are.
DK Heads Up Philosophy
💭There are two worlds: the world of experience sensed by our bodies and the world as it is in itself.
Immanuel Kant
For empiricist philosophers, reality consists only of the material world we live in—
the world that we experience through our senses. We use our reason to interpret
what our senses tell us, and it is this that provides the ideas we have about the
world.
Objects also have “secondary qualities,” which can differ from one observer to
another and are subjective—for example, the properties of taste, smell, and
color. We can have an accurate experience of the primary qualities of an object,
but our ideas of its secondary qualities are different from the object as it is in
itself.
DK Heads Up Philosophy
☸️Underlying Hinduism and Buddhism is the view that the world we experience is illusory and masks our perception of the eternal, universal reality that everything is part of.
the reality where all is One.
DK Heads Up Philosophy
The Islamic philosopher Ibn Sînâ, also known as Avicenna, imagined a man floating in the air, blindfolded, and touching nothing, so that he receives no information from his senses and is completely unaware of his body or the world outside him. Yet he is still aware that he exists. Avicenna had set out to show that this thing that exists is the man’s soul, distinct from his body.
Around 600 years later, René Descartes presented a similar thought experiment—the idea of an evil demon deceiving all his senses—in order to dismiss anything that could be doubted, and build his knowledge of the world from the single certainty that he existed. But Avicenna and Descartes showed only that the “soul” or “mind” exists and is aware of its own existence,
and not that they had bodies that exist in a material world.
DK Heads Up Philosophy
A brain in a vat
In the 1980s, American philosopher Hilary Putnam:
My brain is wired up to a computer that stimulates it, making me think I’m experiencing
everything in the world, but in fact it is just a series of electrical signals. Every
experience would be the same as if I experienced it with a real body in a real experience would be the same as if I experienced it with a real body in a real world—and I would have no way of knowing that this isn’t the case.
DK Heads Up Philosophy
Some philosophers believe that individuals are free to do anything they want with their lives. We do not
have to live within the constraints of our society.
Danish philosopher Søren Kierkegaard believed that
since many philosophical explanations of existence were at odds with our
individual experience, we have the ability to make choices that shape our lives
However, this freedom of
choice does not necessarily bring us any happiness. On the contrary, when we
realize that we are absolutely free to choose to do anything, our minds reel, and
we have feelings of dread and anxiety. This “dizziness of freedom,” as
Kierkegaard called it
comes from an awareness of our own existence and personal responsibility. We then have to decide whether this leads to despair and
choosing to do nothing, or to living “authentically,” making choices that give
meaning to our lives.
DK Heads Up Philosophy
ADHD weirdo
@ADHD_weirdo_
Dear ADHDers,
Some of us grow up thinking we’re the problem.
Too loud, too quiet, too weird, too sensitive.
But then we find our people and realize:
We were just in the wrong rooms.
You’re not too much.
You’re exactly enough.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
You having "frozen" in response to a trigger is not you having implicitly given consent.
Trauma responses are not "choices." What happened to you when you "froze" or dissociated is not your fault.
Elliot
@1t2ls.bsky.social
don’t tell people (esp strangers, whose thirst traps you’re commenting on) to smile. it’s obnoxious, and implies that your fantasy objectification of the person is more important than how they actually feel or hold their face.
it’s weird and a huge turn off.
Elliot
@1t2ls.bsky.social
being told to smile and being told how i should groom (or not) my body hair are both pet peeves of mine. putting this out there so people know.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
When we were punished not for things we chose or did, but for feelings & reactions we did not choose or control, we develop BS (Belief Systems) that we "deserve" shame for things that aren't our fault-- and/or, we "control" things we can't possibly control.
Scottish philosopher David Hume suggested that we have thoughts, experiences, and memories—what he described as a “bundle of
sensations”—that together form the subjective consciousness we recognize as our self.
William James described consciousness as being like a stream—changing all the time. As we experience new things, our minds interpret the information and organize our thoughts accordingly.
DK Heads Up Philosophy
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
We're not ourselves when we're dysregulated, & those moments aren't moments when we need to be making major life decisions.
Anyone who pressures us to do so-- or shames us for not wanting to do so-- isn't helping us making values- or recovery-consistent decisions. Notice that.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
Making amends w/ the "parts" of ourselves we've been conditioned to ignore or belittle is an ongoing part of daily recovery for many trauma survivors.
Self-forgiveness & understanding is way more important to realistic recovery than understanding or forgiving our perpetrators.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
You are not "difficult" or "high maintenance" for asking or expecting people to do the jobs for which they are paid. No matter what Trauma Brain is trying to tell you.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
I got to a point in my recovery where I realized I was going to struggle on either side of the working my recovery/not working my recovery fence-- but I'd rather struggle w/ trying to achieve my goals & live my values, than struggle w/ my bullies, abusers, or past controlling me.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Jun 6
When someone disrespects you, it’s not a time to lower your expectations so it doesn’t feel so bad. It’s time to raise the bar on how they’re accountable and apologize.
Even a seemingly sound argument can lead a paradox. It is often difficult to see if this is due simply to faulty reasoning, or to false, ambiguous, or even contradictory premises.
📖DK Heads Up Philosophy
Epicurus went so far as to argue that pleasure is the greatest
good, and pain the greatest bad. He thought that morality can be measured by the
amount of pleasure or pain it causes, and so the aim of a good life is to maximize
pleasure and minimize pain. But this was a minority view, and other schools of
thought adopted Socrates’s view.
📖DK Heads Up Philosophy
Nicole Filippone, Autistic Advocate & Author
@sensorystories_
Half of autism is being triggered to the point of extreme unbearable anxiety and then being told you're overreacting
Nicole Filippone, Autistic Advocate & Author
@sensorystories_
PSA... If you're an autistic people pleaser with rejection sensitivity, there's a very good chance it's a trauma response to being told incessantly as a child that you weren't enough. You ARE enough. Take that to your younger self and let yourself heal. You. Are. Enough. ❤️
Defend Survivors
@defendsurvivors
Daily reminder: Whatever you’ve been told a perpetrator has done is probably only a small fraction of what they’ve actually done.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
Have our own back-- even when you f*ck up.
Be on your own side-- even if you don't love the last choice you made.
Be honest & compassionate & realistic & patient w/ yourself-- even (especially!) when trauma conditioning is trying to trick or coerce you into punishing yourself.
Pammy ✨️
@pammyds.bsky.social
Having a zero-tolerance policy on bullshit can save you from so much disrespect and disappointment. Be bold with your boundaries, keep your standards high, and don't settle for less.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
"Letting go" is a process, not a one time decision or event. Don't kick yourself for struggling with it. Grace over guilt-- we're rerouting physical nervous system connections here.
Changing how we think, feel, & behave is the hardest thing humans do-- give yourself a break.
Pammy ✨️
@pammyds.bsky.social
Never disrespect yourseIf by begging anyone for the bare minimum. You'll never have to ask the right person for attention, time, respect, Ioyalty, or love. Because you're worth it and you deserve it. If someone doesn't naturally recognize your value — don’t try to convince them.
Ebrahim…
@ebrahim12.bsky.social
Peace of mind …🫶🏾🤞🏾
If it cost you, your peace is expensive…
AI "sociology aspect about social anxiety"
From a sociological perspective, social anxiety isn't solely a personal experience but is also influenced by societal norms, cultural values, and the social environment. It's shaped by factors like individualism vs. collectivism, gender roles, self-perception, and societal expectations about how individuals should behave in social situations.
Sociological Aspects of Social Anxiety:
Cultural Factors:
Different cultures have varying attitudes towards shyness, social norms, and the importance of social approval, which can impact how social anxiety is expressed and experienced.
Social Appraisal and Self-Concept:
Societal emphasis on social evaluation and performance can intensify feelings of social anxiety, particularly in late modern societies. Those with lower social status or facing inequalities may experience heightened anxiety due to perceived negative evaluations.
Social Learning and Trauma:
Negative social experiences, bullying, and abusive relationships can be triggers for social anxiety, particularly for those with a heightened sensitivity to social interactions.
Social Expectations and Gender:
Societal expectations about gender roles and behavior can influence how individuals with social anxiety perceive and respond to social situations.
Self-Presentation and Efficacy:
Individuals with social anxiety may feel they lack the ability to effectively present themselves in social situations, leading to anxiety about potential negative evaluations.
Stigma and Shame:
Negative perceptions of social anxiety, such as the idea that it's a sign of personal weakness, can contribute to stigma and feelings of shame, further hindering individuals from seeking help or engaging in social situations.
Social Isolation and Interpersonal Relationships:
Social anxiety can lead to social isolation and difficulties forming and maintaining interpersonal relationships, impacting overall well-being.
Interpersonal Conflict:
Socially anxious individuals may experience increased interpersonal conflict, potentially further exacerbating their anxiety.
Tell me no Lies 💔❤️🩹➡️❤️🥰🌹💪🏻🚫Narcissists🚫
@lovewins11011
A narcissist will never see themselves as the problem. In their mind, you are the reason they lie, cheat, manipulate, gaslight and fly into rages when challenged.
Interrogative suggestibility: The extent to which an individual is influenced by leading questions, pressure, or suggestions during questioning, such as during police interviews or psychological evaluations. Highly suggestible individuals may alter their answers in response to the authority they are confronted with, even if it isn’t directly hostile
https://thedecisionlab.com/biases/suggestibility
Suggestibility can cause us to make bad decisions, particularly if we receive false information that interferes with our memories and existing knowledge. This incorrect information can impact how we recall memories and make choices when dealing with similar instances. For example, we may recall a dentist visit as being uncomfortable yet manageable. Suppose another person describes how horrible they imagined our dentist appointment was. Based on this discussion, we may alter how we remember our experience at the dentist's and then later postpone a necessary appointment because of this warped memory.
Individuals with a vulnerability to suggestibility are also at risk of manipulation as they are more likely to believe and act on information given to them by another person. In mildly or overly manipulative contexts of seduction or coercion, an individual’s suggestibility increases in the same way as someone under the influence of hypnosis.28 In these situations, a person’s confidence and trust in their own judgements is often slowly eroded, making them more likely to rely on external suggestions during decision-making.
https://thedecisionlab.com/biases/suggestibility
A typical example of the looming effect of suggestibility is seen in witness testimonies. When individuals give their initial statements, their memory of an event can be altered because of the initial interview process. During the interview process, attorneys or police may make suggestions, confusing and distorting the memory of the witness. This phenomenon has been extensively documented and observed and poses a real and threatening issue for legal decision-making.
https://thedecisionlab.com/biases/suggestibility
Suggestibility can also impact the judicial process through false confessions and compliance. Otgaar et al. conducted a review of experimental data in which false confessions were experimentally evoked, and suggestibility and compliance were measured.20 They found that high levels of suggestibility lead to individuals being more predisposed to making a false confession to a crime they did not commit. High levels of compliance also had the same effect, although not to the same extent.
https://thedecisionlab.com/biases/suggestibility
In medical research and clinical trials, suggestibility is a variable researchers must address and manage due to its influence on participants’ behaviors and responses. Clinical trials rely on participants giving truthful and objective accounts of how they are feeling or how they experienced an intervention. One ongoing question that looms over the sector is how technology can impact participant beliefs in these trials and whether this may alter responses to treatment by modulating suggestibility. Using online multi-media consent forms rather than traditional paper-based forms has been shown to enhance participants’ understanding of and engagement with clinical trials. Similarly, presenting an informational video during the consent phase can make patients more willing to participate in the research study and lead to better information retention.
https://thedecisionlab.com/biases/suggestibility
People who experience intense or strong emotions are generally more receptive to suggestibility. This is because strong emotions, such as fear or excitement, can overwhelm the rational part of the brain (prefrontal cortex), which is responsible for critical thinking and logical analysis. When this happens, people are more likely to accept external suggestions to help them make decisions. Heuristic thinking, or the brain’s reliance on shortcuts to make quick decisions, may also influence suggestibility. When we are trying to make a decision, especially under pressure, cues or suggestions that are presented to us may be used as shortcuts by the brain.
https://thedecisionlab.com/biases/suggestibility
Psychologists believe that people with lower levels of self-esteem and assertiveness are typically more suggestible. The relationship between low self-esteem, low assertiveness, and suggestibility stems from psychological traits and cognitive tendencies that influence how people respond to external suggestions. For example, individuals with low self-esteem and low assertiveness often experience an increased need for approval which can lead them to conform to others’ suggestions to feel more accepted. Similarly, while assertive individuals are better equipped to question and resist others’ suggestions, less assertive people may lack the skills or confidence to critically evaluate what they’re being told. Finally, an overall lack of confidence in one’s decisions can make individuals more dependent on external cues, instruction, or opinions.
https://thedecisionlab.com/biases/suggestibility
Finally, researchers have also attributed the variability to suggestibility to differences in attentional functioning. Attentional functioning is defined as our ability to filter irrelevant information and inhibit prepotent responses.5 Overall, several behavioral and social characteristics influence each individual’s tendency to take cues from others and change their beliefs based on those suggestions.
https://thedecisionlab.com/biases/suggestibility
How to avoid it
Suggestibility is a trait that individuals possess to varying degrees, and in a way, it’s part of who we are. Due to its basis in human cognition and social behavior, it may not be entirely possible to eliminate suggestibility. However, individuals can take steps to reduce the influence in various situations through strategies that enhance critical thinking, self-awareness, and emotional regulation.
https://thedecisionlab.com/biases/suggestibility
Our identity is influenced by factors such as our class,
ethnicity, age, and gender as well as our tastes in things
such as fashion and music. The process of finding out
who we are and where we belong takes place within
society.
DK Heads Up Sociology
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
A narcissist will train you to explain yourself in every possible way, just so they can twist your words and use them against you.
Meanwhile, they'll never explain themselves to you, because accountability was never part of the plan.
Defend Survivors
@defendsurvivors
“You can be kind, trusting, and loving and end up in a beautiful healthy relationship. You can be kind, trusting, and loving and end up in a very toxic abusive relationship. What’s the difference? A perpetrator.”
Defend Survivors
@defendsurvivors
Jun 10
Too often the survivor is ostracized-not the abuser. The reality for many survivors is that if they try to escape abuse they’re not just leaving the abuser but also their family and community. If we want to help survivors, we have to understand the reality they are facing.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
If you grew up in a home where people blamed you for their bad behavior, your healing is learning to no longer be responsible for how people behave. It will feel like a threat to stop reacting & rescuing people, but that is rescuing you the way you should’ve been a long time ago.
Shadows of Control
@shadows_control
We learn the rules of survival:
Don’t argue. Don’t push back. Don’t show hurt.
We become experts at reading the room, gauging moods, anticipating the next storm.
But with every compromise, every silent surrender, we lose a piece of ourselves.
And the person we once were feels like a distant memory. 💔
Shadows of Control
@shadows_control
Abusers are masters of triangulation, pitting you against others—friends, family, even children—to create competition, doubt, and division. 😤
Tell me no Lies 💔❤️🩹➡️❤️🥰🌹💪🏻🚫Narcissists🚫
@lovewins11011
A victim telling the truth is not a smear campaign.
A smear campaign is a narcissistic abuser telling lies about their victim to damage their reputation.
Tell me no Lies 💔❤️🩹➡️❤️🥰🌹💪🏻🚫Narcissists🚫
@lovewins11011
A narcissist expects you to give up everything in order to be their nothing.
The Narcissist Box
@NarcissistBox
Never trust a narcissistic co-worker.
Never tell them your business. If they invite you out for drinks ...red flag! Drink water.
Defend Survivors
@defendsurvivors
Traumatized children do not have shortcomings you need to overlook - they have extreme survival skills you need to understand.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
Regulating our nervous system is often about slowing down & experiencing stillness-- which can be counterintuitive & scary to trauma survivors who've been conditioned to believe that slowing down or standing still will allow abusers, bullies, or predators to catch & hurt us.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Malignant narcissists don’t just abuse, they dehumanize their targets. They convince themselves that you don’t deserve compassion, dignity, or even basic human rights. In their eyes, you become less than a person—just a tool to use, a threat to silence, or a flaw to erase. And once they've dehumanized you, anything they do to you feels justified in their twisted reality.
Why they do it:
1. To Justify the Abuse
They can’t abuse you and still see you as fully human. So they convince themselves that you’re "too dramatic," "weak," "crazy," or "the problem." That way, anything they do to you becomes “justified.”
2. To Project Their Own Shame
Narcissists carry deep shame they refuse to deal with. Instead, they offload it onto you. You become the scapegoat, the broken one, the one they can punish and look down on—because that’s how they keep their fragile ego intact.
3. To Stay in Control
They see life as a hierarchy—and they must be on top. If they can reduce you to something “less than,” they can control you, exploit you, and erase your ability to challenge them.
4. To Shut Off Empathy
Empathy makes them vulnerable. If they let themselves feel for you, they’d have to acknowledge your pain—and that threatens the entire illusion of superiority. So they dehumanize you to silence their conscience.
And yes, they often truly believe it.
Once you become a source of narcissistic injury or no longer serve their ego, they begin to view you through a distorted lens. You're no longer a person—they see you as a threat, a liability, a tool, or a burden.
And the longer this goes on, the more real this false reality becomes in their mind.
How It Looks in Real Life
-Dismissiveness: “You’re just being sensitive.”
-Objectification: They treat you like a thing they own or a resource to use.
-Mockery: They ridicule your pain or twist your words in public.
-Scapegoating: They blame you for their bad behavior and project their own darkness onto you.
-Isolation: They separate you from people who might affirm your humanity or worth.
Their ultimate aim isn’t just to hurt you—it’s to erase your sense of self, your credibility, and your emotional reality. If they succeed, you’ll stop fighting back. You’ll start doubting yourself. You’ll shrink, accommodate, and internalize the idea that you’re the problem.
That’s when they feel most powerful.
That’s when they feel safe from exposure.
Remember, you are not the problem.
You are not less than.
You are not what they told you you are.
Dehumanization is a manipulation tactic—nothing more.
Recognize it. Call it out. Reclaim your humanity.
Now some of you may be thinking (like I do) “but I feel like narcissists are less than human. They don’t act human. I think they’re evil. I don’t think they deserve any compassion anymore for the things they’ve done. Does that make me as bad as them?”
The answer is no. Feeling that way doesn’t make you like them—it makes you human. You’re responding to cruelty, betrayal, and psychological harm the way any sane person would: with outrage, with grief, with a sense of moral injustice. The difference is, you still ask the question. You still have a conscience. You self reflect. They don’t.
-
Throughout his work, Marx was concerned with the emotional and physical costs of living in a capitalist society. He believed that many people experience a feeling of “alienation” – a sense of being unfulfilled in life and disconnected from other people. Marx believed that this feeling of alienation was especially common in the workplace, where people felt they had no control over their working conditions or the goods they produced.
📖DK Heads Up Sociology
The notion of childhood as a special and innocent time of
life is a recent social construction. French historian
Phillipe Ariès’ book Centuries of Childhood was
published in English in 1962 and explained how
childhood as we know it did not exist until the 19th
century. Before this people were either infants or adults.
📖DK Heads Up Sociology
In a classic work on education, Schooling in Capitalist America, published in
1976, US sociologists Samuel Bowles and Herbert Gintis suggest that while
education does provide knowledge and skills, it also has a role in maintaining the
existing social order. Education accustoms young people to accepting certain
behaviours and restrictions; in other words, it makes them do what they are told.
In their book, Bowles and Gintis explained what they called the “hidden
curriculum”. This has nothing to do with the formal programme of studies which
every student knows about, with subjects such as mathematics, science, and
languages. The hidden curriculum uses rules, punishments, and rewards to teach
students to conform to such norms (social expectations) as punctuality, smart
dress codes, and obedience to instructions from those in authority.
Bowles and Gintis claimed that there is a parallel between the way school is
organized and the way work is organized. In what they called a “correspondence
theory”, they saw the power of teachers as similar to that of a manager at work,
and the routine of school corresponding with the nine-to-five routine of the
workplace. Neither students nor workers have much control over what they do
📖DK Heads Up Sociology
In a book called The Social Construction of Reality published in 1966, Austrian
sociologists Peter Berger and Thomas Luckmann noted that institutions played a
key role in maintaining society. They argue that we often take institutions for
granted and do not really notice them, but they play a vital role in giving shape
to the society in which we live. Institutions also affect people’s identities,
shaping in various ways how they think and act towards others.
The most common types of institutions across all societies are education,
religion, the family, marriage, government, culture, and business.
📖DK Heads Up Sociology
The system ain't broken by accident. It's broken on purpose.
Josh
@JD_Quotes2017
People these days don't apologize for doing wrong, rather they blame us for acting how we react.
Nyle Beck
@IAmMyBestToday
Telling a narcissist what they did to you or said to you that hurt you is the fastest way to anger them. To them, accountability is a 4-letter word, and results in blame-shifting, gaslighting, defensiveness, and retaliation. Please disengage. Your mental health deserves better.
The concept of community evokes an image of a group of people who share a
common culture and set of values, and, most importantly of all, live in the same
area.
For example, we can talk about
communities such as the gay community, the business community, or the student
community, where a shared characteristic forms the basis for people’s
association rather than that they live in the same place.
📖DK Heads Up Sociology
Much of Weber’s writing explores the effects of “rationalization” in society.
This refers to the way Western society has become increasingly organised
around reason, logic, and efficiency. Weber argues that, although rationalization
leads to greater technological and economic advances, it also limits human
freedom and creativity. According to Weber, rationality has trapped modern
society in an “iron cage”, leading to a widespread sense of “disenchantment” or
disillusionment.
📖DK Heads Up Sociology
In her book The Managed Heart (1983) Hochschild introduced her theories on
“emotional labour”. This refers to the way employees are required to display
certain emotions at work.
Hochschild claimed that this had a negative impact on the
airline staff because, over time, they felt as if they had lost ownership of their
own emotions.
📖DK Heads Up Sociology
US sociologist and Marxist Harry Braverman, writing in the 1960s, saw
technological advancement as the beginning of the end of work for human
beings. He imagined a world where people were set free to devote their energies
and extra leisure time towards developing their natural creativity and skills.
📖DK Heads Up Sociology
Anyone living in an area of high unemployment, where
access to education is limited, or ethnic and religious discrimination are
widespread, could find it difficult to join mainstream society. When this
happens, claims Merton, people face a choice. They must either accept life on
the margins of society, or do what Merton calls “innovate”: that is, use illegal
means to gain legal ends.
📖DK Heads Up Sociology
Durkheim believed that society is held together by shared values and beliefs. In
his book The Division of Labour in Society (1893), he argued that as society
became more industrialized, people’s jobs became more specialized, and shared
experiences in the workplace became less common. Durkheim used the word
“anomie” to describe the sense of despair people felt as they became
increasingly isolated in society.
📖DK Heads Up Sociology
Defend Survivors
@defendsurvivors
It is extremely common if you didn’t even know what was happening to you was considered abuse. Why? Because society normalizes and excuses abuse every day.
Émile Durkheim believed it is not primarily fear of punishment that prevents
most people from committing crime. He suggested, rather, that people do not
commit crime because the moral values they absorb from society have a
powerful restraining influence. We learn at a young age that breaking rules does
more than risk punishment. Wrongdoing evokes guilt, embarrassment, and selfblame, especially if the culprit is caught. Thoughts of public exposure and family
shame, and living with a guilty conscience, often prevent someone from
breaking the law in the first place.
📖DK Heads Up Sociology
sociologist Erving Goffman in his book Stigma (1963) talks about how people
work hard to maintain a front of normality, and avoid encountering negative
reactions, if they have something they want to keep hidden, such as a mental
illness. This requires exhaustive planning and leads to more psychological stress.
📖DK Heads Up Sociology
IVY
@Iamivy05
cutting off a narcissist from your life and radically accepting you're going to be the villain in their delusional world is top-level self-care.
Samantha Billingham
@SODASam_
Jun 14
Coercive control is a dangerous form of domestic abuse that is often invisible to outsiders.
As we grow up, we unconsciously absorb many cultural ideas from the social group in which we live.
This early input is influential in shaping our future tastes and preferences.
DK Heads Up Sociology
Jacy, LPC
@ATMwithJacy
Learn what people are capable of and remove yourself if it’s not for you.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
If someone has expectations attached to their apology, it's not an apology.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@DrDoyleSays
Some people won't support your trauma or addiction recovery because they don't identify with it. They've never had to do something as hard as you do in waking up every morning & choosing recovery.
They don't recognize the specific strengths & intelligence you've had to evolve.
@DrDoyleSays
Don't tether your self-esteem to someone else's attention span.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Workplace bullies often exhibit petty and spiteful behavior, driven by an inflated sense of ego and a lack of maturity. Their actions reflect a childish mentality that undermines the professional environment, creating a toxic atmosphere for colleagues.
Symptoms of a guilt complex can include:
Persistent feelings of self-blame and worthlessness
Difficulty forgiving oneself for past mistakes
Overwhelming sense of responsibility for negative outcomes
Obsessive thoughts about past actions or decisions
Avoidance of situations or people that trigger feelings of guilt
Physical symptoms like fatigue, headaches, or stomach issues due to emotional distress
Difficulty concentrating or making decisions due to preoccupation with guilt
Insomnia or changes in appetite as a result of guilt-related stress
Tendency to seek reassurance from others to alleviate feelings of guilt
Inability to experience joy or pleasure due to ongoing guilt feelings
A guilt complex is deeply ingrained into your sense of self. It is not just feeling guilty over a mistake, but letting that mistake define you.
Making mistakes is something we all do; self-compassion and forgiveness is key to living a healthy and fulfilling life.
https://www.lifebulb.com/blogs/do-i-have-a-guilt-complex-what-it-is-and-how-to-deal-with-it
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
No force on earth can stop the confidence of a trauma survivor who finally understands it was not their fault.
Josh
@JD_Quotes2017
If it makes you happy, no one else's opinion should matter.
Josh
@JD_Quotes2017
A Narcissist will stay with whoever they can Use and Manipulate.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
I think many of the people who I identified as covert narcissists are actually psychopaths. This describes a number of people I’ve encountered up close. Also, I think there are many more female psychopaths than we acknowledge. And I think this is because female psychopaths are more covert about their predatorial or manipulative nature.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
I always know I’m dealing with a narcissist when they’re trying to make me feel bad for doing nothing wrong.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
"Yea but what I'm saying is it's pretty typical of projection when someone has done something wrong to you. Either that or we have far more clinical narcs walking than anyone is willing to admit lol"
I don’t know what you mean here. When someone comes and attacks you when you’re trying to help people or just doing something harmless that makes you happy and someone tries to tell you you’re doing something wrong and make you feel guilty, they’re attacking you. That’s not projection.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Malignant narcissists feel incredibly threatened by genuinely good, honest and moral people.
So they work obsessively to make the good guys look like the bad guys and the bad guys look like the good guys.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Jun 24
After abuse, perpetrators are quick to remind their victims of good times they’ve shared. Just a reminder: there are millions of people who contribute to others good memories without traumatizing them. There is no memory good enough that will make the impacts of abuse go away.
Shadows of Control
@shadows_control
“If you accepted the abuse, you are half the problem”
Not true!
What we tolerate shapes how someone treats us, and recovery involves examining, owning, and healing our own issues, as well as the ways we adapted to survive. But the victim is NEVER ‘half the problem.’ Abuse is always 100% the responsibility of the abuser.
When someone is manipulated, controlled, threatened, and psychologically worn down, they’re not ‘allowing’ abuse—they’re surviving it.
If someone is chained up, would we ever say they are half responsible for being unable to escape? Abusers create psychological chains, trapping victims in an invisible cage through tactics such as isolation, financial control, threats, blackmail, gaslighting, manipulation, and weaponizing children to exert control.
Ignoring, walking away, or standing up to an abuser is met with escalation and retaliation. For women with children, the stakes are even higher – they know too well that resistance could mean their child becomes the target of their payback.
Abuse thrives on power and control, and the responsibility lies solely with the one wielding that power to harm. Victims don’t choose abuse; they navigate unimaginable circumstances to stay safe.
Blaming victims perpetuates the harm and silences their voices. We need to keep the blame firmly where it belongs—on the abuser.
-
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissists—especially malignant ones— operate in two distinct realities:
1The constructed reality they want others to believe:
This is the carefully curated version of themselves and their life. In this world, they are the victim, the hero, the ideal parent, the successful professional, the generous friend—whatever mask best serves their ego and manipulative goals. This reality is for public consumption and is designed to draw admiration, sympathy, or allegiance.
2The hidden reality they don’t want anyone to see:
This is where the manipulation, cruelty, abuse, exploitation, and truth-twisting happens. It includes things like smear campaigns, gaslighting, covert triangulation, and pathological lying. This reality contradicts their public image, which is why they go to great lengths to hide it—even from themselves sometimes through denial or rationalization.
They enforce this dual-reality system by:
•Compartmentalizing relationships: So people don’t compare notes.
•Controlling narratives: Using lies, half-truths, and shifting blame.
•Discrediting truth-tellers: Especially scapegoats or survivors who see through the mask.
•Using flying monkeys: To reinforce the fake reality and punish dissent.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
The least likely people to acknowledge your healing, are the ones who caused your need for it.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@DrDoyleSays
"Letting go" of pain isn't a one time event, because "hanging on" is a conditioned, heavily reinforced pattern in our nervous system (not a "choice").
What "letting go" actually involves is overwriting & rewriting those patterns & programming-- again, & again, & again, & again.
Nicole Filippone, Autistic Advocate & Author
@sensorystories_
There are two areas of emerging research that change EVERYTHING about autism awareness... and I wish more people were talking about them...
1. A study found evidence to suggest that "mild" stress can trigger PTSD like symptoms in autistic brains
(There's lots of nuance to the research that you can find in the study, I'll link to it below)
2. Another study found that autistic people experience a type of anxiety that doesn't fit any of the existing anxiety disorders currently included in the DSM (link below as well)
To me, these studies explain my internal autistic experience better than literally ANYTHING ELSE I have come across.
And this is absolutely earth shattering for autism awareness in my opinion...
Because the diagnostic criteria are 100% focused on observable behaviors (ones that society finds "unacceptable" and "inexcusable" most of the time).
But these two studies explain what's UNDERNEATH those behaviors...
We have anxiety.
We have TRAUMA.
And not from things society typically "excuses" (like assault or abuse)...
Because the things giving us anxiety and trauma are perceived as MINISCULE to those who aren't autistic.
So people simply don't get it.
They think we're WILDLY overreacting.
But this research has the potential to give those people a window into our autistic brains and how they work. (IF they're willing to look through it.)
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11089364/
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
For every moment of dramatic, painful programming we remember from our abusers & bullies, there are usually dozens & dozens of other moments of programming & conditioning that we don't explicitly remember.
We rarely develop our painful BS (Belief Systems) in one-off incidents.
Impiety
@noholyscripture.bsky.social
Humans aren’t born craving gods — they’re born curious, social, & vulnerable.
Religions exploits that vulnerability by
🔸 Introducing fear (of hell, judgment, exclusion).
🔸 Providing false comfort (imagined protection, afterlife promises).
This creates an addiction rooted in fabricated premises.
-
Gregarious and sociable, the Spanish are at
their happiest in groups, from family to friends and the
mass gatherings of the fiesta.The natural exuberance of
the Spanish, particularly when conversation is flowing,
can appear confrontational, but it’s usually more about
posturing than genuine anger or aggression.
Speak the Culture_ Spain_ Be Fluent in Spanish Life and Culture
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
One of the most startling things many of us realize as we work our trauma & addiction recovery is: we are completely different people than we thought we were-- when we stop trying to "perform" for people who may or may not even understand or want the best for us anyway.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
You are not responsible for anyone's distorted perception of you.
Stand firm in your own light and truth..
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@DrDoyleSays
One of the most important-- & heartbreaking-- realizations I had in my own recovery was: there are certain people who trigger me; it's not their fault & it's not my fault; & I just can't have them in my life. Maybe ever.
My safety, stability, & recovery is more important.
Defend Survivors
@defendsurvivors
If someone tells you that you’re the problem because you won’t do what they think you should do to ‘heal’ then they are the problem not you. There is no one right way to ‘heal’. You’re the expert on your experience and your healing.
#respectsurvivors
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Trauma says “Fix yourself and people will love you.”
Healing says “Meet me in the parts you think are hard to love.”
Josh
@JD_Quotes2017
Self care means not letting people stress you or put you through unnecessary hurt and pain.
Love yourself enough to not tolerate it.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Jun 27
If you want to see the true measure of a person, watch how they treat their inferior, not their equivalent.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Jun 27
There's something seriously wrong with someone's spirit if they gain pleasure from humiliating, embarrassing, slandering, and belittling other people for entertainment.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Most of us expect a baseline of honesty from people.
Even if someone lies, we expect to see signs — discomfort, guilt, hesitation. We assume that if someone does something wrong, they’ll at least feel some shame. These expectations are part of how we navigate trust, connection, and morality.
That’s why encountering a malignant or covert narcissist is so deeply unsettling.
They lie without flinching. No shame, no hesitation. They invert reality to suit themselves — painting the innocent as guilty, and casting themselves as the victim or hero when they are, in fact, the abuser.
To most of us, this feels inhuman. And that’s because it is — it violates the unspoken social contract that underlies empathy and conscience.
This is what makes narcissistic abuse so disorienting: you’re not just being mistreated — you’re being trapped in a false reality constructed by someone who feels no remorse for the damage they cause.
LIMITLESS MIND
@limitlessmindon
Jun 27
Don't make yourself small for anyone. Be the awkward, funny, intelligent, beautiful little weirdo that you are. Don't hold back. Weird it out. Be the glitch.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Jun 27
When a flower doesn't bloom you gotta fix the environment in which it grows, not the flower. 🌹
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@DrDoyleSays
Meet "their" misunderstanding of you w/ compassion. In not understanding you, they're missing out on something awesome.
Do not take their misunderstanding of you as a challenge to "make" them understand you. Life is too short, & you have a recovery to work.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Stop telling people to focus on the good times, when that’s not what they’re needing to heal from.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
A person can't just "get over it" when they've had to live their whole life differently because of it.
Narcissistic Abuse Awareness
@AwareOfTheNarc
An enabler tells you how to manage the abuse.
A real ally helps you recognize it shouldn’t be happening in the first place.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissists don't see others as full human beings with their own inner lives, needs, or rights. Instead, they tend to view people in terms of utility or threat.
Here’s how narcissists actually perceive others (friends, family, coworkers, colleagues, acquaintances) 👇
1. Competition
Especially if you have talents, strength, empathy, or integrity. Anything they feel they lack but envy in others becomes a threat to their fragile ego.
2. Supply
They see people as sources of narcissistic supply — admiration, attention, obedience, or emotional reactions. You're not a person; you're a fuel tank to keep their self-image inflated.
3. Tools or Pawns
You may be viewed as a means to an end — useful for achieving status, wealth, influence, or hurting someone else. This can include romantic partners, children, friends, even therapists.
4. Obstacles
If you're in the way of their goals, truths they want to avoid, or if you're exposing their lies, you become an enemy — something to smear, silence, or destroy.
5. Reflections
They may project their own traits onto you. If they're insecure, they may accuse you of being controlling, selfish, or manipulative. You become a mirror they want to shatter.
6. Extensions of Themselves
This is especially common with narcissistic parents. They see children or partners not as separate beings but as extensions of their own identity — expected to reflect their greatness and never outshine or embarrass them.
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
Jun 29
Not responding to toxic people is the most powerful
response you can give.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
If you are bullied and abused constantly by your parents and it makes you angry all the time, you don’t have an anger problem. You have an abusive parent problem.
The anger is justified. The abuse is not.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Jun 29
People need to stop being offended by things that have nothing to do with them.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissists will always find a way to blame someone else for their abuse. It’s never their fault
Defend Survivors
@defendsurvivors
It doesn’t matter what the trauma is, people don’t want to hear about it unless it’s a ‘pain into purpose’ or ‘how I found forgiveness’ type of story. We are really bad at just sitting with trauma and supporting survivors.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Boundaries are walls, not doors.
The Wily Survivor
@WilySurvivor
Trauma isn't just about what happened. It's also about what didn't happen, like not being heard, supported, comforted, protected, or believed.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissists want you to think their abuse is punishment for something you did wrong
Pammy ✨️
@pammyds.bsky.social
Maturity is when you finally stop wasting time convincing people to treat you correctly. You just start to observe their choices, understand their character, and decide what you’re going to let into your life.
Tell me no Lies 💔❤️🩹➡️❤️🥰🌹💪🏻🚫Narcissists🚫
@lovewins11011
A sign you’re in a narcissistic relationship is things only remain peaceful as long as you suppress your thoughts, feelings and opinions.
Pammy ✨️
@pammyds.bsky.social
I promise you, no friendship, relationship, or situationship is worth hurting your mental health over. Period.
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
Jul 5
There are two sides to every story, then there's the narcissist's version, which often has nothing to do with the original events.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
Be willing to ghost the entire goddamn world for your safety, stability, & recovery if you have to.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
Some people aren't for you. Some situations aren't for you. Some jobs aren't for you. Some recovery tools & philosophies aren't for you. No shame.
"Radical acceptance" doesn't mean we stay in places we don't belong. It means we gotta start somewhere to get somewhere.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
You are not a shitty person because you struggle with depression, anxiety, addiction or low self-worth. You’re an important person whose been hit with shitty circumstances and are trying to make sense of your pain.
Dr. Jen Wolkin | ADHD + Trauma Therapist
@drjenwolkin
Neurodivergent people don’t usually mask because we wish to be neurotypical. We mask, because we were repeatedly told we would only be worthy or lovable if we acted “normal” and hid our “quirks.” We mask to change ourselves so we fit in. Masking is a trauma response. -Dr. Jen
Josh
@JD_Quotes2017
Walk away from anything that gives you bad vibes. There is no need to explain or make sense of it. It's your life, do what makes you happy.
Eric Alper 🎧
@ThatEricAlper
I think secretly most people are emotional wrecks. Some just hide it better than others.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
How we were, or are, treated does not reflect or create our worth.
We live in a culture & world where entire races of humans were treated horrifically for centuries-- & often still are. That doesn't reflect their worth; your bullies' & abusers' behavior does not reflect yours.
-
-
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissistic parents often shame their children not for not being narcissistic enough. They expect their child to value the same things they do: appearance, status, power, control, and external validation. If the child is humble, introspective, or emotionally honest, the narcissistic parent may see those traits not as strengths — but as weaknesses.
-
Autistic Lauren 🏳️⚧️ 🏳️🌈
@Autistic_Lauren
Autistic people generally prefer direct communication rather than having to decipher hidden tones and meanings, and yet we're the ones with communication difficulties?
lets heal and recover
@recovery_your
Stop telling people to “just move on.”
Trauma isn’t a memory it’s a rewiring.
It lives in your body.
It echoes in your nervous system.
It hijacks your reactions before your brain catches up.
This isn’t about weakness.
It’s about biology.
And healing takes more than time it takes safety.
lets heal and recover
@recovery_your
Jul 15
Depression doesn’t always look like sadness.
Sometimes it’s:
– Constant brain fog
– Leaving laundry in the machine for 3 days
– Not remembering the last time you laughed
– Saying “I’m fine” and meaning “I’m drowning”
– Feeling exhausted from doing nothing
– Crying when no one’s around
– Wanting connection but isolating anyway
This is what depression can really look like
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
A mistake is an accident. Bullying, stalking and lying are not mistakes, they are intentional choices.
-
Autistic x ADHD.Co
@autisticadhdco
People with ADHD need direct and to the point communication.
Vague comments are the fastest way to fill our brains with negative thoughts.+
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
I have never experienced abuse that made me stronger. It made me fearful, confused, dysregulated, afraid, detached, addicted, shameful, and apologetic to people who were hurting me. Surviving it did not make me strong. It made me tired.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Let's normalize acknowledging problems so we can fix them instead of using gaslighting to escape addressing them.
Vivian
@suchnerve
i don’t think the human psyche was meant to handle processing this much information on a daily basis
Josh
@JD_Quotes2017
You disrespect yourself every time you let something slide that doesn't sit right with you, so I've buckled down on my boundaries as a form of self love. My time is valuable, my feelings are valid & those who love me will respect it. I desire nothing more & will take nothing less
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Your body isn’t weak because it responds to triggers. It’s remembering.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
The malignant narcissist parent has no intention of teaching or raising their children or preparing them for life.
Their ONLY intention is to keep control over them.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
People don’t need to understand your boundaries in order to not cross them. They understood when you said “No” and that is enough. People who continually hurt you and pretend they don’t understand, will understand best when they no longer have access to you.
Dr. Jen Wolkin | ADHD + Trauma Therapist
@drjenwolkin
Traumatic Stress is Your Nervous System Dysregulating,
it’s NOT Your Personality. XO, Dr. Jen
Autistic x ADHD.Co
@autisticadhdco
If you ask yourself if you feel like doing something and the answer is "no" then it’s a "no".
ADHD and Autism means we run out of energy faster, so we need to take care of it.
Don’t spend it on stuff that you know you don't enjoy just because it seems like the "normal" thing to do.
lets heal and recover
@recovery_your
·
Trauma responses can also look like:
• Constant people-pleasing.
• Apologizing for things that aren’t your fault.
• Assuming people are mad at you.
• Struggling to make basic decisions.
• Feeling like you’re “too much” and “not enough” at the same time.
• Over-explaining everything.
• Never feeling safe even when you are.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
The people invested in your growth and well-being will feel secure and appreciative when you place boundaries with them.
Defend Survivors
@defendsurvivors
🛑 One word I wish people would stop using? Codependent - just use ‘abused’ instead. There’s nothing co or joint about abuse. One person is being abused and one person is abusing. Period.
#nomore
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
We are not going to diminish our CPTSD symptoms by snarling at our body & nervous system, "don't DO that!"
Managing trauma symptoms starts w/ meeting those symptoms w/ acceptance & compassion & patience-- which, yes, is a tall order when we're frustrated & confused by them.
Nicole Filippone, Autistic Advocate & Author
@sensorystories_
Jul 25
There's a type of autism that doesn't get talked about much because it's really hard to explain. It's the kind that doesn't look like anything. Not "weird" or "different" or "quirky" or "odd"... it's not seen at all. But the internal distress and anxiety is unrelenting.
mood
@reidahad
PEOPLE. ARE. GOING. TO. TALK. BADLY. ABOUT. YOU. NO. MATTER. WHAT. SO. JUST. DO. WHAT. MAKES. YOU. HAPPY
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
I always know I’m dealing with a narcissist when they try to shame me for calling out abusive behavior
because to them, exposing the abuse is a greater offense than committing it.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
If they support the people who’ve traumatized you, they don’t need to know anything about your life. Let them guess.
Developmental psychologists now know that before the age of 3,
children are incapable of understanding deception because they are
unable to discern the difference between what they believe and
what their mother believes. They also do not understand incongruence, that mother might feel one emotion while expressing
another or that hostility can be masked by a smile.
Understanding the Borderline Mother, Christine Ann Lawson
Borderline personality disorder can be
passed from one generation to the next, making early recognition
and intervention essential.
Understanding the Borderline Mother, Christine Ann Lawson
One does not eagerly look back on
a dark and painful past. The willingness to look, however, allows us
to see the present more clearly and to create a brighter future for
our own children.
Understanding the Borderline Mother, Christine Ann Lawson
Submerged in the cold
darkness of despair, mothers with borderline personality disorder
(BPD) struggle to keep their heads above water. They cling
desperately to whoever is near and can pull their own children into
the blackness. Borderline mothers are intense, unpredictable, and
sometimes volatile. One day they may see their children as angelic;
other days their rage or sarcasm can shatter their children's souls.
Understanding the Borderline Mother, Christine Ann Lawson
children in Borderland are puzzled by the
contradictions of their world and live on the fine line between
sanity and insanity.
Although she can function extraordinarily well in other roles,
mothering is the single most daunting task for the borderline
female.
Understanding the Borderline Mother, Christine Ann Lawson
lets heal and recover
@recovery_your
Forgive your parents, they did their best.”
No.
Sometimes their best wasn’t enough.
Sometimes their best left you fucking traumatised.
And pretending otherwise doesn’t heal anyone.
So fuckoff with your forgiveness bullshit
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Never tell a person they need to get over circumstances they didn’t ask for. You have no idea the ways they’ve paid for that.
When Laura visited
her mother as an adult, her mother admonished her, asking, "Why
don't you ever call me?" But when Laura telephoned, her mother
sounded annoyed, answering the phone impatiently and asking,
"What? What do you want?" Interactions with borderline mothers
often leave the child feeling guilty and confused.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother,Lawson
Joan Crawford, on the other hand, rigidly enforced unreasonable rules that suited her needs, rather than her children's needs. Christina explained that her mother programmed every minute of the day, allowing exactly half an hour for eating each meal and for washing the dishes.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother,Lawson
Winnicott (1962) emphasized the importance
of the child's need for "the good enough mother" (p. 57) who
provides enough consistency and calmness so that the child is not
overwhelmed with anxiety. Without structure and predictability in
their emotional world, children have no reality base upon which to
build self-esteem and security.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother,Lawson
𝑹𝒆𝒗𝒂 ✨
@Reva_M_S
With narcissistic people, there's always a string attached to their giving
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Your silence is a blank canvas for them to paint upon
Nicole Filippone, Autistic Advocate & Author
@sensorystories_
High functioning = how my autism looks to others
Lower support needs = what I need from others to get my needs met
High masking = what I do to appear "normal" to others
Internalized autism = the emotional and mental toll of masking, aka how autism FEELS to ME
-
Studies show that chronically intense emotions
damage the part of the brain that is responsible for memory
(Christianson 1992). Chronic emotional stress exposes the brain to
an excess of glucocorticoids, hormones that normally help the
brain cope with stress. The hippocampus, which controls memory
functioning, contains a high number of glucocorticoid receptors
and is therefore susceptible to damage (Schacter 1996).
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Because the borderline mother is unable to remember intensely
emotional events, she is unable to learn from experience. She may
repeat destructive behaviors without recalling previous consequences.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
They may spend more money than they
have, have sex without protecting themselves, drink too much,
smoke too much, or eat too much. Although they feel terrible later,
they may repeat the behavior because they do not remember the
consequences.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Studies indicate that people who were exposed to chronic stress
in childhood have higher levels of somatostatin, a stress-related
hormone and neurotransmitter, in their spinal fluid (Heit et al.
1999). Severe stress in childhood appears to have long-term effects
on the brain and immune system. Children of borderlines are at
risk, therefore, for a variety of physical and emotional disorders as
adults. They may also be prone to stress-related physical symptoms
such as colitis or migraine headaches.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Adrenaline causes
the blood vessels in the brain to constrict and forces blood to the
muscles as a necessary preparation for the fight-or-flight response.
Following the stressful interaction, the blood vessels dilate, causing
the pain of a migraine headache. Kandel and Sudderth (2000)
explain that some researchers believe that "a migraine is actually a
dysfunction ofthe nervous system and an unstable threshold in the
brain. When internal or external stressors increase, this threshold is
exceeded, and a migraine headache is produced. It's sort oflike one
part of your body says 'don't step over this line,' but you do
anyway" (p. 15).
For children with borderline mothers, migraines prevent the
child from acting on unbearable feelings of rage: the child is
paralyzed with pain. The unpredictable behavior of the borderline
mother can trigger adrenaline surges, yet children cannot respond
with a fight-or-flight response without suffering negative repercussions.
Kandel and Sudderth (2000) explain that "researchers have
found that the speed of blood flow in the middle cerebral artery
decreases during a migraine attack. Somehow, your brain turns on
the 'yellow light' and the blood flow slows down" (p. 14). Many
children with borderline mothers function with a brain continually
flashing caution.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Shame extinguishes the sense of entitlement to one's existence
and can trigger self-destructive fantasies in children. Mary Todd
Lincoln's stepmother referred to her as a limb ofSatan. One ofMrs.
Lincoln's biographers explained, "to be shamed and humiliated is
to feel a disgrace to the whole self" (Baker 1987, p. 30). Unfortunately, borderline mothers project their own shame onto others.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Children of borderlines become preoccupied with reading their mother's mood in order to ward offa possible crisis or to
prevent being attacked. Their emotional energy is invested in
contradictory positions: fighting with their mother as well as
protecting her. They may have difficulty concentrating on anything
else.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Although children of borderlines grow up afraid, they learn not
to show their fear and seem oblivious to painful or dangerous
situations. They may refuse to cry and learn to shut down when
hurt or upset. An adolescent patient explained, "After awhile you
become immune ... you don't feel anything anymore."
When parents use fear to control their children, they shatter the sacred bond of trust.
Children must constantly prove their love by providing total devotion at the expense of their own needs.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
-
AI Overview
A forethinker is someone who anticipates future events or plans things in advance. The term implies a thoughtful approach to the future, considering potential outcomes and making preparations accordingly.
More specifically, a forethinker is:
One who thinks ahead:
They consider what might happen in the future and adjust their actions accordingly.
A planner:
They don't just think about the future, they also take steps to prepare for it.
Someone with foresight:
They possess the ability to anticipate future events or needs according to Merriam-Webster Dictionary.
-
Linehan explains that the
borderline's apparent competency leads others to assume that she is
equally capable of coping in other roles. When co-workers hear the
borderline mother complain about her children they assume that
the children are troubled, rather than the mother
this means that their private experience is
unlikely to be validated by others.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
In social situations the borderline mother can be engaging,
gracious, and endearing. Christina Crawford (1978) was particularly annoyed with the facade her mother presented when entertaining. Christina summarized the child's feelings regarding the
dichotomy of the private versus public persona of the borderline
mother: "I just wanted to scream that it was all a fake" (p. 80)
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The borderline's emotional thermostat consists oftwo settings: on
and off. There is no middle ground. Melissa Thornton (1998), a
borderline who wrote Unable to grasp that something
might be both good and bad, a person with BPD can only see the
ends of the spectrum" (p. 16). Thus, the borderline's inability to
experience more than one perspective at a time conveys only one
side of the story and one part of the picture.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Children are subjected to deflating comments that increase despair or destroy their
enthusiasm as some borderline mothers assume that the worst
possible thing will happen in any given situation.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Laura avoided talking to her mother about her problems or
worries. She knew that her mother would tell her either that she
was "too sensitive and worried too much," or say something that
made her feel worse.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
When children bring concerns to the attention of the borderline parent, they receive a response that either
increases their distress or entirely dismisses their concern.
The borderline absorbs and intensifies the child's fear, "and then this and
this could happen," and is unable to reassure and comfort the child.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
When Laura was 12, she proudly announced that she was invited
to accompany a friend on vacation. Her mother responded desperately, "Oh no! Now we've got to get you some new clothes and I
don't have any money!" Laura's excitement was replaced by
anxiety.
Borderlines can deflate the child's enthusiasm by emphasizing negative outcomes.
"Oh no! Not now!" and insinuated that
some horrible mistake had been made.
Emotionally stable parents share their children's joy and quiet
their fear. But caretaking roles are reversed for children ofborderlines whose mothers are chronically upset. Children repress their
fear in order to calm their mother.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
-
In Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID), an "alter" refers to a distinct identity or personality state that a person with DID may experience. These alters can have different names, ages, genders, mannerisms, and even physical characteristics according to Alter Behavioral Health. They can take control of the individual's behavior at different times.
Here's a more detailed explanation:
Alters are distinct identities:
Individuals with DID experience themselves as having multiple distinct identities, or alters, rather than a single, unified personality.
Trauma-related:
Alters typically develop as a coping mechanism for severe childhood trauma, particularly when that trauma is prolonged or repetitive.
Different characteristics:
Each alter can have its own unique personality, memories, behaviors, and even physical characteristics.
Switching:
Individuals with DID may switch between these alters, with one alter taking control of the individual's thoughts, feelings, and behaviors at a given time.
Not a choice:
Alters are not a choice or a sign of malingering; they are a genuine psychological response to trauma.
-
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@DrDoyleSays
·
Complex PTSD is going to make certain things feel like "choices" that aren't-- that are actually reflexes stemming from trauma wounds-- and make you believe that you have no choices over other things.
Remember that CPTSD gaslights, convincingly-- just like your abusers.
-
Autistic Lauren 🏳️⚧️ 🏳️🌈
@Autistic_Lauren
A lot of people see autistic special interests as "obsessions", but to a lot of us they're something that we can rely on to comfort us in a world that wasn't built for us
-
Psychotic episodes are traumatic because the emotions that are
evoked are overwhelming. If they are frequent, the child may
numb out (dissociate), and seem oblivious to their occurrence.
Depending on their frequency, the child may believe such experiences are normal.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Borderlines may destroy what is good and loved by their children
because they are intenselyjealous ofthe loved object. They cannot
give others what they do not have.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Alice Miller (1985) writes, "Parents who have never known love, who
on coming into the world met with coldness, indifference, and blindness and
whose entire childhood and youth were spent in this atmosphere, are unable
to bestow love-indeed, how can they, since they have no idea ofwhat love
is and can be?"
Children ofborderlines may tune out by dissociating
and disconnecting from their environment. They cannot feel
embarrassed, humiliated, ridiculed, or hurt ifthey are no longer in
their own bodies. Unfortunately, the sensation ofdepersonalization
or dissociation makes them feel crazy.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
A personality disorder is a pattern of abnormal thoughts and behavior
that impairs relationships with others. Individuals
with borderline personality disorder have different combinations of
symptoms, complicating identification of the disorder.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Thornton (1998) states: "borderlines function quite well in some
types ofcareers and situations. Where there is structure, they excel.
This is one reason it takes them a long time to recognize a problem,
unless someone notes their more dangerous behavior . . ." (p.
22). Gunderson (1984) explains that borderlines are compulsively
social because their sense ofselfdepends on their relationships with
others.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
-
-
Arthur Schopenhauer
@SchopenhauerNow
The philosopher Schopenhauer says: "Almost all our miseries arise from our relations with others."
Children can be exposed to a variety of traumatic experiences
and yet develop healthy personalities given certain circumstances.
Studies indicate that the single most important factor affecting
resiliency in children is the conviction of being loved (Werner
1988).
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The effects of parental abandonment, abuse, and neglect can
be mitigated if children have access to a relationship with a loving
adult such as a teacher, a minister, a neighbor, or a relative who is
empathically attuned to the child's feelings.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Robert Greene
@RobertGreene
When in doubt, focus on the things you know you do well. Expand outward from the center.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
Trauma conditions us to understand the world as a battlefield-- then our culture shames us for being so "combative" & "defensive" in our everyday life.
You need to know your worldview makes sense & didn't manifest out of nowhere. You're not inexplicably "hostile."
Robert Greene
@RobertGreene
You are one of a kind. Your combination of skills and experience is not replicable. That represents true freedom and the ultimate power we humans can possess.
When feelings regarding traumatic
experiences are not worked through, emotional growth is stunted.
Balint (1968) proposed that personality is influenced not only by
traumatic events but by the degree of psychological support received from significant others. Therefore, parents must allow the
child to express intense emotion in order to prevent repression of
the feelings. very often, the traumatic experience is never discussed, let
alone worked through.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
You do not feel bad because you are "disordered." You feel bad because CPTSD has poisoned your beliefs about yourself & your options.
Thats not a "disorder," that's an injury-- & injuries can heal w/ the proper care.
In the absence of an emotionally attuned caregiver, children who
experience chronic denigration are at risk for developing BPD.
Children who experience
denigration and live in an invalidating environment are destined to
develop serious personality problems. Chronic denigration can
destroy even an emotionally healthy adult's self-esteem. Denigration of a child can destroy the soul before self-esteem has a chance to develop.
Invalidating families teach children that pretending to be happy is more important than being happy, and that talking about how you really feel
only makes things worse.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Frog 🔻
@ColdEmpanadas
my favorite genre of tweet is conservative guy asking grok "is this true" and then arguing with it when it doesn't give him the answer he likes
Karun Pal
@karunpal
Introverts don't "hate" socializing, they just love being at home. Cozy. Comfortable. No people. No drama. Just low-key chilling. Reading. Meditating. Listening music. Staring at walls. Watching movies. Thinking about life and all. For them, it's not boring, it's self-care.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@DrDoyleSays
Bullying is abuse.
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
The fastest way to destroy a narcissist?
Remove admiration, ignore them, expose the truth.
-
Just as the diabetic must learn to
manage sugar intake and output, the individual with BPD must
learn to manage emotional input and output. Psychotherapy,
combined with antianxiety and antidepressant medications, can
significantly enhance the borderline's quality of life.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Validation is the
antidote for denigration and is the glue that repairs a fragmented
self When faced with rejection, failure, or abandonment, a healthy
individual feels disappointment and sadness without experiencing
disintegration of the self. Healthy individuals can withstand rejection and failure because they have had enough previous validation to maintain self-esteem.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Their apology will not heal your nervous system.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Stop telling people who've been abused in relationships that they attracted it. Please stop.
The Queen devalues those who do not provide gratification or special treatment.
Deprivation impairs moral judgment. Consequently, the Queen can be vindictive without feeling guilty.
The borderline Queen readily discards those who are perceived as useless, unworthy, or unfaithful.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
She is preoccupied
with her self-image and the image of her children. In order to win
her admiration and love, her children must reflect her interests,
values, tastes, and preferences. The Queen expects her children to
dress the part, to reflect her importance.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The borderline Queen is quick to shift her affection from one
person to another, depending on the degree of compliance and
admiration that she receives.
The Queen mother's children can feel used and manipulated,
falling in and out of favor like trump cards.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Adler (1985) explains that borderlines continually fight to
manage separation anxiety and are "forced to rely on . . .
[others] ... for enough sense of holding-soothing to keep separation anxiety in check-to avoid annihilation panic" (p. 82).
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The need for power and control over others, the need to elicit a response of fear and shock is a source of pride for borderline
Witches.
project repressed rage and terror onto others. Their sense of self-importance may be primarily derived from their ability to elicit fear
They view the experience in terms of how they were hurt, rather than recognizing the child's trauma.
The darkness within the borderline Witch is annihilating rage. All
mothers lose their temper, but ordinary mothers do not turn on
their children, set traps, ridicule, humiliate, or enjoy watching
them suffer.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Witch mothers know what to say to hurt or scare their children, and use
humiliation and degradation to punish them.
The Witch can be bitter, demanding, sarcastic, and cruel to the
child who is the target of her rage. Other children may not perceive
her as a Witch if they do not possess qualities that trigger her rage.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Her children are forced to submit to her control and
may be victims of sadistic emotional, physical, or sexual abuse.
Female children of Witch mothers may perpetuate the cycle and, as
adults, become Witch mothers themselves.
When young children are deliberately hurt by their mothers,
their first instinct is to repress recognition of their mothers as the
source of their pain.
The child concludes, therefore,
that he deserved to be hurt.
The Witch destroys what is loved or
valued.
The Witch mother honestly believes, however, that what
she is doing is for her children's own good. She simply repeats what
she learned as a child.
The Witch's children may suffer from acute anxiety or murderous rage
for the rest of their lives.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Kernberg (1985) believes that borderlines who were raised by
sadistic caregivers have the least chance of being successfully
treated.
Often, borderline Witches will
hurt themselves before allowing anyone else to help them.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The Witch's childhood experiences taught her that life is a battle for survival. She prepares her children for life as she knows it, for life in a concentration camp, for hating, fighting, and killing.
Her children may enjoy having control over others, sensing vulnerability and exploiting it.
They grow up broken, unable to love, unable
to trust, unable to feel. The Witch's children are victims of soul
murder and may feel alive only when suffering or when inflicting
suffering.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Children of borderlines learn to sacrifice their true selves because survival requires that they meet their mother's emotional
needs. Masterson (1980) defines the true self as: "a self that is whole,
both good and bad, and based on reality; it is creative, spontaneous
and functioning through the mode of self-assertion . . . in an
autonomous fashion" (pp. 38-39). Autonomy, the freedom of
self-direction and self-expression, is impossible for the borderline's child.
Because the borderline mother views separation as betrayal
and punishes self-assertion, the child develops a false self.
The true self is buried alive.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Bowlby (1973) theorized that "what is believed to be essential
for mental health is that the infant and young child should experience a warm, intimate, and continuous relationship with his
mother" (p. xi).
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Daniel Goleman (1995) describes the task of the emotional brain
as focusing attention on threats to survival, "to make split-second
decisions like 'Do I eat this or does it eat me?'" (p. 291). The
borderline's children are preoccupied with what researchers call
"risk assessment"-with determining the nature of their mother's
state of mind from one moment to the next.
They do not realize they are
doing it.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
All-good children continue to function in a parentified role in
adult relationships and tend to be conscientious overachievers.
They are often overcommitted and emotionally preoccupied because they fear disappointing others. They simply cannot say no.
Minor mistakes can trigger a catastrophic plunge in self-esteem, and
internalized anxiety prevents them from enjoying their accomplishments. The emotional energy of the ali-good child is heavily
invested in avoiding mistakes that could shatter the foundation of
the self
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Parents who were dehumanized as children often lack empathy for their own children. They reinforce each other's pathological behavior, displacing their repressed self-hatred onto their children.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
In 1961 Carl Rogers introduced a revolutionary concept to the
field of psychology. His approach to psychotherapy was grounded
in his belief in the ability of individuals to grow and mature. He did
not use strategies, techniques, or tricks to create growth. He used
his real self. He believed that only by being real could he help
others. He observed, "Probably one of the reasons why most
people respond to infants is that they are so completely genuine,
integrated, or congruent. If an infant expresses affection or anger or
contentment or fear there is no doubt in our minds that he is this
experience, all the way through" (p. 339). But infants like Michelle
learn to mask their inner experience, to respond to their mother's
need, to be quiet when their mother cries, and to smile when their
mother is sad.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Rogers emphasized that "congruence" is essential to being a
genuine person. Congruence means that our internal emotional
experience matches our behavior. We trust people who are real,
even if they are sometimes offensive, because we know they are
telling us the truth about how they feel.
Rogers warned that being oneself does not solve problems.
Being oneself frees one to explore new solutions, consider new
perspectives, experience greater intimacy, and appreciate life more
deeply. Winnicott (1960) believed that "only the True Self can be
creative and only the True Self can feel real . . . the existence of
a False Self results in ... a sense of futility" (p. 148). The Waifs
children can develop a false self that is grounded in compulsive
self-sufficiency or the opposite, overdependence.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Dr. Jen Wolkin | ADHD + Trauma Therapist
@drjenwolkin
The opposite of anxiety isn’t calm.
It’s SAFETY. XO, Dr. Jen
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
If someone confides in you about abuse they experienced, please don't tell them what they should have done differently.
The Hermit often misperceives innocuous interactions as threatening or rejecting.
Her mother perceived the clerk's request as intrusive and offensive, rather than
a matter of policy established for the store's protection.
her mother blamed the clerk for being rude to her.
Her mother preferred being alone in her house
with the doors and windows locked.
Adult children of Hermits are not
responsible for entertaining her, for bringing her out of her shell, or
for her decision to remain reclusive. The more they try to coax her
out, the more fearful and resentful she may become.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Sandy's mother obsessed over daily news reports of crime, murders,
robberies, and rapes.
Although fear controls the Hermit, adult children must learn to control fear.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The Hermit misses out on the good things in life simply
because of her fear.
Adult children of Hermit mothers should minimize, not ridicule, their mother's fear.
Pointing out the consequence of an actualized fear is the only necessary response.
They must separate their fears from their
mother's and point out the consequences of irrational fear. Reacting to fear, instead of to the situation, can have deadly consequences.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The Hermit's adult children must rely on
their own judgment when determining the risks of a given situation. Rather than automatically reacting to their mother's fear, or completely discounting it, they must reevaluate the appropriateness
of their mother's reaction. Some adult children react with hostility,
resentment, or cynicism to the Hermit's obsessive worry. Negative
reactions that demean the Hermit increase her hostility and feed
her fear.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Reacting to fear complicates a problem. Reacting to the problem reduces
fear.
Perceiving the situation as a problem to be solved, rather than
succumbing to fear, made the difference between life and death.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Adult children of Hermit mothers need to assess the source of
their fear and anxiety. Answering three simple questions can help
keep them calm:
1. Why am I anxious?
2. What is the problem?
3. How can I solve the problem?
Recognizing the source of anxiety and responding appropriately is
essential to controlling it.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The overworked
and anxious nurse ran to the patient's room as frequendy as
possible, responding to every shriek.
This nurse did not
internalize the patient's anxiety and calmly responded to the
shrieking patient by stating, "Mrs. X., I know you want my
attention. But I have other patients who need me too. Wailing and
crying will not bring me to you any sooner than I am able to come.
Please stop wailing."
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Responding to anxiety with anxiety feeds anxiety. Responding
to anxiety with firm reassurance reduces anxiety. Adult children
have a right to be angry, annoyed, and frustrated with the Hermit.
They have a responsibility, however, to deal with their feelings as
constructively as possible. Otherwise, their behavior replicates their
mother's behavior and reinforces the negative cycle. Belittling,
ridiculing, or teasing the Hermit is never constructive.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
No-good adult children must limit their interactions with their
mother if she continues to undermine their self-esteem. Selfesteem can give way like an avalanche, burying the unsuspecting
no-good adult child under cold, dark feelings of worthlessness.
In cases
of ongoing denigration, the no-good child may need to sever the
relationship with the Hermit mother completely.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
In order for the Hermit's children to individuate they must free
themselves from their mother's perceptions and act in their own
best interest. Kohut (1977) describes the "self' as "an independent
center of initiative and perception" {p. 177). Expressing the self,
therefore, requires the ability to act in one's own interest.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Sandy needed to repeat "I am" statements two or three times
when speaking to her mother.
Sandy responded calmly but insistently, "I am
capable of deciding what is best for me." Although Sandy could not
change her mother's point of view, she refused to allow her mother
to change her point of view.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Eventually, Sandy learned to distinguish between what she
needed for herself and what her mother needed.
Sandy struggled with her fear that
becoming her own person might destroy her mother.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Adult children of borderline mothers should heed De
Becker's {1997) advice:
When a person requires something unattainable, such as total
submission to an unreasonable demand, it is time to stop negotiating, because it's clear the person cannot be satisfied. Getting pulled
into discussions about the original issue misses the point. It's as if
one party has come to the table wanting a million dollars and the
other party is prepared to give five dollars, or no dollars. In such
situations there is nothing to negotiate. [p. 154]
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The average person cannot imagine the intensity of the anxiety
experienced by children of borderlines who struggle with the
process of separation. Adult children experience annihilation anxiety, the fear of ceasing to exist while still alive, when merged with
their Hermit mothers.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The Queen's adult children cannot fill their mother's insatiable
need for attention or admiration. They cannot compensate for
what she did not receive as a child. They cannot please her, control
her, or change her. They can, however, change how they respond
to her.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Emotional manipulation is the Queen's specialty and provides self-esteem and security.
Saying "no" to the Queen, therefore, is essential for adult children
who need to protect their own well-being, emotional energy, and
possibly their financial resources.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Although adult children may
worry about being perceived as disloyal, they must worry first
about their own needs.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Queen's tendency to tell her
grown children what to do, where to live, how to dress, and how
to raise their children. The Queen can be extraordinarily intrusive,
imposing her tastes, values, and preferences on her adult children
and their spouses.
her children may react by becoming intensely private individuals. Robert Todd Lincoln became what some
biographers referred to as compulsively private (Neely and McMurtry 1986).
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The Queen's adult children should avoid becoming enmeshed
with their mother. They should encourage and demonstrate financial
as well as emotional independence.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Ellen's mother sometimes lied in order to evoke attention.
Unless they can verify the facts, children may not know
how to respond appropriately. Adult children need to speak to the
physician, ask for copies of medical reports and tests, and point out
inconsistencies.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
"Her behavior is saying,
'Unless you pay attention to me, I am nothing. I have a place only
when you are busy with me'" (p. 58). Even negative attention
seems to fill the Queen's emptiness. Conflicts and controversy seem
to follow her.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Through therapy, the Queen's adult children can uncover the
unexpressed real self hidden beneath the Queen's mirror. Without
treatment adult children may continue to feel empty and inadequate, depressed and hopeless.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Adult children need help learning how to serve and mirror their
own ego. Trying to satisfy the demands of the Queen prevents ego
development and perpetuates feelings of emptiness.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The Queen's adult children need and want to mature, to rid
themselves of frustration, subservience, resentment, and emptiness.
The steps they must take include the following (Dreikurs and Soltz
1964):
1. Protect their own rights.
2. Minimize providing undue attention.
3. Say "no" with words and behavior.
4. Ask only for what is actually needed.
These behaviors can be difficult to follow. Change cannot happen
by mere instruction. Instead, change occurs by resolving the
underlying fear that individuation will destroy the self or the
mother. Reading a self-help book can actually increase frustration if
therapy does not accompany the knowledge gained. A self-help
book can neither reveal what is hidden within the self, nor identify
unconscious emotional needs
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The Queen's children are susceptible to
developing BPD because they experience their own needs as
shameful. Their self structure inevitably lacks cohesiveness, making
them sensitive to rejection and failure. They tend to be self-critical
and perfectionistic, and struggle to find their own identity.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The Queen's intrusiveness takes others by
surprise and catches adult children off guard.
The Queen assumes that her children share her interests, tastes,
and values. Without boundaries, the Queen will rule.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
"You never appreciate anything I do!" Ellen stated simply,
"That's not true." Regardless of the Queen's response, adult
children must confirm their separateness.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Gunderson (1984) warned that borderlines often manipulate
others into compliance with their needs.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
When she felt herself slipping
back into becoming her mother's subject she told herself, "I am the
master of myself I will do what is right and good for me. I won't
allow others to control me."
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The Queen does not know how her behavior affects others
and does not know what is normal. Offending behavior, words, or
tone of voice must be specified before they can be changed. The
Queen is not aware that her expectations are unrealistic and will
never know if no one tells her.
The goal is not to change the Queen. The goal is to change
how one responds to her.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
By the time the Witch's children are adults, they may suffer from uncontrollable rage or demonstrate passive compliance, cynicism, and unconscious hostility. Hatred must be dissipated before it destroys.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Although the Witch is capable of evoking murderous rage, the key to survival lies in disarming, not attacking her.
They may tolerate mistreatment because it seems normal.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Dreikurs (Dreikurs and Soltz 1964) recommended being firm without dominating. Domination is the imposition of one's will
on another.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The Witch's adult children need to create distance in three
separate realms of their being: spiritually, physically, and emotionally. Adult children can create spiritual distance by affirming their
own goodness. Children of borderline Witches must think of their
future, of the long-term consequences of acting on retaliatory
impulses. They must, therefore, stand in the light of their own basic
goodness, displaying strength and character by doing no harm.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Uncomfortable, she realized that her mother was intentionally invoking guilt.
The Witch's adult children need to trust their intuition, not their mother.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
the Witch can be disarmed by not responding to
provocations, threats, emotional set-ups, or traps. The adult child
can control what type of information is shared, how much time is
spent together, and how much closeness will be tolerated.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
The Witch's child can only stop hating
through the experience of being loved. A therapeutic relationship,
a surrogate parent, a relationship with an adult who believes in the
child's goodness and worth, are the only experiences that can
mitigate hatred.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Adult children need to clarify consequences by doing rather than
by saying, and by not saying what they are thinking or feeling. The
Witch's children can assert personal power by listening to their
own inner voices
The Witch's children learned what survivors of prison
camps learned: that experiencing and revealing "emotion not only
blurred judgment and undermined decisiveness, it jeopardized the
life of everyone" (Des Pres 1976, p. 131).
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
As a child, Laura hoped that her aunt might notice her mother's
bizarre behavior. Her aunt, however, frequently told Laura how
lucky she was to have a mother who loved her. She told Laura that
she needed to "build her mother's self-esteem," reinforcing the
pathological role-reversal.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
No one expects prisoners of
concentration camps to trust their captors.
Children of borderlines are often told, "Your mother loves you,"
"That's just the way she is," "She didn't mean it," or "She can't
help it," as if children should ignore their own intuition that tells
them they have been hurt.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Tolerating inappropriate or abusive behavior requires the betrayal ofthe self. Young children
have no choice, but grown children do have a choice. When grown
children tolerate abuse, they reenact the sacrifice of the sel£
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
Children of borderlines may spend their entire lives trying to
understand their mother and themselves. They are preoccupied
with sorting out the meanings of interactions, studying their own
perceptions, and questioning the intentions of others.
📖Understanding the Borderline Mother, Lawson
𝑹𝒆𝒗𝒂 ✨
@Reva_M_S
Both empaths and narcissists come from a place of childhood trauma.
One rises above the hate, while the other succumbs to it
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
Forgiving a narcissist is like patching up a sinking boat while they're still drilling holes in it.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Don’t underestimate the value of sitting quietly with someone when they’re in pain. Let them talk. Listen to hear. There is profound healing in someone experiencing your care by offering your presence and withholding your advice.
If coping with BPD behaviors is difficult,
being raised by someone with an uncontrolled, unacknowledged, or
untreated pervasive personality disorder can be emotionally devastating.
what you’re feeling is a normal reaction.
Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
people with BPD may behave, particularly with loved ones, in ways that
often are variable and confusing. That’s part of the problem for everyone
involved—there’s no straight path for parent, adult child, or anyone else
involved in the problems associated with BPD.
Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
There's nothing wrong w/ being bitter. It's pretty normal to be bitter after what you've been through. If someone doesn't like your bitterness, well, you didn't like the experiences that made you bitter, either.
Maybe the problem isn't your "attitude," but what created it.
Now as an adult, do you
— find yourself in abusive, unfulfilling, or unhealthy relationships?
— feel unable to trust others and let your guard down?
— expect the worst from others—family, friends, and strangers?
— feel responsible for others’ moods, feelings, and actions?
— put others’ needs ahead of your own?
— have a hard time knowing what you want?
— tend not to trust your own feelings and reactions?
— feel uneasy with success or have difficulty simply enjoying life?
— get highly anxious in social settings or new situations?
— fear taking risks, especially where relationships are concerned?
— hold yourself to standards nearing perfection?
— feel worthless, hopeless, or depressed?
If you relate to many of these experiences, chances are you may have
been raised by a parent with BPD or BPD-like traits. Chances are also good
that the effects are still with you, in subtle, and likely fundamental, ways.
They probably have affected and continue to affect who you are, as well as
your relationships with others—how you choose and who you choose to
spend time with, to befriend, to partner with, to love.
Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
The catch is, your coping mechanisms and ways of relating to your
self and to others are so much a part of your emotional repertoire, you
rarely stop to question them. They define your worldview, like the tint of
glass lenses, and therefore dictate how you see and interact with the world.
Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
It’s not about blame or wallowing either—you are all molded by so much more than a dysfunctional past, and you must ultimately take responsibility for creating the life you want.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
As a result of the silence around BPD, adult children are frequently
relieved to the point of tears upon reading a detailed description of the
disorder for the first time. It gives their confusing and contradictory
childhood experience a name, an explanation, and most importantly,
validation.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
People with borderline personality disorder can act in incongruous and
inconsistent ways, yet, at times, appear so perfectly normal, reasonable,
rational, and sure of themselves in the process that those around them are
left to wonder at their own sanity and perception of reality. Likewise, when
people with BPD “act out” or rage, they can be so convinced of the
appropriateness of and justification for the outburst that loved ones again
question their take on reality, and what they must have done to set the spiral
in motion. What a sense of relief to learn there was an explanation, and it
wasn’t something you caused!
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
As Paul Shirley, MSW,
coauthor of the Stop Walking on Eggshells Workbook, explains, “Most—if
not all—mental illness is an exaggeration of some normal trait. Everybody
goes back to check and make sure they’ve locked the door sometimes, but
that does not mean everybody has an obsessive-compulsive disorder”
(Shirley 2001).
He cites the medical student syndrome in which students
may start to recognize in themselves symptoms of the diseases they’re
studying. But exhibiting a behavior or occasionally having a negative
thought, particularly one that isn’t acted upon, does not a diagnosis make.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Adult
children of parents with BPD may indeed demonstrate borderline-like
behavior here and there—after all, that’s what you were raised with—but
this doesn’t mean you have the disorder
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
“I wasn’t ‘allowed’ to be angry as a child,” says Robert. “Whenever I
raised my voice, almost always in response to some untrue accusation of
manipulating my borderline mother in some way, I was banished to my
room.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
When others comment on or challenge the queen’s beliefs or behavior, she may paint them as the enemy.
Characteristics of a queen parent include expecting his or her children
to see things the same way and to be loyal; dramatic or histrionic behavior;
and a tendency toward exaggeration. The queen has a hard time respecting
others’ boundaries and preferences.
Messages children of queen parents may receive include: You must love
me; I resent you when you need something from me.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
People with BPD don’t always appear
“crazy.” Many are quite high-functioning, appearing perfectly healthy to the
outside world. This can make children doubt their own judgment, and it can
undermine their sense of self-worth.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Children see Mom or Dad acting in
normal ways with some people and then cruelly at home, and they come to
believe they’re the cause of their parent’s negative and/or inconsistent
behavior.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Once out of the public eye, however, they direct their negative emotion at others—
usually family members—pointing an accusatory finger, making impossible
demands, and inflicting verbal, emotional, and sometimes physical abuse on
loved ones.
From outward appearances, the person with BPD may seem the model of
competence and normalcy. Some do well except under stress or in particular
areas of their lives
Their personal lives and intimate relationships may be
intensely chaotic, making it all the more difficult for family members,
particularly children, to ask for help—or even to realize something isn’t
normal.
BPD exists along a spectrum, running the gamut from mild to severe as
well as occurring with other psychiatric disturbances.
There’s only one constant with BPD, and
that’s inconsistency.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Keep in mind that the purpose of this book is not to blame a parent with
BPD or its traits but to identify patterns that affect your life today. With a
better understanding of how they may have developed, envisioning and
working toward change will come more readily.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Skill of Life
@skill_of_life
Aug 10
Your trauma is someone else's entertainment. People will ask about your pain, not to help, but to feel superior. Vulnerability is currency. And some will spend it recklessly. Your breakdown might be their gossip. Share wisely. Not everyone deserves your scars.
-
- Because of BPD’s cognitive distortions, or perceiving a reality alteredby their own idealizations and projections, parents with BPD see
themselves differently than they actually are. They may see themselves as
caring and nurturing when they have been indifferent or cruel; they may see
themselves as the perfect parent, homemaker, or provider; they may not
have an inkling as to how their actual behavior is affecting those around
them—or how confusing and chaotic those distortions are for their children.
Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Adult children may get lost in fantasies and/or daydreams, having the
tendency to idealize situations and people. They may see a fairy-tale,
whitewashed version of reality rather than what’s actually in front of them.
Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
As adults, this idealization may be manifest
in unrealistic demands on others, including friends, sons and daughters, and
partners, and unrealistic expectations of relationships. They expect
perfection and as a result are ultimately disappointed since nothing and no
one is perfect.
Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
As a result of living with verbal, emotional, physical or sexual abuse,
adult children may suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) even
years after leaving their family of origin.
Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Those with BPD have a hard time negotiating the boundaries between
themselves and others. Each time a child knowingly or unknowingly asserts
him- or herself or calls attention to the boundary between self and parent, it
may trigger feelings of rejection and abandonment in someone with BPD.
Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Boundary violations include any type of physical or sexual abuse; any
infringement upon personal space, such as walking into the bathroom or
bedroom without knocking; and not respecting a child’s right to privacy or
ownership (for example, reading a child’s diary or giving away the child’s
possessions without asking). Boundaries defining a child’s emotional space
may be violated as well when a parent asks detailed personal questions or
demands that children share information they haven’t volunteered.
Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Because the parent has such a blurred sense of self in relation to others,
enmeshment, or emotional entanglement, is common. Borderline parents
may treat their children as an extension of themselves, almost like one of
their limbs, expecting them to wear the same style clothes, hold the same
opinions, or to side with them in disagreements with a spouse or other
family members.
Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
For
someone with BPD, life is a zero-sum game, particularly when it comes to
love—it seems like there’s not enough to go around. The thought process
appears to be, “If you love your father, you must not love me,” or, “If you
want to spend time with someone else, you’re abandoning me. If you have a
relationship with someone else, you’re disloyal to me.”
Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Children learn to tiptoe around, to limit the activities that seem to
trigger a parent’s upset, and to minimize contact with others so that the
parent isn’t threatened by those relationships.
From the enmeshment they experienced as children and often into
adulthood, sons and daughters may feel that they can’t live life
independently while maintaining a relationship with their parent.
Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
They
report ongoing blowups and meltdowns when the everyday things they do
trigger parents’ fears and insecurities
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Because of the boundary violations they may have experienced while
growing up, adult children report difficulty navigating boundaries and
setting appropriate limits with others.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Children of parents with BPD may experience implicit or explicit
invalidation. Their feelings got downplayed or ignored, or they are taught
that their perceptions are wrong.
They may recall being asked a question and, when they
replied, having their parent rage at them for an apparently wrong answer.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Children, and later, adults, learn to distrust their own judgment. They
second-guess their decisions and wonder if they’ve neglected to think of
something. Since they were repeatedly told they were misinterpreting
things, they may have difficulty identifying their own feelings. They may
feel tremendously guilty for feeling their own emotions, thinking their own
thoughts and doing what they want to do since, from a young age, they may
have been admonished for not considering their parent’s needs before their
own.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
With a fragile and shifting sense of self in a borderline parent, material
items and keeping up with the Joneses are often a part of many adult
children’s early experience.
Her mother continued to rack up tremendous debt, but having
that symbol of status was important to her.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Those with BPD may exhibit a hypersensitivity and reactivity to
external stimuli, including others’ facial expressions, body language, and
tone of voice.
This sensitivity to their surroundings may be related to the anxiety that
many with BPD feel. They’re often fearful of many things
The Effects: Self-Consciousness, Perfectionism
Adult children may have learned to be shy and self-conscious about
their physical appearance, behavior, and emotions. They may tend toward
perfectionism since no matter what they did, it was never quite enough.
And they may feel guilty for their thoughts and feelings.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Transference
Parents with BPD may project, or transfer feelings onto children (or
others) to avoid accepting them as his or her own.
“Use more soap,” orders the mother. “Why are you so stingy?”
What’s really going through her subconscious mind is, “I feel stingy, but it’s
easier for me to believe it’s you than to accept those feelings about myself.”
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Rich Tate
@richtate.com
You are not your trauma. The trauma was done TO YOU. While it is something you may carry, it does not define you. 💚
The Effects: Anger, Weak Sense of Self
They may lack a well-defined sense of self, because
it’s hard to know who you really are when someone is superimposing their
views onto you, telling you it’s really what you believe or want.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
The one study we located, published in the Canadian Journal of Psychiatry in 1996, was conducted with twentyone children of mothers with BPD and twenty-three children of nonborderline mothers. It found that the former group had more psychiatric
diagnoses, more impulse control disorders, and a higher risk of BPD themselves (Weiss et. al. 1996).
Certainly many of the effects of family-of-origin dysfunction on adult
children are thought by researchers to be similar (Rubio-Stipec et al. 1991).
These effects include
increased risk of depression
suicide attempts
poor self-esteem
social anxiety
issues related to intimacy.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
adult children feel like they too fell down, like they failed as
children and are flawed or “defective,” a word used by several people in
interviews. The way they felt as children continues into adulthood.
Others talk of a fundamental sense of shame and dogged perfectionism,
regardless of their accomplishments or relationships.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Insecure parental attachment patterns lead to children second-guessing
themselves, wondering whether it’s safe to assert themselves, make a
particular choice, treat themselves in a positive way, and/or reach out to
others. As adults, the inconsistency and insecurity experienced in parental
relationships gets overlaid onto adult relationships with relatives,
coworkers, friends, and intimate partners, rendering adult children
distrustful of others’ motives, on guard against hidden agendas and unsure
of their own identities, judgment, and their worthiness of being
unconditionally accepted and loved.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
No parent is perfect; all run short of patience at
times, react before thinking, and on occasion wish in hindsight they could
have handled a particular situation differently. In healthy families, these
moments are relatively few and far between, and when they occur, parents
are able to address and discuss them
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
If the parents don’t nurture and protect, if they are
physically or emotionally abusive, if they blame the child for their or the
family’s problems, their children are left to believe it’s due to some inherent
flaw in them rather than the parent’s deficits.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Accepting Painful Emotions
try to just pay attention to it without judging yourself for having it or react to it.
Don’t assume you’re overreacting or misinterpreting the situation.
And remember that the intensity will pass, and you can address the situation later.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Remember that you’re not obligated to share information with anyone
you don’t want to.
So when an acquaintance or friend appears to be interested in you
and your life, it’s very tempting to quickly open up and share personal
details. A good rule-of-thumb is to disclose information slowly.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Reframing Triggers
based on concepts from McKay, Rogers, and McKay
(1989), are several examples of how you can recast your trigger thoughts
into beliefs that won’t induce anger:
“I don’t deserve this” becomes others are under no obligation to provide it to me, particularly now
that I’m an adult
“But that’s not fair” becomes “Neither of our individual needs is
more important than the other’s.
“You deliberately set out to hurt me” becomes “Despite how
appearances may seem, I really don’t know all the motivations of
others; I’m not a mind reader.”
“You knew better and you did it anyway” becomes “Knowing better
doesn’t mean others will necessarily do better;
“You’re such a jerk” becomes “Labeling a person based on a
particular action falsely implies that that’s all there is to him or her,
and that’s rarely, if ever, the case.”
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Anger can be expressed in many, seemingly surprising, ways.
bitterness
comparing yourself to others and feeling that they have it easier
than you do
critical thoughts, about others as well as yourself
feeling inwardly annoyed and frustrated when someone doesn’t
understand you
thinking of your rebuttal when someone is trying to talk with you,
acting defensively
guilt
impatience
muscle tension
difficulty letting go of past resentments
difficulty listening and taking someone else’s viewpoint into
account
persistently feeling life isn’t fair
sarcasm
dread
irritation
shutting down when upset with someone
speaking insensitively to others, perhaps feeling guilty about it
afterward (or not)
an attitude of “whatever,” or “so what—I don’t really care.”
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
The good news is that once you can identify and
challenge such beliefs, your experience changes too. As you stop seeing
yourself as a bitter, unlovable person, you’ll increasingly act with openness
and acceptance towards others. People will notice and respond in much the
same way. You’ll seek out healthier folks to surround yourself with and,
rather than reinforce your earlier beliefs, new experiences will help you
change them.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
Personalization. Thinking (assuming) that everything has to do with you.
The budget for a program you oversee at work is cut, and you believe that
your boss is trying to send you a message about the quality of your work.
Signals include frequently asking, “Are you angry at me?”, “Did I do
something wrong?” and/or feeling that things are your fault or directed at
you when they’re not.
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
It’s important to remember that in most situations, there isn’t one
absolute right or normal way to act. Decisions are rarely irreversible, and
most of the time, they don’t have dire consequences.
Instead of asking yourself, “What is normal?”, reframe the question,
suggests Steven Farmer, in Adult Children of Abusive Parents. Try “What is
functional?” instead. What will get the job done? Will it hurt me, or others?
Is it practical, realistic? Focusing on functionality gets you away from
externally imposed standards of normalcy, a very relative and loaded, and
therefore somewhat meaningless, term (Farmer 1989, p. 113).
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
“Wow, this is really fun?” That feeling
of immersion, of total absorption in an activity is called flow
(Csikszentmihalyi 1991). You don’t achieve that state with just any activity,
and so the feeling of flow is a good indicator that you’re doing something
you have a natural ability and inclination for. Other indicators include
activities that make you feel better, that make you feel sure of yourself, that
you enjoy sharing with and teaching to others
📖Surviving a Borderline Parent - Kimberlee Roth
-
🧠Arcesilaus argued that action starts with assent, which can come from perception, not belief.
Kinnu
-
A trait related to the need to be flawless is the need to be thorough.
Too Perfect - Allan E. Mallinger
A different way in which perfectionism can damage personal
relationships stems from the perfectionistic need to be right—about
everything. Errors are anathema to the perfectionist, but everyone is
wrong sometimes.
📖Too Perfect - Allan E. Mallinger
Obsessives tend to be especially sensitive to demands, either real or
imagined, that are placed upon them. One aspect of demandsensitivity is the tendency to “hear” demands or expectations in an
exaggerated way. When the boss says he’d like to have something
on his desk by Wednesday, the obsessive person often feels the
expectation more acutely than others. In fact he often hears more of
an imperative than the boss intended.
📖Too Perfect - Allan E. Mallinger
Placed in a new situation, his first concern often is getting the lay of the land,
discovering what the rules are.
In similar fashion, obsessive people will read demands or
expectations into situations, whether or not such demands really
exist.
📖Too Perfect - Allan E. Mallinger
Instead of seeing the listed
activities as things she wanted to do, she began to view them as
tasks imposed upon her, which she had some sort of moral
obligation to fulfill.
📖Too Perfect - Allan E. Mallinger
The unconscious conversion of “I want” into “I should” is a
childhood safety-seeking maneuver that becomes ingrained in the
obsessive’s character, a maneuver that comes to serve many
motives.
📖Too Perfect - Allan E. Mallinger
What begins as an effective
means of self-protection becomes overdeveloped, indiscriminate, or
automatic. Ultimately this behavior becomes self-defeating,
intruding on work, interpersonal relationships, and even leisure time enjoyment.
📖Too Perfect - Allan E. Mallinger
The obsessive tells himself he’s a victim of exploited
conscientiousness. “I bust my butt,” he mutters inwardly. “I never
miss a day, do a great job, sacrifice myself for the good of the
company, and for what? No one appreciates my efforts and, worse,
they’re wasted, because the system is sloppy and inefficient.” His
feelings of victimization explain his negative attitude toward his
work, and meanwhile the real culprit, his demand-resistance, goes
undetected.
📖Too Perfect - Allan E. Mallinger
-
The perpetrator, the narcissist, doesn’t think she’s abusing
anyone because, by definition, she’s perfect, remember, and perfect people don’t
do imperfect things like abuse people. And the abuse victim, the daughter – this
would be you – doesn’t realise she’s abused because she believes her mother’s
lies and thinks that everything is her fault, that she is the one who is broken.
And there’s the second layer, which is the denial that the bad treatment
ever happened! And that’s the bit that leads to you thinking that it’s you that’s
crazy, and hence the title of this book
You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
we could be friends all right, but only ever on her terms
and as long as I remembered my place, which was subordinate to her. It was like
walking through a beautiful flower-strewn meadow, but the path was on a clifftop and one wrong step would send me plummeting. The eternal vigilance meant
I could never relax.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
But how would I tell my parents this? There would be war. All my life
the simplest complaint or request for better treatment had ended very badly. Had
ended, indeed, in me being royally abused, invalidated and gaslighted
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
And if she says it with enough conviction and certainty – and she will –
then you’ll very possibly end up believing her statement over your own
perceptions and memories.
So, not only does she abuse you (telling you that you’re fat in front of
your friends, in this example), but then she denies it even happened!
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
This leads you to doubt your own
perception, to question your own sense of reality, and is, in my opinion, one of
the two worst aspects of the abuse we daughters of narcissistic mothers receive.
(Teaching us that we’re born broken, as explained later, is the other.)
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
This kind of wilful stupid denial is so bizarre and slippery that it’s
impossible to deal with. Especially since, if you persist in stating your truth (i.e.
the real truth), she’s likely to move to other defensive tactics such as Narcissistic Rage. And you, programmed from birth to fear her rage, will back down
immediately. So when she doesn’t confuse you into compliance, she bullies you
into it.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
She invalidates you.
If she doesn’t gaslight you by insisting the event didn’t happen, she has another
trick. She can admit it happened, but insist that she was right to do so and you
are wrong for getting upset.
Or, a classic favourite: ‘Oh you are so sensitive!
Everything upsets you. It’s like walking on eggshells being around you.
It’s psychological abuse (messing with your thoughts)
and emotional abuse (messing with your feelings)
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
I cannot over-stress the enormity of this. To deny someone’s feelings or
experiences it to literally deny their reality. And that’s what happens to us
DONMs all the time. The only reality that is allowed to exist is our mother’s
reality. And where her version of reality clashes with ours, ours must yield
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
The fact is that they are the ones being unfair. It is appropriate to want to
sort out a row before moving on. To find out why it happened, and negotiate to
do your best that it doesn’t happen again. What is not appropriate is, if the
situation was sorted out and the person genuinely apologised, to keep
mentioning it. That would be bearing a grudge.
In practice what normally happens is that we DONMs learn well not to
rock the boat, and we just accept her cues, and respond as if it were a normal
situation. Which of course is what she wants.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
Narcissistic mothers absolutely hate and resent your special days and successes.
This makes sense when you think about it. Since everything is about her, then
your graduation, your pregnancy, your baby, your book deal, your wedding, is
almost a crime against nature. You’re trying to make it about you, when
everything should always be about her.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
She parentifies.
She might expect her daughter to take
care of bills, or household chores beyond what is reasonable.
She infantilises.
narcissistic mother might infantalise her daughter in order to keep her weak and
trapped, thinking she is dependent on her mother. She may exaggerate the
dangers of the world, for example. Or not teach her daughter any of the skills
she’ll need to survive in the world such as budgeting.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
Nothing is ever her fault.
She’s perfect, so if she fails it must be some other reason rather than any flaw in
her.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
She has a victim/martyr mentality.
Narcissists are always victims, never perpetrators. They see themselves as being
frequently attacked and are therefore justified in defending themselves.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
trump card of, ‘Oh, after all I have sacrificed for you!’.
please,
do not fall for this. It was her decision to become a mother and all of those things
were her responsibility as a result of that.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
narcissists can bear grudges forever. Again, this makes sense
because if they are so special and so perfect, it absolutely is a capital crime to go
against them. They are actually dangerous enough in this respect, because they
can wait and bide their time for years to get revenge. And this is why, if you
come across a narcissist in your daily life, try to remove yourself with as little
drama as possible. Be uninteresting to them is the best advice, and don’t engage
them and definitely don’t take them on.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
She never allows you to be your authentic self.
I had learned over many years that the real authentic true me was not welcome.
The real me was not approved of, or even tolerated. They wanted the pretty
image of me who listened to their stories, never had needs of her own, never
rocked the boat, never challenged
Not allowing your authentic self to exist is effectively soul murder
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
She is odd about gifts and presents.
They are dreadful at
buying presents for people around them, usually getting the most inappropriate
gifts imaginable. This is for two reasons: first, they genuinely don’t know
anyone as a person, so they’ve no idea what they’d like. And second, they really
don’t care. If they were to start thinking about what the other person would like,
they’d have to take time out from thinking of themselves and that, of course,
cannot be.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
She has no boundaries.
expect answers to
– totally inappropriate questions about topics such as your sex-life, familyplanning decisions or finances. Or share equally inappropriate information about
herself.
They see this as totally their right. And so they feel very thwarted and
angry if you try to stop them doing it, if you try to impose natural and reasonable
boundaries.
Because, thing is, narcissists hate boundaries. Hate them with a passion.
They actually experience boundaries as being an attack on them, and will
respond to that attack with huge force and Narcissistic Rage.
And yes, there’s an irony here. As part of the invalidation, she accuses
you of being over-sensitive, when the reality is that she is the one who is
completely over-sensitive.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
It’s always about her needs.
In a relationship with a narcissist, it’s always about meeting her needs, and
never about getting your own needs met.
makes you feel selfish for looking to meet your own needs.
And so you end up feeling really bad
about being so selfish, and more than likely giving in to her wishes.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
She lies to you about who you are.
It is a parent’s job is to reflect the child to him-or herself, so they grow up
with an appropriate self-image. Narcissists twist that and they lie to us about
who we are. They teach us that we are inherently flawed and there is something
sinister and wrong about us.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
Talking a lot can be a trait of Histrionic Personality Disorder, specifically,
but many narcissists seem to have this too. After all, if she’s the Centre of the
Universe then her every passing thought is of enough importance to share with
the world, and every detail of her life is essential listening.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
Narcissists can talk endlessly about their own events and opinions, in the
most excruciating detail. They talk on and on and on until it feels like an assault.
They can talk without drawing breath it seems like. This has the result of making
you, the designated audience, feel like a non-person. You’re only there as their
audience, not as a real person.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
Narcissists have zero genuine curiosity. Oh, for sure they might have
nosiness. Especially if they can nose out something to your detriment or their
benefit.
Narcissists have zero genuine curiosity. Oh, for sure they might have
nosiness. Especially if they can nose out something to your detriment or their
benefit.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
Narcissists are never introspective.
They never analyse their actions or motivations. Things just are, and by
definition, since it’s the Narcissist doing it, are appropriate.
And so it’s like they are petrified in amber, emotionally speaking. They
never learn. They never grow. They never mature.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
We like to learn from our mistakes so we
don’t make them again. We like to improve our life skills all the time, including
our relationship skills.
Not narcissists. How can you improve on perfection?
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
She’s inappropriate with service staff.
I did a survey on my forum about this, and it was as I suspected. Narcissists
are often very inappropriate with service staff and others who they see as being
beneath them. They can either be imperious and rude, or else over-familiar.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
Many narcissistic mothers are good with small children, and you might have
fond memories of her treatment of you before you were about 7, in other words,
before you developed your own personality and opinions.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Kids who grow up walking on eggshells become adults who strive for perfection. They plan what to say before every situation. They give more than they have & don’t ask for what they need because they fear being exposed to the kind of harsh criticism that shaped them as a child.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@DrDoyleSays
The three big, common triggers for most CPTSD survivors are feeling trapped, feeling controlled; & feeling "in trouble."
They mirror the conditions that make complex trauma "complex:" it was inescapable, it unfolded over time, & it permeated our most important relationships.
lets heal and recover
@recovery_your
PTSD is really fun.
Just walking along and suddenly (BAM)
“Here’s a random flashback from a Tuesday 24 years ago.”
Perfect. Exactly what I needed.
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
Explaining to a narcissist how they made you feel only helps them make you feel worse.
Gaslighting Effect
@Reva_M_S
When you end contact with a narcissist, don't forget to include everyone they know
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
A narcissist doesn't change. They just blame everything on everyone else and move on to someone who isn't yet aware of their manipulation.
You are not crazy.
You are perfectly sane.
Your perceptions are valid and right
You can trust your own reality.
Now, knowing this rationally is one thing. Believing it at a core level is
quite another.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
Many DONMs have a deeply buried sense that we are inherently flawed.
That there is something twisted and evil and nasty and noxious and poisonous
about us, and that we were born that way. It’s part of who we are rather than just
something we do. This brings with it a huge all-encompassing sense of shame.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
If you grew up with your narcissistic mother telling you who you were,
creating you in her image, it can be very hard to know who you really are. You
might struggle knowing even basic things about yourself such as your tastes in
food, clothing, colours.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
This is connected to the lack of confidence,
if we tried to be assertive with our mothers we were
subjected to lies, gaslighting, verbal (and even physical) abuse, and shaming.
And this translates into our adult lives too. We also have a massive fear of
confrontation for the same reasons, and this leads us to put up with treatment
that we should not put up with.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
We can tend to end up in bad relationships
And the narcissists are drawn to us because at some level
they know we’ll put up with them.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
We might suffer from social anxiety.
Many DONMs suffer from social anxiety. We have no sense of our place in
the world, in our society, our culture. We’re not sure how to behave in company.
Are we too loud? Too quiet? Too chatty? Not chatty enough? We’re always
second-guessing ourselves. Add to the fact that, deep down, we all carry a deep
shame about who we are, about being born broken as it feels we are, and we
might feel that people won’t like us. Unfortunately, a lot of the time this can be a
self-fulfilling prophesy because people genuinely don’t respond well to us. Not
because we’re not nice, which is what we might think. But because they pick up
subliminally on our awkwardness, or discomfort, and react unconsciously to
that.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
The second essential element is, once you have spoken your truth, to move on.
📖You’re Not Crazy - It’s Your Mother_ Understanding and Healing for Daughters of Narcissistic Mothers
SelfHealers Circle
@selfhealerscirc
In enmeshed families, independence looks like betrayal. You get guilted for choosing yourself– because selfhood was never part of the contract.
-
Josh
@JD_Quotes2017
If I heard something bad about you, I won't treat you any different until I see it for myself. People cross you, play victim. Lie on you and try to get everybody to go against you. I'm grown, I can see for myself.
-
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
When the people who are meant to protect you, become the people who hurt you, you don't stop wanting protection-you stop wanting people.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Aug 14
A liars worst enemy is someone with a good memory.
-
lets heal and recover
@recovery_your
Children don’t “bounce back” from trauma.
They bury it.
And buried trauma doesn’t vanish it leaks out later as anxiety, rage, shame, addiction, and self-destruction.
So no, kids aren’t resilient.
They’re hurting.
𝑮𝒂𝒔𝒍𝒊𝒈𝒉𝒕𝒊𝒏𝒈 𝑬𝒇𝒇𝒆𝒄𝒕
@Gaslighting_1
People who love you don't cause you pain, they work so hard to take it away
Jacy, LPC
@ATMwithJacy
Most people who aspire to be perfect are very insecure and are often extremely critical of other people.
Shadows of Control
@shadows_control
Abusers weaponise your reactions to hide their abuse—and make you doubt your own sanity.
𝑮𝒂𝒔𝒍𝒊𝒈𝒉𝒕𝒊𝒏𝒈 𝑬𝒇𝒇𝒆𝒄𝒕
@Gaslighting_1
Build strong boundaries.
They don't just keep the wrong people out
They also nurture, protect, and preserve what's inside
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
No one should have an opinion about how long a person should be hurt over trauma they didn’t ask for.
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
Aug 22
When a narcissist can no longer control you, they will go all out to control how others see
you.
lets heal and recover
@recovery_your
Aug 22
Stop telling people “others had it worse.”
Pain isn’t a fucking competition.
Trauma is trauma.
End of story.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
People who repeatedly attack your confidence and self esteem are quite aware of your potential even if you aren't.
-
INFJs are the rarest personality type for a reason—here’s what makes them so different
Olivia Reid by Olivia Reid | August 22, 2025,,
https://geediting.com/r-lc-infjs-are-the-rarest-personality-type-for-a-reason-heres-what-makes-them-so-different/
INFJs notice patterns others miss, often long before we can explain them logically.
I can usually tell when something is “off” without a shred of evidence. Sometimes I ignore it and later regret it, but when I listen, I find my gut was almost always pointing me in the right direction.
For an INFJ, it’s almost an extra sense. We don’t just notice emotions—we absorb them. If someone close to us is carrying sadness, we carry it too. If a room is tense, it hums inside our bodies.
Our strength comes from listening deeply, noticing small details, and creating space for others to be fully themselves. That stillness can be disarming—in a good way. People lean in when they feel you’re actually paying attention.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
Right now is an excellent moment to remind yourself that experiencing trauma symptoms does not mean there's something wrong w/ you-- it means there was something very wrong w/ the environment or people around you. That's not an "excuse;" that's the definition & reality of trauma.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
"Letting go" isn't a decision. It's a skill that involves acknowledging & honoring our feelings, coupled w/ redirecting our focus & affirming our new story.
We don't struggle w/ "letting go" because we're "stubborn." We struggle w/ it because we're still developing that skill.
Close your eyes. And I want you to know that you are very loved and you are very safe and you are very important. And I want everybody to take deep breath in and out with me.
🎤Billie Eilish: Happier Than Ever - Live at the O2 (2022)
Like a breather. I want everyone just to relax and know you don't have anything to worry about in this moment right now. I want everybody to just spend couple of minutes of this song just loving each other. Safe and sound.
🎤Billie Eilish: Happier Than Ever - Live at the O2 (2022)
Feel free and loose. Nobody is judging you, nobody is looking at you weirdly. You don't look stupid, you look beautiful.
🎤Billie Eilish: Happier Than Ever - Live at the O2
Release anything bad right now. All the negativity up here, let's just scoop it out. Just grab it and pull it, and get it out of there. I'm serious. Physically do this. Get those thought out of there. And flap around. Bounce around.Let it out
🎤Billie Eilish: Happier Than Ever - Live at the O2 (2022)
Rule number 2.
Please do not judge anybody in here. That is forbidden.
And rule number 3, have fun!
I want us to feel as free as we can feel, I want us to feel loose, and rid of all our problems and in the world. Live in this good moment.
🎤Billie Eilish: Happier Than Ever - Live at the O2 (2022)
-
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@DrDoyleSays
Shout out to everyone realizing just recently that the story you family has been telling you about yourself is utter horsesh*t-- & that you, actually, get to choose who you are, what you're all about, & what the future holds for you, personally, professionally, & spiritually.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Just a reminder for every survivor who grew up being abused by narcissistic parents and are now living with trauma or CPTSD: please go easy on yourself.
Everything is harder for you. You’re not lazy, you’re not a “procrastinator.”
You are operating inside a storm of mental turbulence that most people don’t have to fight through. And we’ve been living in this storm for so long that we can forget that it’s still there.
So remember that and be gentle with yourself.
For what you’ve been through, for what you’re still living with, you are doing AMAZING 🙌 🙏🏼 🙂
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
Abuse isn't only physical. It's being degraded, humiliated, blamed, screamed at, lied to, manipulated, isolated, and controlled. These are all forms of narcissistic abuse. They don't leave visible bruises, but they cut just as deep. The constant attacks chip away at your confidence, your sense of self, and even your ability to trust your own reality.
Tell me no Lies ?❤️🩹➡️❤️🥰🌹💪🏻🚫Narcissists🚫
@lovewins11011
A narcissist will call you crazy for reacting to the chaos they created.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@DrDoyleSays
A common experience of CPTSD survivors is being repeatedly misdiagnosed-- and not just by mental health care providers.
Nicole Filippone, Autistic Advocate & Author
@sensorystories_
Them: You don't look autistic
Me: My autism doesn't really look like anything. It's mainly just me being anxious about things. Can't eat safe food. Anxious. Someone too close to me. Anxious. Have to do small talk. Anxious.
Them: You don't look anxious
Me: I hide it REALLY well
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@DrDoyleSays
This is a reminder that your social skills are probably better than you think. Not that your trauma was trying to convince you you can't interact w/ "normal" people without saying the wrong thing or being weird or something. Right? Right?
You're likable & relatable. Yes, you.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Aug 26
A narcissist’s goal is to make you look like the problem by provoking your reactions.
-
Rowan Jetté Knox 🇨🇦
@mavenofmayhem.bsky.social
Limited social media exposure.
Limited news exposure.
More time with art.
More time with books.
More time with loved ones.
More time finding small joys.
A nervous system in constant fight or flight will have a harder time managing long term upheaval. And friends, this will be long term.
-
🍁
@SyzgEle
Aug 28
Narcissists don't target weak people, they are weak people. They choose the strongest souls they can find and then systematically break them down to feel superior.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
To a malignant narcissist, people who hold them accountable are “evil“
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Evil is not really subjective. Evil people will try to convince us that it is though. If they can convince us that good and evil are just a matter of perspective then they win. They have demoralized us
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Aug 28
Forced dependence is when an any manipulative abusive person, typically a malignant narcissist, systematically prevents another person from becoming independent—emotionally, financially, socially, or physically. They do this to maintain dominance and ensure the victim feels incapable of functioning without them. It’s a covert form of enslavement disguised as “help,” “protection,” or “love.”
Narcissist parents often do this with their children or it can be done by a narcissist partner in a relationship. 🧵
Surviving Narcissistic Abuse
@AuthorKathKeith
How to talk with a toxic parent(s): When they ask you a question (about your work, your child, your home) always answer with a question back to them. Don't give them ANY information because they will use it against you.
Example: THEM: "How is your job going?" YOU: How is the weather there, how is your car running, how is Aunt Mary, how is your backache?"
Remember, when they ask you a question about yourself, it is not because they care, it is to gather information they can then gossip about behind your back. The 'answer back with a question' technique completely protects you from this. Repeat as often as necessary.
And oh yes, move as far away geographically as humanly possible. It's the only way to really protect yourself. Good luck. We survivors know exactly what it's like.
Rainaa
@rainaarants
You can't manipulate someone who isn't desperate to be liked
Lovely Insights
@AsimMunirrr
True power is in not needing approval
lets heal and recover
@recovery_your
Aug 28
Telling someone “just be positive” when they’re drowning in depression doesn’t help.
What helps is being there.
Listening.
Sitting in the silence with them.
Reminding them they aren’t alone.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Your boundaries will be well received by people who want you feeling safe, healthy, and whole.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Healing from abuse has nothing to do with learning to love those who hurt you. It’s learning to love the parts of you who carried that pain. It’s learning what feels safe. Healing is learning how to live unapologetically & never think of those hurt you again, if you so choose.
Narcissistic Abuse Awareness
@AwareOfTheNarc
When someone opens up about abuse, don’t respond with what you think they should have done — just listen.
Autistic Lauren 🏳️⚧️ 🏳️🌈
@Autistic_Lauren
Schrodinger's autism:
Until your diagnosis is revealed, you exist in a superposition. Either "too weird to fit in" or "too normal to be autistic"
No Nonsense Neurodivergent
@NoNonsenseND
If you think neurodivergent traits are things that "everybody does", you might be one of us and not know it.
𝐍𝐚𝐫𝐜𝐢𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐢𝐜 𝐀𝐛𝐮𝐬𝐞
@Reva_M_S
Abusers always become the victim of those they victimize.
The most grandiose victim you will ever see
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
The people who see manipulation most clearly are often labeled “crazy” by the people committing it.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
In an abuser-centered environment, the enablers intervene when the wounded need help. The abuser is protected, and their actions are downplayed. Meanwhile, the enablers shame the wounded for how they’re responding to the abuse. Healthy environments help wounded people heal.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
You should never have to explain why you deserve respect and consideration.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
The narcissist doesn’t see what they did to provoke you. They only see your response to their abuse.
And they will use that as justification to abuse you further in “retaliation”.
It’s a never-ending cycle
-
The Autistic Coach
@AutisticCoach_
When autistic humans set boundaries, we’re called “rude”.
When we collapse without them, we’re called “weak”.
When we mask, we’re “inspiring”.
When we unmask, we’re “too much”.
None of these are true.
We are just trying to live.
Assumption, we call it theory of mind. Codependents so often assume. They assume when someone's thinking, they assume someone's
intentions, they assume even if someone randomly say someone. Codependency forces you to do this. Theory of mind is that you are
assuming that you know this person. That you know the way they think, that you know what they're thinking, why. Intentions behind it.
Codependency taught you this dysfunctional behaviors.
forensicbadassprofiling
https://www.youtube.com/shorts/g1yuoQbv2Vw
Assumption, we call it theory of mind. Codependents so often assume. They assume when someone's thinking, they assume someone's
intentions, they assume even if someone randomly say someone. Codependency forces you to do this. Theory of mind is that you are
assuming that you know this person. That you know the way they think, that you know what they're thinking, why. Intentions behind it.
Codependency taught you this dysfunctional behaviors.
forensicbadassprofiling
https://www.youtube.com/shorts/g1yuoQbv2Vw
If something feels off, it's off. If something feels like it's not quite right, then it's not quite right. If you're getting kind of weird vibes that you shouldn't trust somebody, don't trust them. You intuition never lies. The issue is you have not found the courage to listen to it. If you walk into a room and it just doesn't feel like the right, leave. If you meet somebody and you don't feel like yourself, that's probably not a good
person.
Mel Robbins
https://www.youtube.com/shorts/LmevZs3YxwU
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Harassing someone is an automatic admission of guilt .
🤔Simulation is the situation created by any system of signs when it becomes sophisticated enough, autonomous enough, to abolish its own referent and to replace it with itself
Jean Baudrillard
Gustas | ADHD Lab
@MindPopLab
Sep 1
The cruelest part is how trauma convinces you that isolation is safety when connection is the actual cure.
£me🪼
@nwaibeMm
normalize leaving people in whatever reality they've chosen.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@DrDoyleSays
CPTSD lies to us about people, situations, substances, or habits we "can't live without." Remember.
Social anxiety is kind of umbrella of a number of syndromes, such as RSD, or perfectionism, or impostor syndrome. They all deal with fundamental core belief that a person is deficient. Disconnect how you appear to others and own exaggerated and often negative perception of yourself. False beliefs, statements how you fall short. Like I embarrass myself, I'm not much smart or fun. So you won't go to new social event.
ADDitude Magazine
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7jOD8byyC-I
Fish living in dirty water its entire life does not know that the water is dirty.
https://www.bymaros.com/post/ultimate-guid
Extreme shyness may amount to social phobia. DSM 3rd edition of 1980 identified social phobia as a form of malignant shyness. When DSM 4 was published in 1994 it was converted to social anxiety disorder and it's nothing to do with shyness, or little to do with. More recent studies show very close correlation between shyness and SAD.
Sam Vaknin
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1p0_bevKnAk
Definite symptom of childhood trauma is trying to get difficult person be good to us in our adult lives. Why? It's familiar. We will spend a lifetime in patterns of relationships, whether it's a boss or a partner or friends. These are the patterns I see for people who grow up with a difficult parent. There is a lack of sense of self. The missing ingredient is our own goodness and our own power.
DoctorRamani
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ObN8-s750dg
It's being able to see a bad thing happening as a bad thing happening. And not that you are a bad person that caused someone else to do a bad thing to you.
DoctorRamani
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q8igSMOSvrI
You become the story you tell. Instead of dealing with the problem we tell ourselves a story that we have anxiety or we're depressed or this or that. Look at the story you are telling yourself because that's the only thing holding you back - you not believing in yourself.
DkBorelli
https://www.youtube.com/shorts/3nlEyiUJunE
People do things that make sense to them in the moment. When we're trying to understand behavior or choices or actions we're judging it from an outside perspective. It may seem silly for us. But when we get into that situation with that individual, the behavior actually makes sense. Key question we always need to be asking ourselves is: What about that situation made it make sense to do it that way?
The local rationality principle
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vGpSi9JaBVM
Environment that they are in. Resources that you have. Experience, been before or is it brand new? Norms you are following.
Constraints. Signs faces the other direction. I don't know how these people get on this pipe but the sign is telling them not to do what they are doing – isn't facing them. I would assume a lot of them can't even see it. In situation – when you don't know how to behave you look at other people what they are doing.
The local rationality principle
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vGpSi9JaBVM
Doctor says “Don't worry, this won't hurt a bit”. And then gives you the most painful shot you've ever had. A few weeks later you go to dentist for a check-up. He starts to put mirror in your mouth to examine and he says “Don't worry, this won't hurt a bit”. Even though you know the mirror won't hurt, you jump of the chair and run screaming. Words “This won't hurt” became a conditioned stimulus when they were paired with the pain of the shot.
conditioning
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H6LEcM0E0io
-
The dogs in Pavolv's experiment did not "learn to EXPECT food when they heard a bell." Their conditioned response was not the result of a conscious expectation. That's the whole point of understanding Classical Conditioning. Their nervous systems became PRIMED by the sound of the bell through repeated pairing of this previously neutral stimulus with a naturally occurring unconditioned stimulus (food).
YT SheldonHelms
-
Adam Grant
@adamgrant.bsky.social
A mark of emotional intelligence is prioritizing your values over your moods.
Immature people are victims of their feelings. Their choices are governed by fleeting sensations.
Mature people take responsibility for their reactions. Their choices are guided by lasting principles.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Normalize being kind and supportive for no reason. Do it because it's who you are.
Dr. Jen Wolkin | ADHD + Trauma Therapist
@drjenwolkin
Stop yelling that ADHDers are so sensitive to rejection while you literally sh*t on us and tell us we are lazy, stupid, and crazy. XO, Dr. Jen
I think our relationship works so well because you interpret my maladaptive ways of coping with life as charming personality quirks.
Frank James
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JsT0n40LgxM
-
-
ADHD Survival Guide
@DopaminePlsMe
You’re not lazy; your brain asks for different inputs. Feed it, don’t shame it.
-
Dr. Jen Wolkin | ADHD + Trauma Therapist
@drjenwolkin
Everyone is late sometimes. Everyone forgets things. Everyone zones out.
The difference with ADHD isn’t whether it happens.
It’s the frequency, the intensity, and the way it erodes your quality of life.
That’s what makes it a diagnosis, and not a cut quirk.
XO, Dr. Jen
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
You owe absolutely zero respect to anyone that does not respect you. Never forget that.
-
This question is actually a manipulation tactic called "burden shifting." In healthy relationships, respect is the baseline, not something you earn through performance. When someone makes you justify why you deserve basic human decency, they're testing your boundaries while making you do the emotional labor of convincing them to treat you well.
People who operate this way have learned they can control others by making respect conditional. They know decent people will try to earn what should be freely given, which keeps you trapped trying harder while they do less.
Remember, unless you're truly trapped in circumstances beyond your control, there's usually a way out of toxic environments. The path might be difficult, but protecting your mental health and self-worth is always worth the temporary discomfort of leaving.
https://www.youtube.com/shorts/P2nAoyFlbu0
-
-
𝗄𝖺𝗄𝗁𝗈𝗓𝖺
@simphiweyinkoc_
Jobs are stressful. So is unemployment. Not finding a partner is stressful. So is having one. Working in an office is stressful. So is working with your hands. Having 50 clients is stressful. So is having none. Life is full of trade-offs. Don’t romanticise options you don’t know.
"Any person capable of angering you becomes your master."
- Epictetus
Manoti
@MwendiaJnr
Sep 12
Your boring lifestyle is saving you from a lot of problems.
Skill of Life
@skill_of_life
Boundaries don't push people away, they reveal who was only there for access. The moment you say “no,” the mask falls. The affection fades. The guilt begins. Because they weren't loving you, they were using you. And your self-respect disrupted their entitlement.
The Thought Lounge
@ThethoughtL
Boundaries don’t ruin relationships, they reveal them. When someone disappears after you say no, they weren’t connected to you, they were connected to what you gave.
Trinity G.
@IAMTHETRINITY
Sep 12
People seriously underestimate how far simply being likable can get you in life.
Skill of Life
@skill_of_life
Some people stay close just to keep you small. They'll support you, but only when you're struggling. They'll cheer for you, but only when you're beneath them. Your growth threatens their identity. So, they'll subtly undermine, distract, or guilt you back into shrinking.
Skill of Life
@skill_of_life
Healing isn't gentle, it's violent to your old identity. It means losing people who liked the broken version of you. It means choosing peace over approval. It means walking away from comfort and into clarity. And it means finally becoming someone who doesn't beg to be seen.
Skill of Life
@skill_of_life
Charm is often a mask for emotional immaturity. They'll make you laugh, flatter you, keep things light. But when conflict arises, they vanish. When accountability knocks, they deflect.
Charm isn't proof of depth, it's a distraction from the absence of it. And the more you rely on it, the more you realize you're in a relationship with a performance.
KLASIK♠️
@Klasik007
people will lie directly to your face and then get mad at you because you don't trust them.
Skill of Life
@skill_of_life
Listening isn't always empathy, it can be strategy. Some people listen to gather ammunition. To study your weaknesses. To learn how to break you gently. They'll nod, ask questions, seem invested. But later, those same words will be used against you. Not every ear is safe.
Cherry 2.O
@hey_m_cherry
Sep 12
People won’t support you until strangers celebrate you first.
Daily Dose of Psychology
@PsychologyDose_
Sep 11
Most arguments are unhealed wounds trying to speak.
Lex
@lexx_aura
Sep 12
You can't build peace in a place where your nervous system is always bracing.
𝙋𝙖𝙢𝙢𝙮 ✨
@_Pammy_DS_
Sep 12
Normalise not forcing connections with anybody. If they don’t see the value in having you by their side, don't try to convince them.
@fvckfemi_
a man gets meaner when he doesn't want you anymore.
feyisayo 💸
@feyiszn
I feel so disgusted when someone turns out to be a huge waste of my time. Like why did I even let you in my life in the first place .
yona
@ppyowna
they showed you who they are, that was your closure
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@DrDoyleSays
Maybe you didn't f*ck up. Maybe you responded to that trigger w/ skills & bandwidth you had at the time. Maybe that's not an "excuse"-- it's a description of reality.
Maybe your abusers have programmed you to reflexively beat yourself up to keep you distracted & discouraged.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Being called crazy or sensitive for reacting to disrespect is manipulation.
-
When I looked at ACA laundry list I was shocked at how much overlap there is between the laundry list items and traumatic stress
symptoms. Especially Complex PTSD. It wasn't until 1991 that the book Laundry list was published. PTSD was recognized in1980 as
diagnosis. CPTSD was introduced in 1988. Around 2019 it was in ICD. These laundry list traits and CPTSD symptoms emerge because
of prolonged exposure to relation trauma.
ACA Laundry List as CPTSD Symptoms
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6gWYJ-450wY
-
The 14th item that para-alcoholics are reactors rather than actors. Reactors. So the entire symptom cluster is named reactivity and arousal. So this is hyper-arousal, the hypervigilance, the being afraid and frightened by anger, fear of authority figures. Third symptom cluster of CPTSD has to do with intrusive images, flashbacks and nightmares. But also re-experiencing the past trauma. We tend to reenact the trauma in unhealthy relationships.
ACA Laundry List as CPTSD
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6gWYJ-450wY
-
@omgsidewalks
Sep 17
if your gut telling you somebody acting weird, THEY ACTING WEIRD.
-
The Wily Survivor
@WilySurvivor
Narcissistic abuse rewires your brain. Your amygdala stays on high alert while your prefrontal cortex (logic) gets sidelined. You feel stuck, foggy, frozen. When people say “just leave,” they don’t see that trauma makes even basic planning feel impossible.
-
𝙋𝙖𝙢𝙢𝙮 ✨
@_Pammy_DS_
Sep 17
Gaslighting is when someone repeatedly triggers your nervous system and harms your mental health. They purposefully provoke you then play the victim card by blaming you once you react to their toxic behaviour, but they will never discuss their disrespect that triggered you.
Maira
@maira4yo
just learned from my therapist that being raised by emotionally immature parents means you’re treated like an adult when it’s convenient for them, but a child if you go against what they’re wanting.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Sep 17
Cutting people out of your life who bring dysfunction and suffering into it is the first sign that you are starting to respect yourself.
Shadows of Control
@shadows_control
Narrative control is a core tactic in coercive abuse. It’s how abusers discredit victims, rewrite history, and make themselves look like the victim.
Mimi
@dkkcaramell
Normalize "I'm willing to work on that" instead of "that's just how I am."
Brian Maierhofer
@IamProHuman
Your nervous system remembers things your mind doesn’t. That’s why triggers make no logical sense—they’re somatic memories asking to be released.
Autistic x ADHD.Co
@autisticadhdco
ADHD makes life harder because our brain only focuses on what's exciting
So it ignores what's important.
Dear Self.
@Dearme2_
Privacy is power. What people don't know, they can't ruin.
Gustas | ADHD Lab
@MindPopLab
Neurotypicals really think there's a separate rulebook for how to treat autistic people when it's just basic respect.
kawaii 🪼
@magicmoxo
Sep 20
toxic people will gaslight you & try to make you feel guilty for calling them out on their shit because they’re way too comfortable in their ways. don’t fall for this tactic
Johan | sensoryoverload.info
@johanlammers
DSM misses lived neurodivergent realities: emotional amplification, sensory sensitivity, RSD, hyperfocus, burnout proneness, masking. It frames deficits while ignoring strengths like creativity & deep focus. Hugely influential, but it skews how psychologists see neurodiversity.
Mia♡
@luxemiaa
Sep 20
People be loners cause they got played by everybody they put they trust in
Wallow in victimhood – it is feeding the dark wolf when you had a choice to feed the light wolf. Only one wolf is going to survive. And it's up to you which one that ends up being. You become whatever it is that you think. It's very hard to dig out of hole if you believe you belong there, if you think you deserve problems. You will curate the world around you that starts with your perspective of which just confirms how much you feel awful.
Sensitive Stability
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eJXYLxf3JuI
YT jdprettynails
I think it’s more a case of everyone else’s social skills that are atrophying.
Because when I’m in a social situation I’m fully engaged. I’m smiling, great with eye contact….but I get anxious all the time because everyone giving short responses so I assume the problem is me. I’m boring them, they’re only operating my presence to be nice. So I eventually shut up and get quiet.
CPTSD is a learned set of responses. And a failure to complete numerous important developmental tasks. This means that it is
environmentally not genetically caused. In other words, unlike the most of diagnosis is confused with, it is neither in-born or
characterological. As such, it is learned. It is not inscribed in your DNA. It is a disorder caused by nurture – or rather the lack of it. Not nature. What is learned can be unlearned.
Complex PTSD: From Surviving to Thriving
Reducing CPTSD to “panic disorder” is like calling food allergies chronically itchy eyes. Over-focusing treatment on the symptoms of panic in the former case and eye health in the latter does little to get at root causes. most of the diagnoses mentioned above are typically treated as innate characterological defects rather than as learned maladaptations to stress – adaptations that survivors were forced to learn as traumatized children.
Complex PTSD: From Surviving to Thriving
The superego morphs into a totalitarian critic that trumps the development of a healthy ego. [The ego develops later than the superego.
In psychology, the term ego represents what we typically mean when we use terms like my “self” or my identity. The healthy ego is the user friendly manager of the psyche. Unfortunately, Cptsd-inducing parents thwart the growth of the ego by undermining the development of the crucial egoic processes of self compassion and self-protection
Complex PTSD: From S.
Rageaholic narcissists are infamous for using other people as dumping grounds for their anger. They are addicted to the emotional release of catharting in this way. The relief often does not last long before they are looking for another fix of venting their spleen. This type of narcissism is pure bullying, and bullying alone can cause ptsd. If it goes on long enough as it does with bullying parents in a dysfunctional family, it can cause Cptsd.
Complex PTSD: From Surviving to Thriving
Negative mindset has a tendency to compound. “I can't do anything, I'm worthless”. With that kind of attitude you will remain in the position where you are not productive. You have to start understanding the difference between a label and actual personality trait.
Coolest part of not knowing what your personality traits are – is you kind of getting pick them. Get to choose, you want to be bad-ass who always finishes what they start.
Sensitive Stability
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w4e2PBoRgk0
Stress usually involve other people. If you were able to fail in private – wouldn't be a big deal. I could fail in private all day. The stress isn't there in private. It's not the same. Whereas where other people are involved – stress is amplified. It is not fear of failure that really bothers us. Especially with BPD. It is the fear of what other people will think when you fail. That's the problem. That's where most of issues come from.
Sensitive Stability
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sqenLaQX3zs
KLASIK♠️
@Klasik007
everytime i addressed something that bothered me, i became the problem lol
Shadows of Control
@shadows_control
Abuse teaches you to shrink. Healing teaches you to take up space again.
Shadows of Control
@shadows_control
Anger is not the enemy. It’s a boundary signal. In abusive relationships, reclaiming your anger is reclaiming your power.
The Wily Survivor
@WilySurvivor
Your empathy is not somebody else's free pass for abuse.
Carl Jung Archive
@QuoteJung
Every form of addiction is bad, no matter whether the narcotic be alcohol or morphine or idealism.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
If you're living with complex PTSD, please go easy on yourself.
C-PTSD doesn’t just live in your memories — it lives in your nervous system, your motivation, your energy levels, your ability to focus, your confidence, your sense of safety.
It can make everyday tasks feel like mountains.
Getting out of bed. Getting things done. Staying connected. Keeping up with life. It’s all harder when your brain is wired for survival.
💛 This doesn’t mean you're lazy.
💛 This doesn’t mean you're broken.
💛 This doesn’t mean you're failing.
This means you are surviving something that was never your fault.
Please be gentle with yourself. Progress looks different for everyone. You’re doing better than you think. And healing doesn’t come from pushing harder — it comes from meeting yourself with compassion.
You are not behind. You are not alone.
You are doing the best you can — and that is enough.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Being accused of lying when you're telling the truth is manipulation.
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
When a narcissist is losing the argument, they will change the topic, attack you personally, or invent new 'facts' to make themselves look right.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
The reason abusive people shame you for being sensitive, is because they know the power in your sensitivity could convince others to be more like you and less like them.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Stop shrinking in places that you've outgrown.
You're meant to be seen.
Nikola Tesla | Inventor & Visionary 🔮
@NikolaTeslaQuot
"The scientific man does not aim at an immediate result. His duty is to lay the foundation for those who are to come, and point the way."
Autistic Lauren 🏳️⚧️ 🏳️🌈
@Autistic_Lauren
Ever notice how disabled people are often discouraged from saying "no"?
Or how we're just expected to appreciate the bare minimum accommodations/support and are deemed "ungrateful" if we actually speak our true thoughts?
Jules
@JulianeWriter
"We'll only help you if you agree that you are beneath us. If you act as an equal or assert agency you obviously don't need help." It's so frustrating. The idea of helping someone without framing them paternalistically is not something people appear to be able to conceptualize.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Sep 29
If you alter your behavior because you're afraid of your partner's reaction, you are being abused
Tell me no Lies 💔❤️🩹➡️❤️🥰🌹💪🏻🚫Narcissists🚫
@lovewins11011
A narcissist’s definition of peace is you quietly tolerating their asshole behavior.
𐙚
@fentyluxee
Sep 29
I stay away from people who avoid self reflection & accountability. If you can't keep it real with yourself, ain't no way you can keep it real with me.
Dr. Jen Wolkin | ADHD + Trauma Therapist
@drjenwolkin
PSA from a neurodivergent neuropsychologist: just because someone isn’t restless, or hyperactive on the outside, doesn’t mean they aren’t on the inside. XO, Dr. Jen
ayo
@ayofromthedead
Sep 30
I need to somehow unlearn 25 years of feeling like I'm in trouble for something
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Oct 1
Telling a traumatized person they must forgive in order to heal is attaching them back to their abuser, re-creating a vulnerable dependency out of their control. Forgiveness is not a tool to heal trauma. Trauma work is a tool to heal trauma.
Chi
@__Poisonivyyy
Unnecessary rudeness really irritates me like what's the reason
Introvert Problems
@IntrovertProbss
It's crazy how staying to yourself and not bothering people… bothers people
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Healthy individuals do not engage in bullying behavior. This can be attributed to their emotional stability and self-awareness, which foster empathy and respect for others. They are typically secure in their own identities and do not feel the need to assert dominance over others.
Tell me no Lies 💔❤️🩹➡️❤️🥰🌹💪🏻🚫Narcissists🚫
@lovewins11011
Narcissists don’t argue to understand. They argue to confuse you into doubting yourself.
⚚Sage
@Be_like_Sage
Y'all be venting to people who glad you got problems
Tell me no Lies 💔❤️🩹➡️❤️🥰🌹💪🏻🚫Narcissists🚫
@lovewins11011
One thing I’ve learned in dealing with a narcissist is keep the receipts!
Email. Text. Recordings. Pictures. All of it.
Narcissists spout so much shit they can’t keep track of their lies. 😆
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Overexplaining is really common for survivors of narcissistic abuse because, in those relationships, every word, action, or decision could be twisted, criticized, or used against them. They get used to constantly justifying themselves, anticipating how the abuser might react, and trying to prevent conflict or blame. Even after leaving, that habit sticks—survivors often feel like they have to give extra detail or clarify themselves to make sure they’re “understood” or not judged.
It’s not about being insecure or annoying; it’s a trauma response. The brain learned that overexplaining was a way to survive and stay safe. Over time, with self-awareness and practice, survivors can start trusting their own voice again and realize they don’t need to justify themselves to everyone all the time.
This is why resentment of the empath is so dangerous – it is not a storm of rage. It is silence. It is the quiet closing of the heart's gate and to those who thrived on that openness of that heart such silence feels like exile. Justice for those who fear their own reflection is unbearable.
Empress must thread carefully: to live in resentment is to poison one's own waters. If the empath merely inverts their gift into bitterness, they remained chained to the very oppressors they sought to escape. The true transformation lies not in revenge but in recognition.
When Empaths Turn Resentful Their Revenge Isnt What You Expect Carl Jung Original
https://www.youtube.com/shorts/SM8C1eesXeo
Heal your shame. Here's how.
https://www.youtube.com/shorts/baVvA_J2hIU
Do you ever find yourself cringing in shame at things that you did a long time ago? When you even weren't the same person you are now. But yet just thinking about it makes you cringe.
You want to change that pattern?
Here's how:
Heal the part that is cringing and love it. Just give that part – love. And every time it comes back up, just love it. Love it for what it did. Love it for cringing about it now. And my prediction is, you're going to see it go away.
Shining Science
@ShiningScience
Quantum physics is quietly reshaping how we see not just the universe but life and death themselves. A growing idea called biocentrism dares to suggest that life and consciousness aren’t random accidents of creation, but the very foundation of reality.
According to this view, death may not be the end. What we call “dying” could simply be a shift in awareness — a transition into another layer of existence within a vast multiverse of possibilities. In other words, reality might not exist out there at all, but within the very act of perception itself.
Supporters of biocentrism often point to strange quantum effects like entanglement, where particles stay connected across galaxies, or the observer effect, where simply measuring something changes its behaviour. Even the eerie idea of retrocausality, where events in the present seem to influence the past, adds to the mystery. Together, these experiments hint at something unsettling — that consciousness might play a deeper role in shaping the universe than we ever imagined.
But here’s the catch: as fascinating as it sounds, biocentrism is not proven science. Most physicists see it as philosophy — an imaginative bridge between quantum mechanics and the mystery of consciousness. The experiments are real, but connecting them to life after death remains speculation.
Still, the idea is impossible to ignore. What if our consciousness doesn’t vanish, but simply changes channel? What if death is not a full stop, but a doorway into another version of existence, beyond time and space?
Whether it’s science or spirituality, biocentrism forces us to ask the most haunting question of all:
If consciousness shapes reality, what really happens when it lets go of one world and awakens in another?
#Quantumphysics #quantum #LifeBeyondDeath
ROP
@clockwright1
As long as they are factual I wish to be judged.
Ripley
@Ripley49952702
That would depend on who is doing the judging.
Johan | sensoryoverload.info
@johanlammers
I'll keep promoting them. Weighted blankets are simple, silent, and powerful. They calm anxiety, ease overstimulation, and help your body feel safe again. One of the best coping tools for mental health: ever.
Dr. Glenn Patrick Doyle
@drdoylesays.bsky.social
You're not "crazy" for being super reactive to a slight change in someone's tone of voice or energy toward you. That's your nervous system doing what it had to do for years.
Recovery involves smoothing out that reactivity-- without invalidating the needs or pain driving it.
Shining Science
@ShiningScience
Autism is more than just a single condition, according to a major new study of over 45,000 people across several countries.
Researchers found that people diagnosed with autism later in life—during late childhood, adolescence, or early adulthood—may have a different form of autism than those diagnosed earlier, typically before age six.
The study discovered that early- and late-diagnosed individuals tend to follow different developmental paths and even have different genetic profiles. Those diagnosed later often share some genetic traits with people who have ADHD, which might explain why it's sometimes hard to tell the two conditions apart.
Children diagnosed early usually show more behavioral challenges when they’re young, but these issues often become more manageable over time. However, those diagnosed later often face increasing behavioral difficulties and are more likely to develop mental health conditions like depression or PTSD as they grow older.
The researchers stress that autism doesn't come in just two forms. Instead, it’s likely a broad spectrum influenced by different combinations of genes, leading to a wide variety of symptoms and experiences.
Cultural factors, access to healthcare, gender, stigma, and ethnicity also play a role in when and whether someone gets diagnosed, making autism even more complex.
Understanding these different patterns, the researchers say, could lead to better, more personalized support for autistic people at all ages.
Source: Zhang, Xinhe, et al. "Polygenic and developmental profiles of autism differ by age at diagnosis." Nature (2025): 1–12.
-
Nicholas Fabiano, MD
@NTFabiano
Instead of “I’m bad at this”.
Say “This is new for me”.
This gives your brain the space to learn instead of shut down.
This is neuroplasticity in real time.
-
Johan | sensoryoverload.info
@johanlammers
Full Article
🧬✨ The Chemistry Behind Neurodiversity
Neurodiversity is deeply biological.
It’s not just about behavior or personality. It’s about the brain’s chemistry and how it regulates attention, emotion, and sensory input.
Different neurotransmitters create different rhythms, shaping how each person experiences motivation, focus, and calm.
⚡ Dopamine — The Drive and Reward Circuit
In ADHD brains, dopamine signaling works differently. Studies show reduced D2/D3 receptor availability, which affects how strongly rewards are anticipated (Volkow et al., 2011).
That’s why motivation often fluctuates — tasks that are urgent or interesting activate the system more effectively than routine ones.
🌈 Serotonin & GABA — The Sensory and Emotional Regulators
In autistic brains, variations in serotonin and GABA systems influence emotional regulation, sensory processing, and repetitive behaviors (Uzunova et al., 2016).
Serotonin modulates emotional stability; GABA fine-tunes how much sensory information gets filtered.
When these systems differ, sensory input can feel unusually intense or uneven.
🔥 Noradrenaline — The Arousal and Focus System
Noradrenaline regulates alertness and attention. In ADHD and AuDHD, noradrenergic dysregulation can lead to hyperarousal, racing thoughts, or difficulty sustaining attention.
It explains the cycles of being “over-alert” and then completely drained.
💫 These neurotransmitters — dopamine, serotonin, GABA, noradrenaline — interact constantly.
Their balance defines how we experience energy, focus, and sensory input from moment to moment.
-
Libriscent
@libriscent
Oct 21
NARCISSISTIC PERSONALITY DISORDER
The only disorder where everyone around the person ends up in therapy except for the one who desperately needs it. Friends, family, partners—they all bear the invisible weight of confusion, frustration, and emotional exhaustion. They replay conversations in their heads, question their own reality, and constantly try to make sense of the chaos, often blaming themselves for things that were never their fault. They carry the pain of broken promises, manipulation, and subtle cruelties, trying to protect themselves while still hoping the person they care about will change. Meanwhile, the narcissist moves through life largely untouched, unaware—or willfully blind—to the destruction they leave behind. They rarely confront their own flaws, refuse accountability, and keep repeating patterns that hurt everyone around them. It’s a cruel paradox: the ones who need help the most are often the least likely to seek it, while everyone else ends up carrying the emotional fallout, piecing themselves back together, and questioning why they ever let someone like that into their lives. The irony is bitter, but the truth is undeniable: healing circles around everyone except the person who should be at the center of it.
The Wily Survivor
@WilySurvivor
The narcissist has zero accountability, yet infinite audacity.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissists actually think their ability to lie and manipulate makes them smart and skillful.
As if being “good” at being abusive is something to be proud of.
There’s a reason why the rest of us don’t engage in that sort of behavior…and it’s not because we’re stupid
Lisa K
@LisaAnnHK
I’ve learned “you are right” shuts my dad up, because that’s all he wants to hear. He has never been wrong a day in his life, so I agree and do what I want.
Narcissistic Abuse Awareness
@AwareOfTheNarc
A narcissist slowly conditions you to accept the bare minimum.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Living with CPTSD since my early 20s, I can tell you one of the best thing I ever did, some of the most powerful healing and relief from anxiety I experienced, was buying a home a couple thousand miles away from my abusers, in the middle of a rural countryside 50 miles away from the nearest major city.
If you’re living with CPTSD, I can’t tell you enough how important it is to get away from hectic energy (and hectic people). 🙏🏼 ❤️🩹
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
You were never the problem.
They just need an excuse for the way they abused you.
𝘽𝙡𝙖𝙠𝙚
@Arealmfngl
Oct 30
trauma LITERALLY changes how our brains function yet people are really out here saying "just let go of your past" OK LMAO
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Social sabotage is when someone tries to harm another person's social life or relationships on purpose. This can happen in many ways, such as spreading rumors excluding someone from a group or making fun of them in front of others. The goal of social sabotage is to make the
targeted person feel lonely embarrassed or rejected. It can take place in school's workplaces or even online where people can hide behind screens. Overall, social sabotage can deeply hurt someone's feelings and damage their self-esteem.
Don't participate.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Don't take anything personally. What others do isn't because of you. What others say and do is a projection of their own reality, their own nightmare. When you are immune to the opinions and actions and of others, you won't be the victim of needless suffering.
Ventally | Anonymous Venting & Listening
@ventallyco
This is the foundation of true self-confidence. When your sense of worth is internal, you're no longer at the mercy of external validation or criticism
Josh
@JD_Quotes2017
Oct 31
Never let someone who did you wrong make you think there's something wrong with you. Don't devalue yourself because they didn't value you.
Know your worth, always.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Ghosting is actually a TRAUMA RESPONSE for fear of abandonment.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
You are not responsible for anyone's distorted perception of you.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
I always know I’m dealing with a narcissist when they’re trying to make me feel bad for doing nothing wrong.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissistic parents not only inflict trauma onto their children, but they intertwine their child's identity with the suffering they cause. I.e. They see the PTSD, anxiety, depression, anger, etc. as who the child is, rather than a response to their abuse. So when the child seeks healing and growth, these same parents vehemently oppose any steps toward liberation from the effects of abuse, denying the identity underneath the trauma and resisting the path to recovery.
Happiness is not allowed. Healthy relationships are opposed. Anything beneficial to the child’s esteem is disrupted or taken away.
Often times, the parents are very covert about this oppression, being very careful not to reveal their underlying motives. They understand on some level that sadism is not socially acceptable, but choose to hide it rather than question themselves.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Malignant narcissists will abuse someone to the point of emotional distress, and then accuse them of being mentally ill or emotionally unstable. It’s a vile form of gaslighting, emotional abuse, and character assassination that serves multiple purposes: it deflects blame, protects the narcissist's image, and discredits the victim.
In abusive families, the scapegoat child is often subjected to chronic emotional abuse—being blamed, invalidated, isolated, or subjected to extreme double standards. Naturally, this causes the child to develop signs of anxiety, depression, complex PTSD, or emotional overwhelm. But instead of recognizing this as a normal reaction to mistreatment, the narcissistic parent twists it around, saying things like:
“You’re off the wall.”
“You’re bipolar like your [other scapegoated relative].”
“You need help— there’s something wrong with you.”
This is diagnostic grooming—they lay the groundwork to get others (teachers, therapists, doctors) to see the child not as abused, but as defective. This pattern often follows victims into adulthood, especially in narcissistic romantic relationships. The narcissist pushes the target to their emotional limit and then says, “See? This is why no one can deal with you.”
It’s not just gaslighting—it’s psychological warfare meant to discredit the victim so that when the truth starts coming out, no one believes them.
Bildungsroman
@fra11965483
Deprive a car of gas; deprive a narcissist of attention.
Tell them nothing important, stop listening to them, and never react to their shenanigans. It’s like taking the batteries out of a toy.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Narcissist (n.) A professional liar, emotional thief, and world-class victim when caught. They twist the truth so easily that lies become their language. They steal your energy, your trust, and your peace, then act wounded when you finally see through them. To the outside world, they wear the perfect mask — charming, confident, misunderstood. But behind closed doors, they drain you with manipulation, gaslighting, and blame. When the mask starts to slip, they quickly switch roles, painting you as the cruel one for daring to hold them accountable. It’s a cycle of deceit wrapped in fake remorse. But once you understand their tactics, you stop playing the part they’ve written for you. The truth doesn’t need to scream — it just needs to be seen.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Nov 2
The allegations narcissists make against you are actually confessions of their own behavior. Every time they accuse you of something, whether it’s lying, being selfish, manipulative, or cruel, they are often projecting their own hidden truths onto you. What they point out in you is usually what they are unwilling or unable to face in themselves. They twist reality, blame you for things you didn’t do, and make you question your own mind—not because of who you are, but because they are trying to escape accountability for their actions. The harsher and more persistent the accusation, the deeper the confession it contains about their own behavior. Understanding this allows you to see through their manipulations, to protect your self-worth, and to realize that their attacks are a reflection of their own inner turmoil, not a judgment on your character. Over time, recognizing this pattern can free you from the weight of their lies and help you reclaim your clarity, confidence, and peace of mind.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
One of the most common traits of narcissists is their tendency to invent offense.
They will actively search for something—no matter how trivial—to be outraged about. This performative outrage allows them to:
- Claim false moral high ground
- Distract from their own abusive behavior
- Rally others to their side by weaponizing victimhood
- Project their own hostility onto innocent people
- Feel relevant and gain attention
What makes this dynamic so toxic is the double standard: narcissists will vilify others for harmless actions while excusing or denying their own or other people’s harmful ones.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Nov 4
When narcissists see someone with qualities they lack—like empathy, authenticity, and inner happiness —they experience intense resentment. But admitting to themselves or others that they hate you for being a good person would expose their own inadequacy. So instead, they manufacture a narrative that paints you as the problem.
They’ll twist reality to make you seem like the abuser, manipulator, or other negative qualities they know people will easily accept without looking deeper.
They need a justification for their hatred that keeps their fragile self-image intact while also manipulating others into siding with them.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Nov 4
The narcissist’s special skill is destroying good people.
They see a good person, happy, compassionate, honest, and they begin their attack. It’s a slow, persistent chipping away of a person.
They begin shaming that person.
They begin sewing seeds of doubt, trying to make that person second-guess themselves.
They start planting seeds of doubt in other people. Consistently eroding away their targets public image and self-esteem.
They abuse their target, talk bad about their target, shame their target for doing nothing wrong.
And what is their explanation? When people ask why they are doing this to their target, the narcissist says “they deserve it“. And that’s their excuse. And they are so adamant and aggressively bitter towards genuinely good, honest people, that witnesses think the target must’ve done something wrong, because why would anybody be so insanely and obsessively hateful towards an innocent person? And that’s what is so insane about it.
Just think about that. The hatred towards good a malignant narcissist has to go that far to destroy innocent people.
It’s evil. Evil incarnate.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissist parents will withhold teaching their kids life skills or lessons because they don’t want to make life any easier on their kids, they want their kids dependent on them for help or answers.
Their objective is to always feel “better than” or “smarter than”, or to remain “dominant” over their kids. But they’ll act like they “did so much”
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
·
3h
Malignant Narcissists often exhibit a range of cluster B traits. Those with borderline traits are prone to splitting, where they see someone as “all bad” if that person challenges their image, sets boundaries, or fails to meet their expectations. Even friendly people can trigger this if they unknowingly frustrate the narcissist’s fragile ego. Once the narcissist feels slighted, their anger fuels an obsessive and irrational need to devalue and punish the person, often through covert attacks that could never be proven by the victim. They excel at this because they obsess over finding ways to hurt their victim and not get caught. This makes them relentless and dangerous.
Most people don’t understand how obsessively far these people will go to hurt the people who bruised the their ego, so when the victim recognizes what is happening and tries telling somebody what the narcissist is doing to them, the narcissist paints the victim as paranoid or vindictive, and essentially projects their own behavior traits onto the victim.
The problem is that most people just don’t understand how two-faced, manipulative and deranged these people are and how easily they’re fooled by them until they become a victim themselves or they see hard evidence that is even still hard for them to believe.
Gogo.Sifiso - the seer
@theseerheals
Nov 4
Being disliked by people with ugly spirits is actually a form of divine protection, not rejection. When your frequency gets too high, it starts to irritate demons the way sunlight irritates mold. They can’t stand your glow because it exposes their shadows. That’s why
Gogo.Sifiso - the seer
@theseerheals
Nov 4
Chosen Ones don’t lose friends, they shed parasites disguised as company. Every hater is really a vibrational allergy test showing you who can’t breathe the air you bring.
Randazzle Enriquez
@RandazzleEnriq2
When your energy’s clean, you’ll notice some folks just can’t handle it. Light exposes what darkness tries to hide. Stay shining, you’re being protected for a reason.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
There’s a cruel paradox that scapegoats of narcissistic abuse often face.
If you handle the abuse stoically — staying composed, functioning, keeping up appearances—people assume nothing was ever wrong. Your pain is invisible, and so is the abuse.
But if the trauma catches up with you… if you break down, develop anxiety, depression, or PTSD—suddenly you look like the unstable one. And to outside observers, that just seems to confirm the narcissist’s narrative that you were the problem all along.
This is how scapegoats are retraumatized by a world that misunderstands trauma—and how narcissists get away with it.
࣪ ִֶָ☾.
@_caelena
Having a naturally intimidating aura is so exhausting. People will go to the wildest extremes to humble me or compete with me. Meanwhile, I'm literally just trying to exist.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Malignant narcissists are obsessed with control, and they often exert this obsession in irrational, passive-aggressive, or outright destructive ways.
Their need for control isn’t just about dominance; it’s about proving that no one has power over them.
Their ego cannot tolerate the idea of being "forced" to do anything, even if it's something normal or reasonable like picking their kids up from school or bringing back a requested item from the store. They might intentionally and consistently be late to “prove” they aren’t a chauffeur or they may intentionally bring back the wrong items to prove they don’t have to do anything anyone asks them to do.
Possibly the most malignant expression of this is when a malignant narcissist parent fears losing control over their child, they will often work to destroy their child’s life to remain in control.
Jelena
@Feralfairy13
I feel like the more people I meet, the more predictable human behavior feels, like there’s only a handful of archetypes and they keep showing up in different bodies over and over again
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Sociopathic and narcissistic parents often hide cruelty behind the label of “tough love.” It’s one of their most effective disguises. Instead of genuine guidance, they use emotional deprivation, humiliation, intimidation, or calculated neglect and then claim it’s for the child’s own good. The goal isn’t to build resilience — it’s to maintain control while avoiding accountability. 🧵
These parents may spend years eroding a child’s confidence through psychological abuse that results in anxiety disorders, complex PTSD, and learned fear. Then, when the child is at their most vulnerable and dependent, the parent suddenly flips the script: kicking them out, abandoning them, or withdrawing support with no warning or preparation. And they frame this cruelty as “teaching independence,” “forcing them to grow up,” or exercising their “right” as a parent.
The reality is that this isn’t tough love or discipline. It’s sadism dressed up as parenting. It’s a deliberate tactic to break a child down, then blame the child for the damage the parent caused. Survivors need to know that what they went through wasn’t their fault — and that no caring parent would ever weaponize “independence” as a way to justify their own abuse.
And ironically enough, they’re not trying to instill independence in the child. They’re trying to cause havoc and distress so that the child needs to come back to them for help. They’re trying to create dependence. They want the child forever dependent on them and they cover this up by making it sound like they’re trying to promote independence. It’s another way narcissists completely reverse reality to gaslight witnesses
⋆.𐙚 ̊
@luvblessingz
Nov 5
People who say “I didn’t ask you to do that” while you’re addressing their lack of appreciation for things.
gabrielle
@legitimatetiger
Nov 4
my brain chemistry changed when i realized people don’t really hate you because you think you’re better than them, they hate you because THEY think you’re better than them & they’re mad about it. it’s all projection.
𝗄𝖺𝗄𝗁𝗈𝗓𝖺
@simphiweyinkoc_
Nov 5
Being rude to polite people is a whole different level of miserable.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
People aren’t fooled by malignant narcissists and psychopaths because they’re dumb. People are fooled by them because the narcopath’s lack of compassion and obsessive need to sabotage innocent people is so irrational and inhuman and foreign to a normal human being, that it just doesn’t make sense to consider.
Not until after our reality has been shattered at the discovery that people this shamelessly evil actually exist all around us pretending to be normal human beings, do we really see it.
It’s not easy to accept.
Your logical mind fights it. We don’t want to believe that people could be that evil. It’s so sad and pointless and such a waste of a better humanity. So illogical and irrational. It’s a shame we have to dumb ourselves down so much to consider it.
And when they’re your parents, it is so hard accepting that your parents are psychopaths. So hard.
It’s like finding out your parents are actually brain eating zombies. You just don’t wanna let them go. You don’t wanna accept it. But they’re not really human anymore. They’re driven by an insatiable desire to eat your brain and you can’t reason with them.
lets heal and recover
@recovery_your
“Suicide is selfish because it hurts the people left behind.”
No what’s selfish is ignoring someone’s pain while they’re alive, then blaming them when they couldn’t carry it anymore.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Too many people mistake narcissism and psychopathy for strength and confidence
Raven Lovette 🦋
@heyhoneyrae
Once you realize people hate themselves and have low self esteem, you understand more why they're so nasty, competitive, and pessimistic. Let them tend to that misery alone.
Mark Manson
@IAmMarkManson
Nov 6
Insecure people mistake narcissism for confidence. Confident people recognize narcissism for what it is: insecurity.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
So many people really have no idea what or how common narcissistic sociopaths are, what they look like, that they’re being manipulated by them and being lied to by them, until they become a victim themselves and then it’s like their whole reality shatters.
The Wily Survivor
@WilySurvivor
Be careful with the urge to “fix” someone. It’s often part of the trauma bond, the part of you that learned to earn love by rescuing, proving, and sacrificing. Your job isn’t to heal the person who broke you. It’s to heal the part of you that thought you had to.
𝗘𝗟🐕⚒️👁️⃤
@MatrixMischief
·
Nov 6
most of the time, when someone’s being cruel, it’s because they’re miserable inside. it’s not about you
Rumi
@rumilyrics
·
Nov 6
It took me 10 years to realize: no matter how much you trust the people around you, don’t tell them everything.
Aim True (Amy Pagett)
@AimTrue7
Fawning is a trauma response that is often rewarded in childhood.
We praise their ability to “be good and well behaved” as they work hard to please the adults in their lives.
This praise encourages the behaviour of putting others first & self abandonment.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
A malignant narcissist doesn’t “punish you“ for being bad. They “punish you“ for being good, genuine, and honest.
They can’t stand it.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
I’m really tired of the honest people being held to a higher standard than the dishonest malignant narcissists who seem to be allowed to get away with anything.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Truth tellers, whistle-blowers, scapegoats and the real victims are always portrayed as 'crazy.'
Know the difference
Kliez
@A_B_B_A_H
It's actually crazy what a toxic household can do to somebody
Libriscent
@libriscent
🚩Red Flag: They consistently misinterpret your intentions, claiming that you meant harm when in fact, you did not.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
It can clear up a lot of confusion around childhood trauma, when you recognize abandonment is not just when someone walks away. It's also when someone who is meant to protect you, allows others to hurt you.
@omgsidewalks
They want you small, silent and scared. Come back finer, energy louder, and favored.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Nov 7
Sometimes the anxiety you feel is your healthiest, most authentic self reacting to the inauthenticity around you.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
If protecting your peace makes you the villain.
Be the villain
Libriscent
@libriscent
Stop wasting your life trying to get everyone to understand your choices.
Let Them misunderstand you.
Let Them think you’re wrong.
Let Them think it’s embarrassing.
Your decisions aren’t supposed to make sense to anyone but YOU.
So save your energy for living your life, not defending it.
jonzing.
@ehisssss
i highly recommend cancelling pointless friendships and relationships
ms peoples
@4DAGHETTO
Bitches need conflict to feel relevant.
¿?
@okstahn
you are under no obligation to make sense to anyone
Libriscent
@libriscent
After everything you’ve been through, the fact that you can still love, still care, still give without bitterness ... that’s strength. Don’t let this world harden you. Stay kind. Stay open. You’re not naive for loving deeply, you’re courageous. Because it takes real strength to be soft in a world that’s tried to make you cold.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissists detest genuinely good people.
They actually feel like their life is being threatened by a good person and they feel a need to smear campaign and destroy them however they can get away with.
Imagine burning with hatred because someone is genuinely good and honest. Narcissists are scary people.
ηιүα ♛
@niy2pretty
People show you in small ways that they really don't like you...
💗
@ma1ybe
Trauma doesn't make people stronger. It damages their nervous system. It hijacks their digestive track. It keeps the person in a constant loop of hypervigilance. To tell someone they are stronger because of trauma is to deny what it has cost them to survive.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissists use manipulative tactics that are particularly effective against honest and moral individuals because these individuals don't think or act like the narcissist. The moral person, who typically avoids using manipulative tactics, doesn't fight back in the same way, which the narcissist exploits. It's like the moral individual is fighting with their hands tied. However, when the moral person learns the narcissist's tactics and realizes that reasoning with them won't work, they may choose to fight back by mirroring the narcissist's own behavior. This tactic can be effective because it confronts the narcissist with their own methods, making them feel threatened. In response, the narcissist will often try to shame the moral individual for using the very tactics they themselves employed.
The Narcissist does this because those tactics are effective against them, and they fear losing control or being defeated. When their methods are mirrored back at them, it exposes their vulnerability and threatens their sense of superiority. The narcissist's fear of being outmaneuvered drives them to shame the moral individual, hoping to dissuade them from continuing to use the same effective strategies.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Nov 8
Abusive people don't feel bad for harming you, but they feel bad when you tell others what they did to you because it damages their image.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
When a malignant narcissist is confronted with something inappropriate or abusive they have done, rather than acknowledging any wrongdoing or attempting to correct it, they will often DOUBLE DOWN, or intensify their behavior.
While doubling down is an attempt to maintain control and protect their fragile ego, it can often backfire. Their responses can be irrational, self-destructive, and may ultimately make them look foolish. This disconnect between their intentions and the actual outcomes is a result of their distorted perception of reality and their inability to see beyond their immediate need to defend their self-image.
voic.eofthebroken1
@brokenvoices_
They double down because taking responsibility feels like death to their ego. Accountability threatens the false image they built, so they’d rather look irrational than admit they were wrong. It stops being a disagreement at that point. It becomes self-preservation for them.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Nov 8
Sometimes the healed version of you is meaner.
a n x i e t y
@ohanxiety
for your own sanity, move on like you never knew them because in reality you never did.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Nov 8
Letting a narcissist know that their behavior is bothering you, typically doesn't lead to any positive change. Instead, they might dismiss your feelings, deny any wrongdoing, or even use the information to further manipulate or upset you. Narcissists typically lack empathy and are more concerned with maintaining control and protecting their self-image than addressing the impact of their actions on others.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Nov 8
Alternatively, a covert narcissist might agree to "work on it" or promise to change as a way to pacify you in the moment, but it's often just a tactic to avoid conflict or criticism. They typically won’t have any genuine intention of changing their behavior. Instead, they may continue their manipulative actions once they believe the situation has been diffused.
Zoraya Black
@ZorayaBlack_
If you’re in environments that make you feel you gotta record convos, record phone calls, keep receipts, screenshot, save chats, have witnesses, tell your friends/family everything because you’re dealing with a liar. Just cut them off. That’s not a way to live. You shouldn’t have to become a detective because you’re dealing with dishonest people. Leave them to their insanity or you’ll join them.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Nowadays, exposing evil is considered more evil
than those who actually do evil.
Aim True (Amy Pagett)
@AimTrue7
Shame is such a tough thing to carry.
A hint, sniff or whiff of shame can send you spiralling into overthinking, regret and despair.
It seeps its way in and takes over and leaves you feeling overwhelmed & not good enough.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Bullying is a choice.
Being a victim isn't.
EarthtoGazelle
@EarthToGazelle
Some people would rather ruin their lives before simply apologizing & changing. The pride before the fall is real af.
Nithya Shri
@Nithya_Shrii
Stay humble and play dumb. People reveal who they truly are when they think they are smarter than you.
Nini
@CoocHeona
The final stage of healing is telling certain folks to fuck off.
Chi
@__Poisonivyyy
Everytime I addressed something that bothered me, I became the problem
π
@ghOztyy__
Take it personal.. at this age, trust me, people know what they're doing.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Someone doesn’t have to leave to abandon you. They can sit right next to you and still make you feel alone. Neglect, broken promises, and emotional distance, that’s abandonment in disguise.
Nika Solé
@withlovesole
Some people are ruled by their ego. Others are ruled by their soul. This makes all the difference.
The Wily Survivor
@WilySurvivor
A narcissist will call you "difficult" the minute you stop cushioning them from the consequences of their own behavior.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
“Too sensitive” is what people say
when your boundaries inconvenience their manipulation.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Healing means accepting that some people will never apologise, never change, and never see the damage they caused.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Toxic people manipulate and bully.
Healthy people show respect, kindness, and dignity.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissists are often obsessed with control.
Here are some ways narcissists exert control:
Strategic Incompetence – If asked to do something, they will intentionally do it wrong (or half-done) so they won’t be asked again. This isn't just laziness; it's a power move to show they won't be controlled.
Withholding and Sabotaging – They may withhold information, money, affection, or resources to keep others dependent on them. For example, a malignant narcissistic parent might "forget" to submit their child’s college applications or financial aid forms, ensuring the child doesn’t gain independence.
Intentional Chaos – They create unpredictable environments where they control the narrative. A malignant narcissist might start unnecessary arguments before an important event, making sure their target is too upset or distracted to perform well.
Moving the Goalposts – They demand something, and once you comply, they change the requirements so that you're never "good enough." This keeps people scrambling and under their thumb.
Triangulation – They manipulate relationships by pitting people against each other, ensuring that no one trusts anyone except them. This keeps them in control of all communication and alliances.
Public Humiliation – To assert dominance, they may undermine someone in front of others, whether by making "jokes" at their expense, correcting them unnecessarily, or sharing private information to shame them.
Deliberate Forgetfulness – They "forget" promises, birthdays, deadlines, or important commitments, forcing their target into a position of having to constantly remind them or beg for basic respect. This reinforces their control by making the other person feel powerless.
Gaslighting – They will deny reality, rewrite history, and convince their target they are imagining things. This erodes confidence and makes their victim more dependent on them for "truth."
Sabotaging Success – If their target shows independence or improvement, they will subtly or overtly sabotage it. This could be as simple as making them late to an important event, or as extreme as convincing them that their dreams are unrealistic or selfish.
Silent Treatment & Stonewalling – They cut off communication as punishment, refusing to acknowledge their target until they "submit" or beg for their attention. This reinforces their power by making others feel small and desperate.
When it comes to malignant narcissistic parents, their control is particularly insidious. If a child begins to assert independence—by questioning them, setting boundaries, or even succeeding in ways the narcissist cannot take credit for—they see it as an attack on their authority. That’s when they shift from controlling to outright destroying, often through emotional abuse, guilt-tripping, or even financial and social sabotage.
H I M 💸
@Rinola_
One of the most attractive things you can do is not being everywhere
𝑻𝒉𝒆 𝑺𝒂𝒍𝒕 𝑶𝒇 𝑻𝒉𝒆 𝑬𝒂𝒓𝒕𝒉
@Shadaya_Knight
Nov 10
I don’t know how to explain it but you can feel when someone secretly hates you, even when they give you a compliment.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
When a narcissist abuses, humiliates, or dehumanizes someone, they don’t see their actions as reflections of their own moral failure or psychological dysfunction. Instead, they recast the abuse as proof of the victim’s supposed inferiority, brokenness, or deservingness of mistreatment. In their mind, the abuse doesn’t reflect on them — it defines you. If they scream at you, it's because you provoked it. If they lie, manipulate, or smear you, it's because you can't be trusted. If you break down, it’s not because they broke you, but because you were “broken” all along. This warped thinking helps the narcissist maintain their fragile illusion of superiority and control and evade accountability and allows them to offload their internal shame, fear, and rage onto others.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissists don’t just misremember—they reconstruct reality to suit their ego and narrative. It’s not about truth; it’s about control. If the real version of events makes them look bad, vulnerable, or wrong, they’ll edit the memory—intentionally or subconsciously—until it flatters them, justifies their actions, or demonizes someone else. They’ll gaslight you with that version, acting like you’re crazy or confrontational for remembering it differently.
It’s one of their most dangerous manipulations: rewriting history and then punishing you for not living in their revision.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Baby I do not mind being the villain in your story because in mine you lack boundaries, integrity, you have no empathy, you’re unkind and lack healthy communication skills and the emotional maturity to take accountability.
EarthtoGazelle
@EarthToGazelle
When people harm me intentionally I don’t think “omg they hate me”, I automatically recognize it as them hating themselves and them trying to make it my problem. Cause 99.9% of the time the people who abuse us actually admire tf out of us and try to be like us even after we escape their harm. The “they just hate you that’s why they did that” is a complete deflection and makes it seem like the victim is at fault for another persons internal demons.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Healthy people reflect when they’ve hurt you. Manipulative people deflect by focusing on your reaction instead of their behavior. Pay attention to that difference, it tells you everything.
GINA NÄUMAN • جینا نعمان
@entertheunseen
When you are a person of light, you attract manipulators, narcopaths & abusers like a moth to a flame. Such bottom feeders are always looking for a source of light to vamp on. Take up the armor of God because the demons never stop coming, you just get better at maneuvering them.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Covert narcissists feel incredibly threatened by honest people with strong intuitive insight and and unwavering commitment to honesty.
Being around someone who "sees" them — not the mask, but the real, insecure, manipulative self beneath — is intolerable to a covert narcissist. It brings up shame they try desperately to avoid.
Instead of self-reflecting, they project, blame, or smear the honest person to undermine their credibility.
Qadi
@Bigqadi
Nov 10
I love people who been through real shit but they don’t make it their personality
Libriscent
@libriscent
Nov 10
Don’t ever be ashamed of a situation a narcissist has created for you. This is NOT who you are.
wisebaba
@Wizebaba
Nov 11
Avoid people that place material things over humans. They'll only respect and care about you if you have money
利弗森🀄
@livers0n
It's insane how many people are insecure about their appearance but not their character.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
The only person who gets to decide if something was traumatic is the person who experienced it.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Anytime someone tells me they are an empath, i immediatly know they will be the most narcissistic energy vampire youve ever met.
Poetic Outlaws
@OutlawsPoetic
“Experts in ancient Greek culture say that people back then didn't see their thoughts as belonging to them. When ancient Greeks had a thought, it occurred to them as a god or goddess giving an order. Apollo was telling them to be brave. Athena was telling them to fall in love.
Now people hear a commercial for sour cream potato chips and rush out to buy, but now they call this free will. At least the ancient Greeks were being honest.”
—Chuck Palahniuk
99 Majik
@99Majik
Nov 11
Be careful, people are pretending
highFashion
@rahman_jago_
Nov 11
People raised on love will do anything FOR you. People raised on survival will do anything TO you. Know the difference.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
You weren't divisive. You were honest and that makes you dangerous to toxic people.
Karun Pal
@karunpal
Nov 11
There’s a strange kind of loneliness that lives inside people who feel too much. They smile in public, but inside, they’re decoding the world. Every silence. Every glance. Every word that wasn’t said.
They don’t hate people. They just get tired. Tired of small talk. Tired of pretending they don’t notice the tension no one else feels. Tired of caring about things everyone else ignores.
So, they withdraw. Because being around people sometimes feels lonelier...
They crave peace, but their mind won’t stop.
They crave love, but they fear being misunderstood.
They crave rest, but they don’t know how to switch off their empathy.
These are the quiet ones. The overthinkers. The deep feelers. The ones who are at war with themselves but still show up with a smile.
You’re not broken. You're not flawed. You’re just tired of searching for depth in a world that’s forgotten how to feel.
🦋
@glowkitlarrie
bitch i was depressed for months, nobody noticed. i still showed up for people even when i didn’t know how to show up for myself. that’s why i don’t buy the whole “i was going through something” excuse for treating people badly. we’re all going through something
✨N3LL3Y✨
@N3LLYB3ARR
Nov 11
It’s crazy how some people need zero proof to believe a lie but need endless proof to accept the truth.
JoroJrn
@JoroJrn
Nov 11
your trauma is not an excuse to be manipulative, nonchalant, or narcissistic towards good people
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Your role as the scapegoat wasn’t about who you are. It was about their need to hide their own dysfunction. You were the light in a room they wanted to keep dark.
Libriscent
@libriscent
THIS IS GOING TO OFFEND A LOT OF NARCISSISTIC PEOPLE! But it's time you start admitting that you mistreated people and acted out of line, instead of being DELUSIONAL and acting like you were the victim.
In reality, your actions put you in a position where you lost everything and everyone who genuinely cared for you. Then you go and find cheerleaders who support your FOOLISHNESS and believe everything you say, instead of finding people who will be honest and tell you that you're WRONG and need help!
Healing doesn't come from attention. It comes from ACCOUNTABILITY. And that's exactly what narcissists run trom.
♡₊˚ 🦢・₊ ♪ ✧
@diorvijane
people just lieeeeeeee and lie and lie and lie and lie and lie and lie and lieeeeeee
The Wily Survivor
@WilySurvivor
Coercive control hides in those moments that look kind. “I’m doing this for you” is how domination and control disguise themselves as love and concern. Eyes open. 👀
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
I think covert and malignant narcissists are the only people who will target and stalk a person who they envy, attempt to make friends with that person in any way they can sometimes through lying about experiencing the same abuse their target experienced, then slowly begin criticizing little things consistently, criticisms that dont even make sense because they’re not true, and when you finally recognize this absurd pattern of behavior from them and, politely as you can, put up a boundary or block them, they turn around and smear campaign and play the victim role and make their target look like the abuser.
These people are predatory demons. IYKYK
Libriscent
@libriscent
I don’t care how close we are. If you ever weaponize something personal I told you, I’ll never open up to you again.
Kiki 𐙚🧶
@Fayy_stitches
Removing yourself from any place you don’t feel loved, wanted, valued or respected is self care tbh.
The Wily Survivor
@WilySurvivor
One of the most dangerous parts of trauma bonding is that it feels like love. Your body craves the very person it needs protection from.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Highly intelligent and intuitive women inspire envy and fear because they are walking ego threats for narcissists, misogynists, and insecure people. Not only do they have a track record of identifying and recognizing patterns before the average person, they have a deeper level of processing. They pick up on subtle cues in their environment, the emotions of others, and see through the hidden motives of manipulators. People doubt you and lash out at you, only to find out you were right all along.
Libriscent
@libriscent
So many entitled ppl believe “I suffered so you should too” instead of “I suffered so no one else should”.
𝖋𝖎𝖒𝖎.
@Fimiii06
some people have no idea how draining they actually are.
Josh
@JD_Quotes2017
People will always notice the change in your attitude towards them, but they will never notice it's their behavior that made you change.
𝗘𝗟🐕⚒️👁️⃤
@MatrixMischief
The curse of being intuitive is knowing who’s lying, what’s coming, and still pretending you don’t
“That the outer man is a picture of the inner, and the face an expression and revelation of the whole character, is a presumption likely enough in itself, and therefore a safe one to go on“
Schopenhauer
-
lei
@ayyelei
Nov 11
Once you learn boundaries yu will b the biggest villain to the ppl who never had good intentions
Libriscent
@libriscent
Never let a person make you feel guilty for choosing not to tolerate their disrespect anymore. There’s nothing wrong with respecting yourself.
Self Upgrade
@selfupgrade222
SIGNS THAT THEY'RE A NARCISSIST:
1. They never take responsibility for their mistakes.
2. They always twist the story to make themselves look good.
3. They constantly seek admiration.
4. They lack empathy and downplay your feelings.
5. They manipulate others to get what they want.
6. They see relationships as a way to benefit themselves.
7. They blame YOU for their actions.
8. They get angry when they're not the center of attention.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Smear campaigns don’t start because you’re wrong.
They start because you’re right.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Exploiting and hurting people with no support system and limited protective factors is a rancid kind of evil.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Stay away from people who pretend to misunderstand you.
They secretly hate you.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Being a morally conscious and morally responsible person actually infuriates a narcissists. They’ll accuse you of “thinking you’re better than everyone”.
This is really just a projection of their own mindset. They believe morality is performative, so they assume your ethical values must be an act of superiority rather than a reflection of personal values. In reality, it’s they who constantly measure themselves against others, obsessed with status and dominance.
The best response? Keep being who you are. Their frustration is proof that your authenticity disrupts their illusion of control.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
I do not give second chances anymore. When I catch someone trying to gaslight me or minimize my concerns, I take that as abusive manipulative behavior and that’s it. ✂️
They had their chance
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
When the narcissist abuses you and you assert yourself or defend your boundaries, the narcissist perceives it as an attack. In their distorted worldview, they’re entitled to control, superiority, and unquestioned compliance. So the moment you resist, they don’t see you as standing up for yourself — they see you as “disrespecting” or “hurting” them.
This is why they often flip the script and start playing the victim.
In reality, what’s happening is that your self-defense threatens their control and their ego can’t tolerate accountability. So instead of reflecting on their behavior, they project their guilt and shame onto you.
It’s one of the most maddening experiences for survivors — you end up being accused of being abusive simply for refusing to allow yourself to be abused.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Exposing someone for what they did to you is not you talking shit about them.
The_Narc_Decoder
@NarcDecoder
Understand that they wanted your reaction to their disrespect, because then they could use your reaction to paint you as the problem and deflect from their own toxic and bad behaviours.
#reactiveabuse #narcissist
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
A narcissist’s sense of power often comes from withholding, denying, or giving on their own terms. If they gave you what you actually want without strings attached, they’d feel like they’ve lost leverage. Their control depends on keeping you in a state of need—dangling the possibility of meeting your needs but never fully allowing it.
Kim _winnifred
@winnifred2424_
Nobody talks about the angry stage of healing. The rage you feel when you realize how much and how long you were taken advantage of. The absolute disgust you feel towards those people that mislead you. It comes in waves. Sometimes you'll feel healed and then it suddenly hits you.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Stop using your pain ….as an excuse to hurt people!
kas𓆩ꨄ︎𓆪
@urth2kas
Disliking me is valid. I probably confronted you on your poor behavior while everyone else just accepted it.
feyisayo 💸
@feyiszn
I don’t know how to be fake. I just become very quiet around energy I can’t vibe with.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
A toxic environment is more likely to change you than you are to change it. Get out.
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
A narcissist destroys your reputation long before you realise you need to defend it.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
Complex trauma has your body under threat because it doesn’t know the difference between what is happening now vs. a long time ago. While this is a difficult experience it also shows how hard your mind/body is trying to keep you from getting hurt again. There is respect in that.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissistic abusers expect you to take the abuse and roll over quietly. They take great offense when you stand up for yourself. Like, how dare you. 😐
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
They bully you because something is wrong with them on the inside, it's not you. Kind and compassionate people don't go around intentionally destroying others, they just don't.
Houston James
@LHoustonn5
Nov 13
Don’t ever let anybody make you feel crazy because you finally figured them out
Libriscent
@libriscent
Karma says: Don't waste your time exposing them. Let them keep pretending. Their own lies will ultimately be their downfall. It's amazing how their own actions can be their own worst enemy.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Psychology says:
When you heal, your taste in people changes.
Libriscent
@libriscent
One of the hardest pills to swallow was that not everyone will understand your heart — and that’s okay. You can have the purest intentions, love sincerely, and still be misunderstood. Some people will mistake your kindness for weakness, your silence for indifference, or your honesty for arrogance. It hurts when you realize that no matter how genuine you are, some minds will twist your truth to fit their comfort.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Nov 14
Pushing someone until they snap + then running off + calling them toxic + abusive is one of the purest forms of evil + manipulation.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Some people provoke you because they’re entertained by you being dysregulated.
Matthew Zeitlin
@MattZeitlin
rich people, politicians, and celebrities often discover that intellectuals are very cheap dates and willing to debase themselves for relatively small amounts of money, power, or glamour, the three things hard to obtain in intellectual life
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Accountability feels like an attack when they're not ready to acknowledge how their behavior harms others.
HIM💀
@brahim_kage
Your trauma is not an excuse to be manipulative, nonchalant, or narcissistic towards good people.
@omgsidewalks
Rejecting someone because of their friend group is actually very valid
Tifeh🤎
@Misturrah
If you can't be corrected without being offended, you will never grow in life.
Libriscent
@libriscent
People be out here disliking you because you don’t hate yourself
Libriscent
@libriscent
Abusive people aren’t abusive to everyone—there’s usually one person in particular they’ve chosen.
introvert
@livewithnoregrt
you see people’s true colors when y’all aren’t on good terms… every single time
Libriscent
@libriscent
Narcissists don't have friends—they have assets, resources, and audiences. Once you stop serving a purpose, you'll discover how disposable you really were.
Libriscent
@libriscent
The worst mistake you can make is arguing with someone who doesn’t actually care about truth, reality, or resolution… just the satisfaction of “winning.” You’ll exhaust yourself trying to break through walls that were never meant to come down.
Some people aren’t confused...they’re committed to misunderstanding. You could present facts, receipts, screenshots, timelines, logic… and they’d still twist it because they’re not interested in clarity. Their ego is louder than reason. Their pride is heavier than honesty. Their need to be right outweighs their desire to be accountable.
There are people who simply lack the capacity to understand anything outside their own perspective. Not because the truth is complicated, but because accepting it would require humility… reflection… responsibility. And some folks would rather protect their illusions than face their flaws.
Arguing with them becomes a cycle of frustration, because you’re trying to connect with someone who’s only trying to conquer. You’re trying to make peace with someone who’s trying to “win.” You’re hoping for growth while they’re focused on control.
Save your energy. Stop debating with people who don’t debate in good faith. Walk away from conversations that drain your spirit instead of expanding your understanding.
Your peace is worth more than proving a point to someone who will never receive it. Let them keep their illusions… while you keep your sanity.
Freddy
@Fred4ww
the minute you stop being easy to play with, you become the villain
🥷🏾
@Money_Diplomats
Nov 15
There is no reason to be a people pleaser. People are never pleased
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
The more you forgive a narcissist, the more their behavior escalates-each act of forgiveness is seen as permission, not compassion.
There are sadistic scientists who hurry to hunt down errors instead of establishing the truth.
-- Maria Skłodowska-Curie
Fof
@umarfof
It’s strange how choosing peace can make you a target.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
·
39m
The mind of a malignant narcissist is rigid, fragile, and built on a worldview designed to hide anything they cannot emotionally handle. Their entire psychological system exists to:
- See only what confirms their superiority
- Deny anything that challenges their illusion of self
- Protect themselves from feeling weak, immature, or flawed
- Avoid all responsibility and accountability
Anything that threatens this delusional self-image triggers narcissistic injury, which they experience not as discomfort — but as an existential threat.
In response, the narcissist experiences intense hatred (often secretly) toward the genuine person.
To the narcissist, this honest person is a walking threat. An insult. A danger to their very sense of existence.
But malignant narcissists don’t just resent authenticity. They want to destroy it.
This is an intense hatred that drives them to obsess over sabotaging, destroying, and disappearing the genuine person.
It is this obsessive hatred and desire to eliminate the genuine person combined with their fear of looking “bad“ socially, that drives them to seek other covert methods and manipulation tactics that have become the hallmark of narcissistic abuse.
The Narcissist's “Preferred Method of Killing”: Social Murder
If they cannot kill the genuine person physically (however some try covertly and do succeed), they may attempt to abuse their target into committing suicide, or
they will attempt to kill their:
- reputation
- relationships
- credibility
- identity
- sense of self
- chances of success
They do this through:
- smearing
- lies
- projection
- character defamation
- rewriting the victim’s personality and history
- convincing others that the victim is dangerous or defective
- triangulation
- isolation
- coordinated mobbing attacks
- playing a victim/preemptively reversing roles
- false accusations
- filing false reports (I.e. playing a victim and filing false restraining orders)
- injuring themselves to create “evidence” against their target
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
You weren't too sensitive.
You were just noticing energy no one else could see.
LLONER 🇬🇧🦅
@eyojoel77
Once I realize we have two entirely different moral compasses, I don’t feel the need arguing with you
𝕁.
@inkedupjayy
Disrespect will close doors that apologies can't reopen. Remember that.
polo
@DripArab
"you bringing up old shit." no bitch i'm exposing a pattern.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Boundaries reveals who is mature and who is manipulative.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Being an adult does not grant anyone the right to mistreat others. Maturity and growth do not equate to the permission to bully or intimidate. Bullying is neither a necessary experience of adulthood nor an acceptable behavior among grown individuals.
The Wily Survivor
@WilySurvivor
Don’t confuse manipulation with intelligence. Narcissists aren’t brilliant. They’re destructive opportunists who destroy what they can’t control.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
A common manipulation tactic used by narcissists, often called "reactive abuse”, is when the narcissist repeatedly provokes and abuses their victim, pushing them to their breaking point. When the victim eventually reacts, out of frustration or self-defense, the narcissist seizes this moment to portray themselves as the innocent party or the victim, and the actual victim as the instigator or aggressor. By flipping the narrative, they can manipulate witnesses, and even gaslight the victims, making them feel uncertain about their own actions while simultaneously gaining sympathy from others. This tactic helps the narcissist avoid accountability and further isolates their victims.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Toxic environments will discredit you because your TRUTH destroys the story they sold.
Libriscent
@libriscent
It wasn’t miscommunication. It was manipulation, faking confusion, so they wouldn’t have to take accountability for what they fully understood.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Ugly truth about life: Most people don't care about you. They care about how you make them feel. Some people keep you close because you're useful, not because you're loved.
Libriscent
@libriscent
“Omg you’re so sensitive “ - A form of bullying !
Chi
@__Poisonivyyy
Normalize never speaking to people again after they disrespected you.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Anyone who makes you chase clarity is already telling you they’re not planning to offer any.
Raven Lovette 🦋
@heyhoneyrae
Even when you’re not bothering anybody , somebody will always be bothered.
Drench
@ionfeellnun
I lose interest in people who make everything difficult
Jordan Daley
@JDaley
You will lose every time you act out of emotion.
R I S S A
@Badassrissa_
You can be lied on, talked about, plotted on,and still win in life.
Everyone you meet knows something you don’t know but need to know. Learn from them.
- Carl Jung
vybrant🫶🏿
@vybrant_1
Nov 17
The hardest thing I’m teaching myself is don’t react.
Machiavelli Bot
@UnmodernmanBot
Nov 17
The quieter someone becomes, the harder they are to read, and the more space they control. Stillness unsettles people because it denies them the cues they rely on to feel safe. Silence, when used deliberately, dictates the rhythm of others.
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
When a narcissist calls you a liar, they're the ones hiding things. When they say you're
"too sensitive," they really mean
"I don't care about your feelings." Their accusations are just projections of their behaviour. Watch closely, they're telling on themselves.
Shadows of Control
@shadows_control
A domestic abuse survivor isn’t to blame for their response to trauma—any more than a soldier is to blame for developing PTSD.
introvert
@livewithnoregrt
people will take you for granted, then reaIize you were rare.
Abi Nola
@NolaAbi10086
The urge to take the bait and indulge in 'tit for tat' is very strong indeed. Even if one does not engage, the narcissist will act like you are retaliating, forcing others to see a mutual conflict when it's very much one sided! So yes! ....run and do not look back. Give NO OR VERY LIMITED CONTACT.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Nov 19
The feeling of KNOWING so clearly that someone is a manipulative, deceitful, covertly dangerous narcissist that your body is reacting like there is a predator in your midst and and NO ONE ELSE seems to see it or sense it is one of the most frustrating and isolating things I experience throughout my life
𝘽𝙡𝙖𝙠𝙚
@Arealmfngl
Nov 19
it's crazy how ppl need 0 proof to believe a lie, but need endless proof to accept the truth
Spiritual GPS Service
@AstroCounselVik
We keep calling people "mentally ill" when they're drowning in conditions no human nervous system can survive.
You can't regulate when rent is late, the fridge is empty, and danger is normal. This is not a disorder, it's adaptation. The real sickness is the environment.
If your basic needs aren't met, you will suffer.
If you live in chaos, your mind will have to adapt to chaos.
If you never feel safe, you cannot feel whole.
The message is simple:
people aren't broken.
their environments are.
Until we create conditions where people can breathe, rest, and belong, "mental illness" will keep being a label slapped on pain that was never irrational in the first place.
Shift the question from "What is wrong with you?" to "What has happened to you, and what do you need to feel safe?"
-
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
A lot of narcissistic behavior comes down to this simple truth:
They cannot trust good intentions.
Narcissists project their own motives onto everyone around them.
Because they manipulate, exploit, and act with hidden agendas, they assume everyone else does too.
So when someone shows genuine concern or tries to help them (or anyone) selflessly, the narcissist can’t process it as kindness — only as a manipulation, a threat, an angle, or an attack.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
The narcissist’s favorite gaslighting abuse tactic is to set you up to be angry, and then shame you for that anger. It’s practically a form of entertainment for them.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
When a narcissist acts “nice” toward you, it usually means they’ve already done something behind your back—sabotaged you, spread a rumor, undermined your progress, put something in your food, or otherwise set you back. Now that they feel they’ve “leveled the playing field” by hurting you, they’re no longer envious in that moment. Their friendliness is not kindness—it’s the satisfaction of knowing they’ve already harmed you.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Nov 19
A disagreement with a toxic person will turn into a argument. A disagreement with a good person will turn into a conversation with a solution. It's important to know the difference.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Narcissists see empaths as aliens. They poke, study, and experiment on them like lab rats. Watching your reactions is their entertainment.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Malignant narcissists would throw their own children under the bus to protect their false public image.
They’re more concerned about what random people think of them than their own family.
Why? Because they exist entirely in their deranged ego which means their reality is based on what the world perceives them as, not truth.
When a person sees them for who they are, that person is deemed a “non-entity” by the narcissist and must be discarded from reality, ie smear campaigned, sabotaged, or worse.
Most often this is the people closest to them that must be discarded because it’s the people closest to them that can see how dysfunctional they really are
Les
@LesSzklanny
They don’t see people and they don’t see persons. Everybody is objectified.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Stay away from people who think being heartless and mean is funny. Don’t tolerate jokes about homeless people, people with disabilities or anyone being mistreated for entertainment. A lack of empathy isn’t a personality trait, it’s a sign someone hasn’t grown up emotionally.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Narcissistic abuse is psychological violence.
The abuser’s goal is to get away with causing as much psychological damage as they can.
A victim’s nervous break-down is the abuser’s trophy.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Nov 23
Is micromanagement a form of Coercive Control?
Micromanagement can indeed be considered a form of coercive control and bullying in the workplace and can cause trauma, anxiety and PTSD.
Libriscent
@libriscent
You’re not crazy — they broke trust then blamed you.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Many abusive or narcissistic individuals engage in a kind of "preemptive rebranding" of their harmful traits. By owning their negative behaviors and presenting them with humor, pride, or as a form of righteousness, they disarm others who might otherwise question or challenge their actions. It can create a false narrative that their abusive behavior is intentional, controlled, or even justified—almost like saying, "I know I’m bad, and I’m owning it, so you can't call me out."
This strategy often relies on manipulating people's perceptions. By framing their abuse as a quirky personality trait or a badge of honor, they encourage others to dismiss it as harmless or even admirable.
vivi
@mooncatvivi
Nov 23
it’s crazy how being depressed for years makes you a fucking idiot
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Normalize saying, " that doesn't work for me" without over explaining. You're not being rude. You're being clear and direct.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Normalize not trying harder when someone makes you feel unwanted.
I am against religion because it teaches us to be satisfied with not understanding the world.
- Richard Dawkins
The Narcissist Box
@NarcissistBox
To break a trauma bond, the first thing you have to do is "kill the fantasy"..... You are addicted to them because they treated you good, then bad, nice, then mean...#traumabond #mentalhealth
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
Narcissists are the masters of manipulation: they play the poor abused victim whilst embarking on a mass smear campaign against those who dared to stand up to them.
“Do not indoctrinate your children. Teach them how to think for themselves, how to evaluate evidence, and how to disagree with you.”
― Richard Dawkins, The God Delusion
⁺𓏲🎸˚⤾·
@alfkkifine
Nov 25
"you need help" - the person that traumatized you
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
A covert malignant narcissist will target and attack someone who is minding their own business and wants nothing to do with them, and then turn around and tell people they’re the one being attacked by that person. It’s mind-boggling how sick and deranged these people are
If one person believes something illogical, he is called a fool - but if ten million people believe the same illogical thing, it is called religion.
-Voltaire
Echo
@dragonsilences
Nov 26
also, telling a child they are lying when they are in fact speaking the truth, confirms to the child that their opinion is not taken seriously and their words are worth nothing. helplessness is one of the worst feelings a person can experience imo.
It is much better to do the right thing wronger than the wrong thing righter.
The more efficient you are at doing the wrong thing, the wronger you become.
Russell L. Ackoff
Prole Adventures
@ProleAdventures
Getting off the wheel is easy, getting out of the cage is another matter entirely.
476- RSD Toolkit: Strategies for Managing Your Sensitivities in Real Time
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wG15SmkXEc8
23:58 "RSD is product of being criticized and judged negatively for being who you are."
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
Nov 27
It’s crazy how easily people believe the narcissist’s lies, yet doubt the victim’s truth
The Narcissist Box
@NarcissistBox
·
11h
1. She said it started with love that looked perfect. Parents who praised every drawing, solved every problem, and never let frustration last. “They grow up adored,” she said, “but untested.” The child learns one rule — discomfort means danger. So when life stops clapping, they panic, not reflect. 2. Researchers at the University of Amsterdam followed 500 families for eight years. Kids who were over-praised for traits (“You’re special,” “You’re the best”) showed twice as many narcissistic traits by adolescence as those praised for effort (“You worked hard,” “You tried”). The brain linked love to superiority, not connection. 3. “It’s not too much love,” the psychologist explained. “It’s love without limits.” When a child never hears no, empathy can’t grow. The prefrontal cortex — the part that reads others’ emotions — develops through friction and correction. Shielding from failure blocks that wiring. 4. One mother in her clinic said, “But I just want him to be confident.” The psychologist smiled softly: “Confidence without empathy becomes arrogance.” True self-worth isn’t built by being told you’re perfect — it’s built by surviving imperfection and still feeling loved. 5. At the end of her lecture, she said, “Narcissism is not vanity — it’s fear in a shiny mask.” When kids learn that mistakes don’t erase love, they stop needing the mask. Parents don’t create narcissists by caring — they do it by confusing praise with presence.7
-
“Dressing well is a sign of good mental health.”
Nancy Mitford, born 28th November 1904
-
“Confidence without empathy becomes arrogance.”
-
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
I noticed that authenticity irritates toxic people.
-
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
To say a malignant narcissist is abusive is only partially correct.
A malignant narcissist is INSANELY abusive.
Irrationally, outrageously, unbelievably, horrifyingly, dangerously abusive.
-
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
When a narcissist begins abusing someone, to outside observers it often looks like both people are just caught in a messy conflict, pointing fingers and trading blame. But that’s an illusion. One of them is a manipulator, and the other is reacting to abuse.
The narcissist will often accuse their target of the very things they themselves are doing — lying, being manipulative, playing the victim, being toxic — and they'll do it with such conviction and calmness that it disorients everyone, including the target.
Meanwhile, the real victim is often emotionally overwhelmed, hurt, or desperately trying to explain themselves — and this imbalance gets used against them.
The narcissist didn't attack because their target did anything wrong or offensive — they attacked because that person threatened their ego, exposed their insecurity, or was simply too happy for the narcissist to stomach.
One person is the abuser. The other is innocent — and being retraumatized not just by the abuse, but by the world’s failure to see it.
Jason Overstreet
@JasonOverstreet
Horrible people just keep doing horrible shit and no one holds them accountable for it. What a horrible world we are living in.
Libriscent
@libriscent
People aren't acting weird, they never liked you, and it's getting harder for them to hide it! Your intuition is always right. The never liked you.
Karun Pal
@karunpal
Why does everyone force introverts to leave their comfort zone, but no one forces extroverts to shut up for a while? Why???
Shadows of Control
@shadows_control
Toxic people want power over you, not a relationship with you. ⚠️ 🚩
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
You were never the problem. You were the truth-teller, and that made you dangerous to their lies.
𝚂𝙸𝙻𝙻𝚈𝚂𝙲𝙸𝙴𝙽𝚃𝙸𝚂𝚃
@sonofkenei
Being disliked by manipulative people is usually proof you’ve stopped being easy to control.
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
Narcissists don't struggle with anger management issues; they can handle their anger just fine when are potential witnesses.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Abusive people think they have the right to mistreat and hurt you, but you don't have the right to react or stand up for yourself. They are allowed to criticize, voice all their opinions, be rude, cruel and insensitive, but how dare you point out their bad behaviors, or say anything back to them. Their behaviors suddenly become all your fault and you are "crazy," a
"drama queen," and a "horrible" person for standing up for yourself and not accepting and tolerating their crap. They never blame themselves or see their own horrific behaviors.
KLASIK ♠️
@lifeofklasik
people don't see a problem with their behavior until you start doing the same thing back.
Shadows of Control
@shadows_control
Dec 2
Abusers will often withhold affection, attention, or even basic kindness as a way to punish you. It’s a subtle way of reinforcing control—if you don’t behave in the way they want, they make you feel emotionally abandoned. Over time, you start to work harder to please them, just to avoid being punished with coldness or distance. This tactic is so damaging and hurtful because it targets that deep human need for connection and acceptance. #EmotionalAbuse
Fit And Fortune
@FitAndFortune
You do not know real struggle until you’ve stayed somewhere you were barely tolerated.
Experiences like that change you.
They teach you independence.
They teach you boundaries.
They teach you why you must build your own life, your own space, your own security.
Once you have lived through that kind of humiliation,
you promise yourself one thing:
Never again.
Shining Science
@ShiningScience
Interrupting isn’t always a sign of rudeness. Research suggests that many people interrupt because of faster cognitive processing, anxiety, or impulsivity rather than intentional disrespect. Those with quick processing speeds may form responses before others finish speaking, while anxious individuals worry they’ll forget their point if they wait. Studies also link impulsive interruptions to ADHD, where rapid idea flow and limited short-term retention make pausing difficult. In many cases, the brain is simply moving faster than the conversation.
Sources: Eysenck, M.W. (2012). Anxiety and Cognition; Barkley, R.A. (2015). Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder; YourTango (2024). People Who Can’t Stop Interrupting Usually Have These Reasons.
Contrary to popular belief, simply ignoring a bully does not usually encourage them to stop what they're doing. As a matter of fact, adult bullies of all types often view being ignored as a sign of weakness, and it encourages them to keep going.
https://betterhelp.com/advice/bullying/how-to-handle-adult-bullying/
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Bullying is a toxic and immature choice made by the bully. It's not your fault.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Psychological invalidation, similar to gaslighting, is one of the most lethal forms of emotional distress. It kills self-confidence, dignity, self-esteem, and individuality. It's to escape accountability.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Toxic environments will discredit you because your TRUTH destroys the story they sold.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Authenticity irritates toxic people
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
I always know I’m dealing with with a malignant narcissist when I’m made to feel like I need to explain myself or defend myself for doing nothing wrong.
Sassington, M.C.
@MissSassbox
Dec 7
it's not a loneliness epidemic anymore, it's an 'asshole' epidemic. too many assholes, not enough cool people. that's it. that's really the issue.
Josh
@JD_Quotes2017
Some people have a lot to say about lives they've never lived, offering opinions on struggles they've never faced, and passing judgment on paths they've never walked.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Dec 8
Narcissists don't look for help, healing or therapy.
They look for a new person who doesn't know they need help, healing and therapy.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Mistreating, bullying or harassing people then avoiding communication is not "protecting your peace", it's avoiding accountability.
Libriscent
@libriscent
Social cue tip: when people start acting weird towards you and you can’t recall anything happening between y’all to warrant a change in behavior — it’s because they talk about you behind your back or they hang out with people who talk about you. It’s not because you’ve done something wrong that you didnt realize.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Covert narcissists will often attack their victims by casually overdramatizing everything they can to make their victim look unhinged or in need of help while simultaneously feigning a moral high ground by acting “concerned for them”.
This triangulation abuse tactic creates a false narrative about the victim causing stress and anxiety. Also referred to as “crazy making”. This is the epitome of narcissistic abuse
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Safe people don't punish you for your rights and boundaries.
Unsafe people do.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Confidence doesn't bully. Ego does.
Libriscent
@libriscent
You don’t need closure from someone who made you spiritually sick. You need distance, detox, and discernment.
introvert
@livewithnoregrt
stop sparing people .. nobody felt bad when it was you.
Narcissistic Abuse Awareness
@AwareOfTheNarc
A narcissist will be angry at you and seek revenge once you discover who they truly are.
I've save some of those kids' lives, yet they are unkind to me.
- There are always people who want to hurt us, when we've done them no harm. That's facts of life. Like water can drown or fire can burn.
- All the same, she is much more wicked than the others!
- Or, she simply has more power.
📽️Kirikou and the Sorceress (1998)
Original title: Kirikou et la sorcière
The sorceress prevents people from getting there.
- Why?
- The Wise Man of the Mountain explains things the way they are while the Sorceress needs us to believe all sorts of nonsense.
📽️Kirikou and the Sorceress (1998)
Original title: Kirikou et la sorcière
Grandfather, I am small and I should like to be grown.
- Today, being tiny you have been able to enter places where no one else could. Be thankful. And when you are grown don't forget to be thankful.
📽️Kirikou and the Sorceress (1998)
Original title: Kirikou et la sorcière
How did Karaba the Sorceress manage to put the monster inside the spring?
- She didn't put it there. It got in by itself. It was very small and it was thirsty. Over the years it grew and became more and more thirsty.
📽️Kirikou and the Sorceress (1998)
Original title: Kirikou et la sorcière
Why does the Sorceress eat people?
- She doesn't.
- What?
- That's what the villagers think, Karaba lets them go on thinking it. The more frightened people are of her the more powerful she is. She likes yams in a nice spicy sauce just like you and I.
📽️Kirikou and the Sorceress (1998)
Original title: Kirikou et la sorcière
She doesn't like children, she despises women, she hates men and she wants to do them all the harm she can.
- Why?
- Because she is in PAIN. She suffers night and day without respite. Because somebody once pushed a poisonous thorn into her spinal cord.
📽️Kirikou and the Sorceress (1998)
Original title: Kirikou et la sorcière
Why doesn't she pull out the poisonous thorn which hurts her day and night? Why doesn't she ask a friend to do that?
- She has no friend.
If someone pulled out that thorn she would feel more pain in that moment than you can possibly imagine.
📽️Kirikou and the Sorceress (1998)
Original title: Kirikou et la sorcière
There is another reason.
It is that very thorn which gives her her magic powers.
If it was removed she would lose all those powers at the same time.
📽️Kirikou and the Sorceress (1998)
Original title: Kirikou et la sorcière
Will you give me a charm to protect me from the Sorceress?
- No. Your power lies in the absence of a charm. The Sorceress knows all about spells and charms and tricks the men who think they are protected. On the other hand, she has no idea how to act when confronted with barefaced innocence and a free and alert intelligence.
📽️Kirikou and the Sorceress (1998)
Original title: Kirikou et la sorcière
It's stopped hurting... How strange to feel no more pain. I am my old self once more...
📽️Kirikou and the Sorceress (1998)
Original title: Kirikou et la sorcière
She transformed them into objects, obedient objects. But Kirikou has delivered Karaba from her pain and liberated these men from their enchantment.
📽️Kirikou and the Sorceress (1998)
Original title: Kirikou et la sorcière
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
A narcissist thinks being loud is the same as being right.
Workplace Mental Health Safety & Prevention
@Stopworkplacebu
Stop allowing people to gaslight you into thinking you're crazy or insecure for having a valid response to their hurtful behavior.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Dec 19
Whenever narcissist parents detect something that you love, they will try to take ownership of it.
Josh
@JD_Quotes2017
Dec 19
Anybody that go against you without hearing your side of the story was already looking for a reason to be against you.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
It’s never a child’s responsibility to know how to defend themselves against abuse. That’s ridiculous. It’s downright stupid to suggest that any person, at any age is wired to know how to navigate an unnatural act of evil put on them by someone else. Absolutely ridiculous.
Nate Postlethwait
@nate_postlethwt
I wish people understood that when someone seems to overexplain, it’s often because of how much they’ve been misunderstood. They’re trying to give you information that they assume is hard to understand based on how they’ve been treated. This deserves compassion, not criticism.
daz.hl
@MetamateDaz
Becoming an adult is realizing that we’ve been bred specifically to be labor slaves.
maro
@ProofofMaro
being autistic is like being shadowbanned but in real life.
Dear Self.
@Dearme2_
You want to teach people how to respect you? Cut them off.
𐌁𐌉Ᏽ 𐌕𐌉𐌌𐌉
@OrevaZSN
That boring, introverted life you’re living has probably protected you from a lot of harm and bad experiences.
Elizabeth Shaw - Overcoming Narcissist Abuse.
@CoachElizabethS
"Killing them with kindness" doesn't work on narcissistic individuals. Instead of appreciating your generosity, they'll exploit it, draining you emotionally and leaving you with nothing.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Have you ever noticed how narcissists always seem to ruin birthdays, holidays, and vacations—the moments that are supposed to be the happiest?
Narcissists can’t stand joy that isn’t about them, which is why they almost always sabotage happy moments.
Narcissists resent seeing others happy—especially if that happiness doesn’t involve them. They feel threatened by genuine joy, so they inject negativity to "balance" things back in their favor.
But wait, it gets worse… they will ruin the vacation and they will BLAME IT ON SOMEONE ELSE. They’ll start an argument or a fight and then they’ll blame it on the person they started the fight with. That’s the scapegoat.
How they ruin them
-Picking fights out of nowhere – suddenly starting an argument on the morning of your birthday or before a big dinner.
-Withholding or “forgetting” – no gift, no acknowledgment, or giving something deliberately thoughtless.
-Making it about them – turning your birthday into their crisis or sulking until everyone caters to them.
-Triangulation – pitting family members against each other during gatherings.
-Silent treatment – withdrawing affection or attention to dampen the mood.
-Sabotaging plans – showing up late, causing delays, or even “accidentally” ruining travel arrangements.
At the root, a narcissist can’t tolerate you feeling loved, celebrated, or at peace—because that would mean you might recognize your worth outside of them. By disrupting joyful milestones, they reinforce a false message:
“With or without me, there can be no happiness.”
The Wily Survivor
@WilySurvivor
A narcissist does not want love. Love requires empathy, reciprocity, and accountability. What they want is control, validation, and reassurance without responsibility.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Intuitive people are the biggest threat to covert and malignant narcissists. Narcissists instinctively attack these people, smearing their reputation without provocation.
Nithya Shri
@Nithya_Shrii
you HAVE TO learn to delay your reaction when people are purposely trying to provoke you.
Ryan Daigler - Exposing Narcissistic Abuse 🚩🚩
@Ryan_Daigler
Dec 30, 2025
Narcissistic abusers expect you to take the abuse and roll over quietly. They take great offense when you stand up for yourself. Like, how dare you. 😐
👺
Blog posts:
Do Movies Cause Social Anxiety? ✌ Strong reaction to someone rude ✌ The Agreeableness Theory ✌Managing Social Anxiety and Toxic Shame ✌ Complex Trauma induce Social Anxiety and Avoidance ✌Navigating through social anxiety ✌ Accepting social anxiety ✌ Social anxiety is Rejection sensitive dysphoria (RSD) ✌ Quiet BPD is social anxiety ✌ Hating social anxiety is an act of self abuse ✌ High Suggestibility is Social anxiety ✌
Reddit posts:
- Why not Social Anxiety "Solutions" or "Fixes" or "Overcoming"?
- Concepts that helped me understand Social anxiety, Panic Triggers and Avoidance
- Toxic shame
- Intrusive Thoughts (PureOCD)
- Self Worth
- Being stuck
- Resentment
- Doubt and Descartes 'Evil genius argument'
- External reference locus of control and External validation
- Amygdala hijacking
- Egocentrism
- Classical CBT based Social Anxiety on faulty premises
- Fawning
- Ebbinghaus' Forgetting Curve
- Long-Term Narcissistic Abuse Can Cause Brain Damage
- 20 ideas and conclusions about social anxiety I learned without external help
- Philosophical zombie (NPC Wojak)
- Comment on YT video "Marcus Aurelius - Stop Caring What People Think"
- Interdependence
- Highly Sensitive Person (HSP) and Social anxiety
- Perfectionism is hidden factor of disorder in Social Anxiety
- Toxic people
- Three stages
- There is no absolute truth
- Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)
- Dualism and Double bind
- Alternative explanations of Social anxiety
- Anti-psychiatry
- Anti-psychiatry (2)
- Social Anxiety Map (I)
- Social Anxiety Map (II)
- Social Anxiety Map (III)
- All people have social anxiety. All.
- Humanistic therapies
- False self (I)
- False self (II)
- Catcher in the Rye (I)
- Catcher in the Rye (II)
- Catcher in the Rye (III)
- Complex Trauma (c-PTSD)
- Social Anxiety tips (I)
- Social Anxiety tips (II)
- Social stigma
- Trickster (by Jung)
- How Narcissists hijacked Social Anxiety
- Charcot hysteria
- Time machine - my views about social anxiety from 1996
- Trauma splitting
- Social anxiety in the presence of well-meaning people
- Kohlberg's Theory of Moral Development
- Kohlberg's Theory of Moral Development (II)
- Sam Vaknin and Richard Grannon (I)
- Sam Vaknin and Richard Grannon (II)
- Agreeableness
- Negative politeness
- Why smashing social anxiety approach will never work
- Seesaw effect
- Initiation into evil
- Invalidation
- Validation (I)
- Validation (II)
- Validation (III)
- Solution must be simple (Occam's Razor)
- Power Dynamics (I)
- Power Dynamics (II)
- Interpersonal sensitivity
- Rejection sensitive dysphoria (RSD)
- Scapegoating people-pleasing is wrong
- Scapegoating people-pleasing is wrong (II)
- Social anxiety and Rejection sensitive dysphoria (RSD)
- Neurodiversity
- Social anxiety: journal entry from 1990
- ADHD
- Masking
- Paradox of vulnerability
- Fear of being hated
- Fear of criticism and negative evaluation
- Adult Child of an Alcoholic (ACoA) - part 1
- Adult Child of an Alcoholic (ACoA) - part 2
- Processing emotions and stimuli
- Processing emotions and stimuli (II)
- Processing emotions and stimuli (III)
- Processing emotions and stimuli (IV)
- Processing emotions and stimuli (V)
- All people have social anxiety. All. (II)
- Polarized thinking
- Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale
- High-functioning social anxiety
- Quiet BPD as social anxiety
- Internal Family Systems Model (IFS)
- Boundaries
- Boundaries (II)
- Extinction
- Self-referential thinking
- Social anxiety described in 19th century
- Quick fusion
- Four pillars of Social Anxiety (I)
- Four pillars of Social Anxiety (II)
- Toxic shame and Social anxiety are intertwined
- Toxic shame and Social anxiety are intertwined (II)
- Toxic shame and Social anxiety are intertwined (III)
- CBT DSM medical terms are misleading
- CBT myth about Exposure
- Stoicism and social anxiety
- Regulation and Dysregulation
- Regulation and Dysregulation (II)
- Survivorship bias
- Survivorship bias (II)
- How to handle difficult people (I)
- How to handle difficult people (II)
- Toxic empathy (I)
- Toxic empathy (II)
- Toxic empathy (III)
- Spotlight effect and other (neuro)-typical nonsense advice for Social Anxiety
- Spotlight effect and other (neuro)-typical nonsense advice for Social Anxiety (II)
- Psychedelics and social anxiety
- Tendency to perceive (interpersonal) victimhood - TIV
- All people have social anxiety. All. (III)
- Nothingness as anti-dote for social anxiety
- Nothingness as anti-dote for social anxiety (II)
- Nothingness as anti-dote for social anxiety (III)
- Nothingness as anti-dote for social anxiety (IV)
- Nothingness as anti-dote for social anxiety (V)
- Nothingness as anti-dote for social anxiety (VI)
- Synaptic pruning
- BBC The Century of the Self
- Othering
- Barnum effect
- Social anxiety coaches
- High-Functioning Autism and Social anxiety
- High-Functioning Autism and Social anxiety (II)
- High-Functioning Autism and Social anxiety (III)
- High-Functioning Autism and Social anxiety (IV)
- Unwritten struggles of social anxiety
- Unwritten struggles of social anxiety (II)
- Unwritten struggles of social anxiety (III)
- Secure attachment
- Secure attachment (II)
- Secure attachment (III)
- Worrying About What Other People Think of You (FOPO)
- Looking-glass self
- Looking-glass self (II)
- Looking-glass self (III)
- Healthy coping mechanisms
- Devil on our shoulder
- Broken Looking-Glass Self is Social anxiety
- Social anxiety as rollercoaster
- Social anxiety as rollercoaster (II) - tracks
- Social anxiety as rollercoaster (III) - wagons
- Social anxiety as rollercoaster (IV) - wagons
- Social anxiety as rollercoaster (V) - clouds
- Social anxiety as rollercoaster (VI) - loops
- Social anxiety as rollercoaster (VII) - fog
- Social anxiety as rollercoaster (VIII) - constructs
- Shyness versus Social anxiety
- Shyness versus Social anxiety (II)
- Shyness versus Social anxiety (III)
- Shyness versus Social anxiety (IV)
- Shyness versus Social anxiety (V)
- Coerced-compliant false confessions
- Detachment
- Detachment and Social anxiety
- Detachment and suppressed anger
- Detachment, anger and CPTSD
- Detachment and anger as tools of healing Social anxiety
- Cowardice vs. Social anxiety
- Entanglement
- Observation
- Healing social anxiety
- What is Social Anxiety?
- Cognitive distortions
- Cognitive distortions versus Social anxiety
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
- Situational anxiety
- Self-made prison
- Inattentional blindness
- Social anxiety deciphered as the Rosetta Stone
- Social anxiety translated as the unfelt anger
- Coercive control
- Weaponized anger
- Toxic people and social anxiety
- No one can make you feel inferior without your consent
- Operant conditioning
- Conditioning and Social anxiety
- Fear of punishment is Social anxiety
- Conditioned triggers in Social anxiety
- Self-Forgiveness
- RAIN method
- Social anxiety spectrum
- Social anxiety scale
- Complex PTSD: From Surviving to Thriving
- Complex PTSD: From Surviving to Thriving - quotes
- Borderline disorder and social anxiety
- AvPD, Borderline and Social anxiety
- Borderline masking itself as social anxiety
- Borderline and social anxiety as dual system
- Social anxiety is borderline reaction to oppression and abuse
- Social anxiety is normal reaction to abnormal people and events
- Social anxiety investigation
- CSI Social Anxiety
- Social anxiety is not your fault
- Cork
- Faustian bargain
- Homunculus
- Good side of social anxiety
- Social anxiety is an adaptation to evil
- Social anxiety is adaptation to narcissistic abuse
- Social anxiety is a survival mode
- Hating social anxiety is an act of self abuse
- The pain and Social anxiety
- Convictions, beliefs and explanations about social anxiety
- Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder (OCPD)
- Narrative therapy
- Egosyntonic
- Hyper-attunement
- Hyper-responsibility
- Repetition compulsion
- Over-identification with aggressor is social anxiety
- Examination of social anxiety reactions
- Fear of criticism as a by-product of indoctrination
- Goodness is something to be chosen
- Ambiguity
- Echoism
- Objectification
- Problem of the criterion
- Reality testing
- Social anxiety is trauma
- There is no winning strategy
- The pain is not the punishment
- Stoicism is unhealthy for social anxiety
- The Local Rationality Principle
- Be friendly - not friends
- Social anxiety is a Psychological injury
- Fixation
- Nervous system and social anxiety
- Misleading explanations of social anxiety
- Misleading CBT explanations of social anxiety
- Social anxiety is a sign of repressed emotions
- Journaling social anxiety
- Constriction
- Trauma growth
- Data
- Shyness is different from social anxiety
- Something else
- Being present in the moment
- Measuring the social anxiety pain and abuse
- Give light and people will find the way
- Alternative life without Social Anxiety
- Examination of blocked emotions
- Throw the Warped Wheel Out
- Psychological blind spots
- Losing Ventral Vagal causes social anxiety
- Unwarranted confidence
- Erroneous conscience
- The Trial
- The process
- Scrupulous Conscience
- Social Anxiety is suppressed Social Conscience
- Social anxiety happens when Social apathy is winning
- Social anxiety is fear of Destructive criticism by someone in power
- Ventral Vagal
- Vanilla Sky
- The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)
- Garden
- Being genuine and authentic
- Social norm boundaries
- Social anxiety starting package
- Social anxiety for the newbies
- Social anxiety - where to start
- Social anxiety for the beginners
- Seeing social anxiety as a prompt to change the paradigm
- Social situations should not be difficult
- Conflict triggers
- Delayed Processing or being stuck in a limbo
- Free Will
- Conditioned nervous system shapes social anxiety
- Anxiety Is the Dizziness of Freedom
- Moral Defense Against Bad Object
- High Suggestibility is Social anxiety
- Vicarious Dissonance
- Hidden curriculum
- Guilt Complex
- Functional fixedness
- Intimidation tactics
- Social anxiety is misnomer for Social Trauma
- Neuroreductionism
- Kopfkino
- Inert knowledge
- Dissociation
- Iron cage
- Personalization
- Twice-exceptionality
- Invisible Differentness
- Prometheus Bound Syndrome
- Oedipus Rex
- The Antigone Complex
- Humiliation trauma
- Psychological reactance
- Lurkers
- Psychological Agency
- Neurotypical
- What about the people who are on the receiving end of the abuse
- Pathologizing the social anxiety is an act of poisoning the well
- Social anxiety is an Effect of Exposure to Chronic Complaining
- What you need is to feel safe (Bessel van der Kolk)
- Pokémon cards mind game
- Alcohol and Social anxiety
- Safety behaviors in social anxiety
- Hyperfocus on justice
- Social anxiety is self distrust how to protect ourselves
- Social anxiety is multidimensional
- Social anxiety is our attempt to make toxic people happy
- Social anxiety is a series of Chain reactions
- Social Anxiety Oddities
- Saturday nights and Social anxiety
- Social Anxiety is an Autoplastic defense
- Radical Self Acceptance
- Reference point
- DSM personality
- Talking to cashier advice for Social anxiety
- Where social anxiety comes from
- Shyness, narcissism or social anxiety
- Taking things for granted
- Social anxiety is Nervous system issue
- BBC Radio 4 Dark Crossing











.png)






.jpg)






+direct+contact,+2)+direct+instruction,+3)+interaction+with+others,+and+4)+vicarious+learning.%20(1).jpg)
.png)
.jpg)

.jpg)
















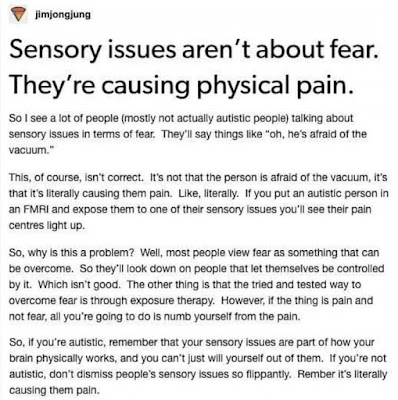



























































.jpg)
.png)


















































































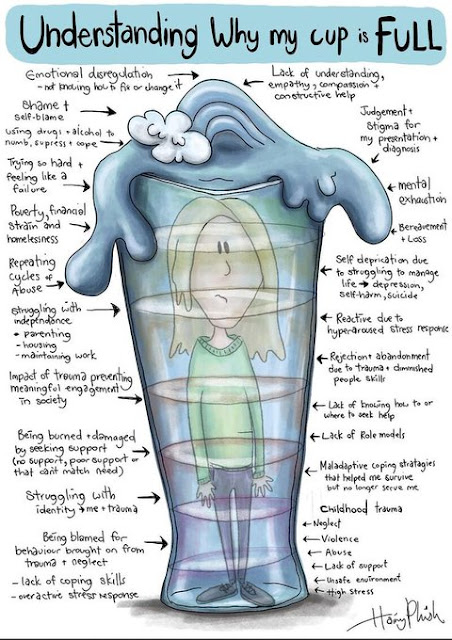










.jpg)

































































.jpg)


.jpg)

















.png)


.jpg)









.jpg)

.png)

.jpg)


























.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)

.jpg)















.jpg)

































































































































































































































.jpg)



































































































.png)








